Volume II - Appropriations Funds and Related Information
Chapter 01 – VA’s Accounting Classification Structure
Questions concerning this policy chapter should be directed to:
- Veterans Health Administration
- Veterans Benefits Administration
- National Cemetery Administration
- Debt Management Center
- Financial Services Center
- Construction and Facilities Management
- All others
0101 Overview
This chapter establishes the Department of Veterans Affairs’ (VA) financial policies regarding VA’s Accounting Classification Structure (ACS). VA’s ACS provides a standardized and comprehensive method to classify accounting data to support budgeting, financial accounting, external reporting, and the generation of the agency’s financial statements.
VA is in a multiyear project to modernize its accounting system. Organizations that have not yet adopted the new accounting system will continue using the legacy Financial Management System (FMS) and its corresponding ACS. Organizations that have moved to the new Integrated Financial and Acquisition Management System (iFAMS) will adopt its ACS.
Key points covered in this chapter:
- VA’s ACS will comply with guidance issued by;
- Office of Management and Budget (OMB),
- Department of Treasury, and
- Federal Accounting Standards Advisory Board (FASAB).
- VA’s ACS will classify accounting data to allow reporting in alignment with reporting standards.
0102 Revisions
| Section | Revision | Requesting Office | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appendix B | Targeted change to update FSC email distribution and Station Suffix Modifiers table | OFP | To provide reader relevant guidance | July 2024 |
| Appendix D | Targeted change to update contact information on the Agency Location Code listing | OFP | Annual Review | July 2024 |
| Appendix G | Targeted change to update content to align to current process when submitting accounting transactions | OFP | To provide reader relevant guidance | July 2024 |
| Appendix H | Targeted change to revise procedure and added Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Guide for iFAMS Users | FMBT | To provide iFAMS users relevant information and provide CRM guide for iFAMS users | July 2024 |
| Appendix I | Targeted change to align procedure to the rest of the appendices | OFP | To provide reader relevant guidance | July 2024 |
For a complete listing of previous policy revisions, see Appendix A.
0103 Definitions
Accounting Classification Structure – The categorization of accounting data along several dimensions allowing the retrieval, summarization, and reporting of information in a meaningful way.
Agency Location Code (ALC) – A numeric symbol assigned by Treasury to identify an agency accounting and/or reporting office.
Budget Object Class (BOC) Code – Categories in a classification system that present obligations by the items or services purchased by the Federal Government.
Budgetary Account – An account that reflects budgetary operations and conditions, such as estimated revenues, appropriations, and obligations.
Cost Center – A four to six-digit code used to accumulate costs incurred by area of responsibility or geographic region (e.g., 301000, [Veterans Benefits Administration (VBA)] Executive Director). The cost center field only relates to Administrations and Staff Offices that utilize FMS. iFAMS contains a non-ACS field for the FMS cost center (does not impact the iFAMS ACS or iFAMS GL).
Direct Obligation – An obligation financed by appropriations, in contrast to reimbursable obligations.
Division Code – Classifies financial transactions by the entities responsible for managing resources and carrying out the programs and activities of the Federal Government. The Division Code represents the top level of the hierarchical structure in iFAMS, followed by the Organization Code.
Governmentwide Treasury Account Symbol Adjusted Trial Balance System (GTAS) – A Treasury operated Government-wide web-based accounting system used by Federal agencies to submit both budgetary and proprietary financial data.
Integrated Financial and Acquisition Management System (iFAMS) – The system replacing VA’s legacy accounting system, FMS as the official financial and acquisition system of record. VA is implementing iFAMS in waves beginning in 2020.
Location Code – Represents the physical address of each organizational unit in VA’s Administrations and Staff Offices.
Object Class – Categorization of financial obligations and expenditures according to the nature of the services or items purchased as defined in OMB Circular A-11, Section 83.
Organization Code – Classifies financial transactions by the entities responsible for managing resources and carrying out the programs and activities of the federal government. The organization code represents the lower levels of the hierarchical structure below the Division Code in iFAMS.
Proprietary Account – Accounts used to recognize and track assets, liabilities, net position accounts, revenues, and expenses.
Reimbursable Obligation – An obligation financed by offsetting collections credited to an expenditure account in payment for goods and services provided by that account.
Revenue – The inflow of resources brought into VA, earned through exchange transaction activity or received through non-exchange transactions. This may include sales of products (sales), rendering of services (revenues) and earnings from interest, dividends, lease income and royalties.
Revenue Source Code – A standard agency-defined code which classifies revenue and receipt transactions by the type or source of revenue.
Station Number – A three-digit identifier to recognize a VA installation or a parent relationship. A station may be stand-alone facility with a single number, or it may be a parent station with substations as children. The substations are generally smaller facilities (e.g., outpatient clinics) under the authority of the parent station. Station numbers are only applicable to Administrations and Staff Offices utilizing FMS and are replaced by Division and Organization Codes in iFAMS.
Treasury Account Symbol (TAS) – An identification code assigned by Treasury, in collaboration with OMB and VA, to an individual appropriation, receipt, or other fund account.
Treasury Appropriation Fund Symbol (TAFS) – Refers to account identification codes assigned by the Department of Treasury to individual appropriation, receipt, or other fund accounts. All financial transactions of the federal government are classified by TAS for reporting to the Department of Treasury and OMB. A TAS includes all the component pieces of Treasury Appropriation Fund Symbol, plus any sub-accounts established by Treasury.
U.S. Standard General Ledger (USSGL) Account – Identifies one of the standard GL account codes established by Treasury to reinforce and aid in consistent recording of financial events, as well as the preparation of standard external reports required by OMB and Treasury.
0104 Roles and Responsibilities
Office of Financial Policy (OFP) is responsible for reviewing and concurring on updates to VA General Ledger (GL) accounts upon request, and the annual publication of the updated ALC listing.
Office of Financial Reporting (OFR) is responsible preparing VA’s comprehensive financial reports, including the agency’s financial statements and the Agency Financial Report (AFR). Financial Management System Services, within OFR, is responsible for making system updates to approved GL accounts.
Office of Budget (OB) provides guidance and support to the Department’s Administrations and Staff Offices on matters relating to budget formulation and execution. The ultimate objective of the formulation process is to ensure the timely, accurate and informed submission of VA’s budget request to OMB and the President’s budget request to Congress. OB serves as the primary liaison with OMB and relevant Congressional committees during the formulation process, defending and promoting VA’s program plans and budget estimates before examiners and committee staff. OB also obtains apportionments from OMB and issues Financial Management Allowances and Transfer of Disbursing Authority documents to establish funds controls in VA’s accounting system, and monitors execution for funds control and adherence to operating plans.
VA’s Station Identification Officer is responsible for assigning and maintaining the uniform station number system in FMS, as detailed in Appendix B, VA Station Numbers.
Financial Services Center (FSC) is responsible for maintaining the VA Standard General Ledger accounts, budget object classes, and revenue source codes. FSC is also responsible for the yearly update of the ALC Point of Contact listing.
Manpower Management Services within the Office of Human Resources and Administration (OHRA) is responsible for the maintenance of the Division, Organization, Location and Cost Organization Codes elements within iFAMS.
0105 Policies
010501 General Policies
- An ACS is a comprehensive schema that supports the traceability and data interoperability of financial information to support budget, financial accounting, and performance reporting requirements.
- The ACS will allow accounting systems to:
- Provide managers with accurate and complete financial data, including total operating expenses and total acquisition cost of real and personal property, to enable informed decision-making;
- Provide for uniform treatment of similar accounting transactions used by all VA organizations;
- Produce expense and cost information concerning programs, projects, and other activities, in accordance with internal management needs;
- Provide data to meet reporting requirements of OMB, Treasury, and the Chief Financial Officers Act of 1990; and
- Provide other financial data, as needed, for both internal and external reporting requirements.
010502 Accounting Classification Structure (FMS)
The following minimum elements are required by the Accounting Classification Structure. VA will comply with this structure, to the extent possible given limitations within FMS.
- The Treasury Account Symbol is an identification code assigned by Treasury, in collaboration with OMB and VA, to an individual appropriation, receipt, or other fund account. Refer to Volume II, Chapter 2, VA’s Budget Cycle and Fund Symbols, for additional information.
- Budget Fiscal Year refers to the fiscal year in which the obligation is made and captured on the obligating document; it is used to distinguish whether subsequent adjustments affect a prior year or the current year. The budget fiscal year differs from the TAS period of availability. VA’s accounting system uses Budget Fiscal Year to denote the period of availability, establish a base year, or denote year of funding for a no year. It is not the equivalent of the obligation year.
- The Accounting Period is the period in which a transaction is established in the general ledger. In most instances, the accounting period pertains to a fiscal month within a fiscal year. However, in some instances, it represents a period that falls before or after the fiscal month and is used for recording opening balances to the period or period-end adjustments applicable to a month, quarter, or fiscal year. Accounting periods are used to group transactions by the period in which they are reported. The accounting system periods are from 00 (beginning) to 15 (closing).
- The Internal Fund Code is an agency-assigned code for a fund. It is a shorthand code entered on transactions and enables the derivation of the account identification codes (appropriation, receipt, or other TAS) required for reporting externally to Treasury (for reporting the TAS) and OMB (for reporting the budget account). VA will maintain appropriation fund codes in accordance with Treasury guidance. VA will establish separate fund accounts for direct and reimbursable obligations; these funds shall not be co-mingled. Refer to Volume II, Chapter 2, VA’s Budget Cycle and Fund Symbols.
- Organization Code, often referred to as Station Number, is the official identification number for funding and budgetary purposes and for describing the sphere of authority of an organizational entity designated by the Secretary. A uniform station number methodology provides a unique identifier for each station and allows for easier association and integration of data among systems.
- The FSC Executive Director and FSC Deputy Executive Director, or other designee (as assigned by the Deputy Chief Financial Officer), are assigned VA’s Station Identification Officers. The Station Identification Officer is responsible for approving, assigning, and maintaining the VA station number system. A listing of VA facilities and station numbers can be found at the VA Facility Listing website.
- VA administrations and staff offices will designate an individual who will serve as a station number liaison on all station number matters affecting proposed changes to their field facilities. The liaison will be responsible for ensuring that the official request is accurate, complete, and forwarded to the VAFSC Financial Accounting Service Program Office in the timeframe as specified on Appendix B, VA Station Numbers.
- Program, Project, and Activity Codes, also referred to as Accounting Classification Codes (ACCs), provide VA the means to categorize financial information to support budget execution and reporting functions. The ACC generally represents the lowest level of budget distribution. Refer to VA Volume II, Chapter 2, VA’s Budget Cycle and Fund Symbols, for additional information on the budget process. Detailed reference information for Accounting Classification Codes, Budget Object Codes, Cost Centers, End of Month Reports, Funds, and other accounting transaction reports is available on the FMS Home website ()VA Staff only.
- Program – An agency-assigned code that categorizes financial information by strategic goal, program, and line of business; it is used to describe what an agency does and the types of things for which it is funded.
- Project – An agency-assigned code that identifies a planned undertaking of something to be accomplished or produced, or an undertaking having a finite beginning and end. Examples are a construction project, a research and development project, and a reimbursable project.
- Activity – Identifies the actual work task or step performed in producing and delivering products and services, or the aggregation of actions performed within an organization that is useful for purposes of activity-based costing. An activity, in this context, differs from a “budget activity,” which is generally another name for a program.
- VA will ensure that the ACC data elements and definitions are uniform and efficient for budget and accounting treatment, classification, and reporting.
- VA’s accounting classification code is a nine-digit character code that is defined in FMS. The ACCs are established for each budget fiscal year. FMS contains information on standard ACCs used by more than one station and non-standard codes that are used by a single station. Users may identify the standard ACCs by an asterisk in the Station field.
- Cost Center is an agency-assigned code that identifies a logical grouping of one or more related activities or organizational units into a common pool to identify the cost incurred. The VA cost center is distinguished by areas of responsibility or geographic region and are symbolized by a four to six-digit code used to identify the organizational elements. Refer to Volume XIII, Chapter 1, Cost Centers, for further information.
- Object Class Code, referred to as Budget Object Code (BOC), classifies obligations by the items or services purchased by the Federal government (e.g., personnel compensation, supplies, rent, or equipment). While OMB Circular A-11 establishes the standard codes, titles, and definitions of the object class, an agency may further define extensions for capturing additional detail to support internal information needs. Refer to Volume XIII Chapter 2, Budget Object Codes, for detailed information.
- Revenue Source Code is used to track the revenue lifecycle from the initial order, processing, and finally to output, providing a history of financial activity related to the receipts. The code is agency-assigned and classifies revenue and receipt transactions by the type or source of revenue. The Revenue Source Codes is a unique four-digit code used to define revenue sources within different VA programs. The code in FMS also represents the mechanism to identify the applicable accounts receivable to move into the next fiscal year as part of the annual close process for Tricare and Shared Medical Resource bills under PL 104-262.
- Existing revenue source codes fall into two categories: (1) asset management revenue source codes, and (2) non-asset management revenue source codes.
- VA will comply with the revenue recognition as required by FASAB, Statement of Federal Financial Accounting Standards (SFFAS) 7: Accounting for Revenue and Other Financing Sources and Concepts for Reconciling Budgetary and Financial Accounting, and OMB A-11, Budget Preparation, Submission, and Execution of the Budget.
- VA will maintain a revenue system, inclusive of revenue source codes, that will provide the capability to trace transactions from their initial source through all stages of related system processing. VA activities that generate income and are identified with associated revenue source codes include, but are not limited to, donations, rental income, enhanced-use leasing, and recycling and waste reduction programs.
- VA administration CFOs, or their designees, or the heads of applicable staff offices or their designees, will approve revenue source codes prior to implementation. A list of personnel approved to submit a request for revenue source codes will be furnished to the Director of VA’s Financial Management System (FMS) Service at the beginning of each fiscal year.
- Requests for new revenue source codes or changes/deletions to current revenue source codes will be forwarded to the Office of Financial Reporting via Microsoft Outlook mailbox, “ACC\FCP Requests.”
- FMS has moderate flexibility to accommodate new and emerging reporting requirements, both internally and externally, to enable individual operating components to carry out program responsibilities effectively and efficiently.
- VA’s revenue source codes are assigned by using a standardized and unique numbering scheme as follows:
- Enhanced sharing assets must begin with an alpha character of “A” followed by three sequential numbers;
- Enhanced-use lease assets must begin with an alpha character of “E” followed by three sequential numbers; and
- Out-lease assets must begin with an alpha character of “U” followed by three sequential numbers.
- The numbering scheme supports the following activities:
- Transactions that record revenues based on sales of products or services, where the products or services are delivered prior to or concurrent with the payment.
- Transactions that allocate receipts to unearned revenue/advances (e.g., allow for entry of receipts to an advance USSGL account, either on an individual transaction basis or for a class of transactions, based on a predefined attribute or combination of attributes).
- Transactions that reclassify prior receipts to earned revenue based on some predetermined factor, such as an application process that allows for the earning of 25 percent of the fee as earned revenue as each step of the process is completed.
- VA’s revenue source codes are assigned by using a standardized and unique numbering scheme as follows:
- VA uses revenue source codes in the following activities:
- Supply Fund activities use a numbering scheme that begins with “SF,” “SM,” or “SR,” followed by two numeric characters for its revenue activities.
- VHA uses revenue source codes for the Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) revenue activities and other reimbursable activities. The numbering scheme will begin with either code “81” through “89” with a combination of alpha-numeric for the third and fourth positions – or – with code “8A” through “8P” with a combination of alpha-numeric for the third and fourth positions. VHA will use a numbering scheme that begins with an “80” for all non-MCCF revenues and reimbursable activities.
- VHA General Post Fund and NCA National Cemetery Gift Fund activities use a numbering scheme that begins with a “9” for revenue activities.
- VBA Loan Guarantee Programs use a numbering scheme that begins with an “L” for revenue activities. Education and Insurance will use a numbering scheme that begins with a “V” for revenue activities.
- Budget Function and Budget Sub-Function Code is a USSGL account attribute, used with the Internal Fund Code to classify data according to major purpose served or national need addressed for reporting purposes. These codes may be derived based on other data. Classifications are required by OMB Circular A-11. The VA budget function or sub-function codes are derived during the operations process in FMS.
- A Trading Partner is a federal entity that is party to intragovernmental transactions with another federal entity.
- Procedures for updating elements of the ACS and VA SGL in FMS are found in Appendices G and I.
010503 Accounting Classification Structure (iFAMS)
- The Financial Management Business Transformation (FMBT) Accounting Classification Structure document contains the comprehensive ACS structure within iFAMS. A copy of the document is found on the FMBT ACS VA SharePoint site.
- The Treasury Account Symbol (TAS) is an identification code assigned by Treasury, in collaboration with OMB and VA, to an individual appropriation, receipt, or other fund account. Refer to Volume II, Chapter 2, VA’s Budget Cycle and Fund Symbols, for additional information.
- The Budget Fiscal Year is divided into Beginning Budget Fiscal Year (BBFY) and Ending Budget Fiscal Year (EBFY). In an annual fund, the BBFY identifies the year of funds availability under law that the appropriation may incur new obligations. In a multi-year fund, the BBFY identifies the first year of availability, and the EBFY identifies the last year the appropriation account may incur new obligations. In appropriations that are available until expended (no-year), a new BBFY is established each year to track obligations/activity by funding year and has no bearing on overall funds availability for the no-year appropriation.
- The Accounting Period is the period in which a transaction is effective in the general ledger. In most instances, the accounting period pertains to a fiscal month within a fiscal year. However, in some instances, it represents a period that falls before or after the fiscal month and is used for recording opening balances to the period or period-end adjustments applicable to a month, quarter, or fiscal year. Accounting periods are used to group transactions by the period in which they are reported. The accounting system periods are from 00 to 14 (closing).
- Period 00 – Beginning balances for the new fiscal year;
- Periods 01 to 12 – Monthly activity;
- Period 13 – Adjusting entries; and
- Period 14 – Closing entries.
- The Internal Fund Code is an agency-assigned code value for a fund. The Fund Code and its attributes are used by agencies to classify financial transactions for reporting purposes. An agency’s Treasury Account Symbol (TAS) and Budget Accounts are also part of this category but are typically used for external reporting to Treasury and OMB, respectively. VA will maintain appropriation fund codes in accordance with Treasury guidance. VA will establish separate fund accounts for direct and reimbursable obligations; these funds shall not be co-mingled. Refer to Volume II, Chapter 2, VA’s Budget Cycle and Fund Symbols.
- The Division Code in iFAMS represents the top level of hierarchical structure for organizational elements in the ACS. The next level of organizational element in the ACS is the Organization Code (referred to as station identification numbers in FMS). These are the official identification numbers for funding and budgetary purposes and for describing the sphere of authority of an organizational entity designated by the Secretary. A uniform organization system provides a unique identifier for each organization and allows for easier association and integration of data among systems which require unique identification in automated information systems.
- VA administrations and staff offices will designate an individual who will serve as an organization code liaison on all organization code matters affecting proposed changes to their field facilities. The liaison will be responsible for ensuring that the official request is accurate, complete and forwarded to the VAFSC Financial Accounting Service Program Office in the timeframe as specified in Appendix B, VA Station Numbers.
- The FSC Executive Director and FSC Deputy Executive Director, or other designee, are assigned as VA’s Organization Code Officer. The Organization Code Officer is responsible for approving, assigning, and maintaining the VA organization number system. A listing of VA facilities and organization / FMS station numbers is found at the VA Facility Listing website.
- In iFAMS, the FSC Director and FSC Deputy Director will initially approve the Organization / Station Identification codes and upload documentation into iFAMS as an attachment to be routed to Manpower Management Service for final approval as they are the data owner for Division, Organization, Location, and Cost Organization Codes.
- Program, Project, and Activity (PPA) Codes provide VA the means to categorize financial information to support budget execution and reporting functions. The PPA Codes generally represent the lowest level of budget distribution. Refer to VA Volume II, Chapter 2, VA’s Budget Cycle and Fund Symbols, for additional information on the budget process. Detailed reference information for Accounting Classification Codes, Budget Object Codes, Cost Centers, End of Month Reports, Funds, and other accounting transaction reports is available on the FMS Home websiteVA Staff only.
- Budget Program Code (BPC) – Defines distinct lines of work performed by organizations responsible for carrying out that function. The BPC reflects the application of authorized budgetary resources used for that function (unobligated balances, appropriations, borrowing authority, prior year recoveries, transfers, and collections). The BPC is also used to capture the application of budgetary resources to obligations by program activity, subject to reporting requirements in OMB’s MAX A-11 database and the Digital Accountability and Transparency Act (DATA Act).
- VA Program Code – Identifies an organized set of programs directed toward a common purpose or goal that an agency undertakes or proposes to carry out its responsibilities. VA Administrations and Staff Offices determine the VA Program Codes to meet their tracking and reporting requirements.
- Project – identifies a planned undertaking of something to be accomplished or produced, or an undertaking having a finite beginning and finite ending. Project Task Code – Identifies the actual work task or step performed in producing and delivering products and services within a project. It also captures the aggregation of actions performed within an organization that are useful for the purposes of activity-based costing. A Project Task Code must be used in conjunction with Project Code.
- Activity Code – represents business functions performed by VA. In many cases, business functions have subordinate sub-functions. The Activity Codes are intended to enable the aggregation of similar business functions across the VA (e.g., budget management, contract administration, talent development, podiatry, manage patient safety, occupational health management, etc.).
1. VA will ensure that the PPA data elements and definitions are uniform and efficient for budget and accounting treatment, classification, and reporting.
2. PPA are established for each budget fiscal year. IFAMS contains information on standard PPA used by more than one organization / station and non-standard codes that are used by a single organization / station. Users may identify the standard ACS by an asterisk in the Station field.
- In iFAMS, the organization class value is representative of the FMS Cost Center, where the FMS cost centers are organizationally based. The FMS cost center is housed in iFAMS as a non-ACS user-defined field. iFAMS will maintain the integrity of the standardized data and provide the user with an understanding of how FMS cost centers relate to the new iFAMS ACS.
- Object Class Extension, referred to as Budget Object Class (BOC) Code, classifies obligations by the items or services purchased by the Federal government (e.g., personnel compensation, supplies, rent, or equipment). While OMB Circular A-11 establishes the standard codes, titles, and definitions of the object class, an agency may further define extensions for capturing additional detail to support internal information needs. Refer to Volume XIII Chapter 2, Budget Object Class Codes, for detailed information.
- Revenue Source Code (RSC) is used to track the life of revenue from the initial order, processing, and finally to output, providing a history of financial activity related to the receipts. The code is agency-assigned and classifies revenue and receipt transactions by the type or source of revenue. The RSC is used to define revenue sources within different VA programs. The code in iFAMS also represents the mechanism to identify the applicable accounts receivable to move into the next fiscal year as part of the annual close process for Tricare and Shared Medical Resource bills under PL 104-262.
- Existing RSCs fall into two categories: (1) asset management RSCs, and (2) non-asset management RSCs.
- VA will comply with the revenue recognition as required by FASAB, Statement of Federal Financial Accounting Standards (SFFAS) 7: Accounting for Revenue and Other Financing Sources and Concepts for Reconciling Budgetary and Financial Accounting, and OMB A-11, Budget Preparation, Submission, and Execution of the Budget.
- VA will maintain a revenue system, inclusive of RSCs, that will provide the capability to trace transactions from their initial source through all stages of related system processing. VA activities that generate income and are identified with associated RSCs include, but are not limited to, donations, rental income, enhanced-use leasing, and recycling and waste reduction programs.
- VA administration CFOs, or their designees, or the heads of applicable staff offices or their designees, will approve RSCs prior to implementation. A list of personnel approved to submit a request for RSCs will be furnished to the FSC at the beginning of each fiscal year.
- Requests for any new RSCs or changes/deletions to current RSCs will be forwarded through the FSC Customer Relationship Management (CRM) application. iFAMS ACS requests are submitted through the ACS Governance tool, a component of the FSC CRM application.
- iFAMS has flexibility to accommodate new and emerging reporting requirements, both internally and externally, to enable individual operating components to carry out program responsibilities effectively and efficiently. See Appendices E and F for a listing of RSCs used in VA’s accounting system. The numbering scheme supports the following activities:
- Transactions that record revenues based on sales of products or services, where the products or services are delivered prior to or concurrent with the payment.
- Transactions that allocate receipts to unearned revenue/advances (e.g., allow for entry of receipts to an advance USSGL account, either on an individual transaction basis or for a class of transactions, based on a predefined attribute or combination of attributes).
- Transactions that reclassify prior receipts to earned revenue based on some predetermined factor, such as an application process that allows for the earning of 25 percent of the fee as earned revenue as each step of the process is completed.
- A Trading Partner is a federal entity that is party to intragovernmental transactions with another federal entity.
- Procedures for updating elements of the ACS in iFAMS are found in Appendix H, Updating Elements in VA’s Accounting System (iFAMS).
010504 United States Standard General Ledger
- VA’s ACS will support Treasury’s reporting requirements via compliance with the Treasury Financial Manual and the United States Standard General Ledger (USSGL).
- Proprietary asset and liability accounts cover the receipt of funds in the Treasury, the proper classification of assets (such as receivables, prepayment, inventory, and fixed assets), and the recognition and proper classification of liabilities. The transactions in these accounts provide information on how operations are functioning, as well as ensure that the basic accounting equation remains in proper balance. Revenue and expense accounts measure the realization of revenues from reimbursements and the recognition of costs through the use and consumption of assets. The financial control provided through accounting records for property provides managers with a tool that helps to effectively discharge their stewardship function for those resources.
- Budgetary accounts reflect the recording of appropriation, apportionment, allocation, commitment, obligation, reimbursement, and expenditure processed. The transactions involve anticipating resources, realizing resources, or changing the status of resources.
010505 VA Standard General Ledger
- VA’s Chart of Accounts will be based upon the USSGL, thus providing a consistent basis for recording and reporting financial transactions and resource balances. The Chart of Accounts will also provide the basic structure for VA’s proprietary and budgetary reporting functions. In iFAMS, the General Ledger Account Code dimension consists of the USSGL Account and Extension Code, which is at the lowest level. The four roll-ups associated with the General Ledger Account Code are Category, Class, Group and Type, which are characteristics of the GL Account.
- VA SGLs must point to or roll into a valid USSGL.
- VA may use SGL accounts in its accounting system that are more detailed than the USSGL chart of accounts to provide detailed information for decision making or reporting purposes.
- VA will use, maintain, and record SGL accounts for all appropriations and fund activities, regardless of the source of funds.
- In addition to the USSGL accounts published by Treasury, VA may use SGL accounts in the accounting systems that are different from the USSGL Chart of Accounts when it is deemed necessary and the internal SGLs are rolled into a valid USSGL. VA’s six-digit SGL accounts are classified as follows:
- 100000 Assets;
- 200000 Liabilities;
- 300000 Net Position;
- 400000 Budgetary;
- 500000 Revenues and Financing Sources;
- 600000 Expense;
- 700000 Gains/Losses/Extraordinary Items, etc.;
- 800000 Memorandum (currently used by VBA for credit reform transactions and by all organizations to capture purchases of PP&E); and
- 900000 Memorandum
- VA will record all transactions (e.g., resources acquired and used by VA and claims against those resources) to the appropriate SGL (transaction level) in VA’s accounting system.
- Refer to Appendix I, General Ledger Request Process, for the procedures for establishing and maintaining VA SGL Accounts in FMS and submitting requests for MinX.
- Refer to CRM guide within Appendix H, Updating Elements in VA’s Accounting System (iFAMS), for procedures on establishing and maintaining VA SGL Accounts in iFAMS.
010506 Agency Location Codes
- The ALC is a unique symbol assigned by Treasury’s Bureau of Fiscal Service, also referred to as “Treasury Fiscal Service”, for reporting purposes. Refer to
- Appendix D, VA Agency Location Codes, for a listing of current VA ALCs.
- VA will ensure that ALCs are used to report receipt and disbursement cash transactions (to include Standard Form (SF) 215s: Deposit Tickets, and/or related SF 5515s: Debit Vouchers) and classify them according to appropriation, fund, and receipt account.
- VA will submit ALC requests, to include new or cancel requests, to Treasury Fiscal Service at least 30 days before the requested effective date.
- The Financial Services Center (FSC) Financial Accounting Service will assign a central point of contact (POC) to maintain the ALC list and provide Treasury Fiscal Service with the name, telephone number, and address of one contact person per designated ALC. The central POC will notify Treasury of the designations or subsequent changes. Requests for designations or changes will be submitted to the designated POC in accordance with procedures identified in Appendix D, VA Agency Location Codes.
- FSC will verify/update the assigned VA ALC contacts, as identified in Appendix D, Active VA ALCs and Contacts annually (December). The accountant will verify by e- mailing or calling the individual contact and make any necessary changes. If the contact does not respond, the official will be contacted.
0106 Authorities and References
- PL 104-262 Veterans’ Health Care Eligibility Reform Act of 1996
- Chief Financial Officers (CFO) Act of 1990
- Customer Relationship Management Self Service Portal (va.gov)
- Federal Financial Management Improvement Act (FFMIA) of 1996
- OMB Circular
- OMB Circular A-11, Preparation, Submission and Execution of the Budget
- OMB Circular A-123, Appendix D, Management of Financial Management Systems – Risk and Compliance
- OMB Circular A-136, Revised, Financial Reporting Requirements
- SFFAS 7, Accounting for Revenue and Other Financing Sources and Concepts for Reconciling Budgetary and Financial Accounting
- Treasury Financial Manual
- Treasury USSGL
- Office of Financial Policy
- Volume II, Chapter 2 – Budget Cycle and Fund Symbols
- Volume VII, Chapter 1 – Financial Reporting
- Volume XIII, Chapter 1 – Cost Centers
- Volume XIII, Chapter 2 – Budget Object Class Codes
- Financial Management System Services Home ()
- FMS General Ledger Account and Proforma Transaction Resource
- VA Facility Listing website
- VA FMBT ACS SharePoint Site ()VA Staff only
0107 Rescissions
Volume II Chapter 1, VA’s Accounting Classification Structure, July 2023.
Appendix A: Prior Policy Revisions
| Section | Revision | Office | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appendix F | Targeted change to update iFAMS Revenue Source Codes | FMBT | Updating iFAMS Revenue Source Codes | July 2023 |
| Appendix D | Updated contact information on the Agency Location Code listing | OFP | Annual Review | October 2022 |
| Various | Updated financial policy to align with iFAMS configuration | FMBT | Implementation of iFAMS accounting system | November 2020 |
| 010503 ACS (iFAMS) | Added policy section for iFAMS ACS | FMBT | Implementation of iFAMS accounting system | November 2020 |
| Appendix C | Added VA Organization Codes for iFAMS | FMBT | Implementation of iFAMS accounting system | November 2020 |
| Appendix D | Updated contact information on the Agency Location Code listing | OFP | Annual review | November 2020 |
| Appendices E and F | Incorporated charts of VA Revenue Source Codes (RSCs) for FMS and iFAMS | OFP | Implementation of iFAMS accounting system | November 2020 |
| Appendices G, H, and I | Incorporated procedures for updating elements in VA’s ACS and VA SGL | OFP | Implementation of iFAMS and Removal of Procedures from Volume I, Chapter 4 – Compliance with Federal Financial Management Improvement Act | November 2020 |
| Various | Reformatted to new policy format and completed five-year update | OFP | Reorganized chapter layout | February 2020 |
| 0102 Policy 0105 Procedures Appendix F, Journal Voucher Procedures | Removed journal voucher information from this policy and created Volume II, Chapter 1A – VA Journal Vouchers | OFP | JV information is more appropriate in a separate policy | February 2020 |
| VA SGL Account Procedures (Formerly Appendix D) | Removed procedures for establishing and maintaining VA SGL Accounts | OFP | Information is contained in Volume I, Chapter 4 – Financial Management Systems | February 2020 |
| Appendix C, Agency Location Codes (Previously numbered Appendix E) | Updated VBA’s contact information on the ALC chart | OFP | Contact information was updated | September 2018 |
| Appendix F | Updated the FSC Accounting e-mail address, FMS JV Approval procedures, and MinX JV Data Field Requirements | OFP | Financial Reporting Corrective Action Plan | September 2018 |
| 0106 Definitions | Added iFAMS definition | OFP | Define iFAMS | June 2018 |
| Appendix E | Updated ALC listing | OFP | Added ALC listing for iFAMS processing | June 2018 |
| Appendix D | Updated responsibilities for maintenance of USSGL accounts | OFP | To reflect current responsibilities and procedures | February 2018 |
| Appendix E | Update Agency Location Code listing | OFP | Update with current information | February 2018 |
| 0102 Policies | Added pre-approval requirement for non-routine FMS and MinX JVs equal to or greater than $100 million | OFP | NFR 15-1, Consolidated Financial Reporting | December 2017 |
| 010201.03 Agency Location Code | Removed references to Treasury FMS 224, Statement of Transactions | OFP | FMS 224 is no longer used | December 2017 |
| 0104 Roles and Responsibilities | Assigned roles and responsibilities for pre-approval of non-routine FMS and MinX JVs equal to or greater than $100 million | OFP | NFR 15-1, Consolidated Financial Reporting | December 2017 |
| Appendix C | Updated RSCs for VHA and VBA | OFP | New codes | December 2017 |
| Appendix F, JV SOP Section 1.2 Responsibilities | Added clarification to the Roles and Responsibilities | OFP | NFR 15-1, Consolidated Financial Reporting | December 2017 |
| Appendix F, JV SOP | Removed references to the JV template | OFP | JV template is no longer used | December 2017 |
| 0101 Overview | Updated Department of Treasury’s Financial Management Service to Bureau of Fiscal Service and removed reference to the CFOC Financial Line of Business, Financial Systems Integration Office | OFP | General update | March 2017 |
| 010201.02D Policies | FSC Financial Accounting Service will assign POCs for ALC | OFP | Added roles and responsibility | March 2017 |
| 010202 Documenting Financial Changes Through Journal Entries | Added reference to JV SOP, Appendix F | OFP | Update per CLA recommendation for NFR 16-4 Financial Reporting | March 2017 |
| 010317 | Reference to OMB Circular A-123, Appendix D, Compliance with the Federal Financial Management Improvement Act (09/20/2013) replaced Financial Systems Integration Office, Federal Financial Management Standards, CGAC Structure | OFP | General update | March 2017 |
| 0105 Procedures | Added reference for Appendix F | OFP | NFR 16-4 Financial Reporting | March 2017 |
| 0107 Rescissions | Updated rescinded volumes | OFP | General Update | March 2017 |
| Appendix B | VA Station Numbers | OFP | VHA requested update to station numbers | March 2017 |
| Appendix E | FSC FAS Director recommends cancellation of ALC request. Updated points of contact on Figure 1E-3, Active VA ALCs and Contacts | OFP | General update | March 2017 |
| Appendix F | Renamed Appendix F and added JV SOP | OFP | Update per CLA recommendation for NFR 16-4 Financial Reporting | March 2017 |
| Appendix F, JV SOP | Updated various sections of JV SOP to reflect current procedures, and added appropriate approvals | OFP | Update per CLA recommendation for NFR 16-4 Financial Reporting | March 2017 |
| Appendix B | VA Station Numbers | OFP | Incorporated into policy | March 2016 |
| 0107 Rescissions | Rescinded Vol II Ch 1 and Ch 1A, policy merged into Vol II Ch 2 and Ch 5. Renumbered Vol II Ch 1A to Ch 1. | OFP | Policy reorganization | September2012 |
| Overall | Rescinded Volume I, Chapters 2, 3, 4A, and 4B, and Bulletin 08GA1.10, merged information into new chapter. | OFP | Policy reorganization | September2012 |
| Overall | Updated chapter to align with FSIO CGAC guidance and relationship to VA. | OFP | New guidance | September2012 |
| Chapter and Appendix B | Reference and policy for station identification updated and incorporated from Dir/Handbook 0030. | OFP | New guidance | September2012 |
| Chapter and Appendix F | Reference and policy for journal entries and journal vouchers updated and incorporated from bulletin. | OFP | New guidance | September2012 |
Appendix B: VA Station Numbers (FMS)
- As displayed in the table below, the three-digit station number also identifies the functional areas of responsibility throughout VA.
| Station Number Range | Functional Areas of Responsibility |
|---|---|
| 100-199 | Central activities |
| 200-299 | Automation Center or Benefits Delivery Centers |
| 300-399 | VBA activities |
| 400-499 | Medical Centers, VA Medical and Regional (VBA) Offices co- located), Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) |
| 500-699 and 776-777 | VHA activities |
| 700-775 and 778-799 | Miscellaneous (Supply Depots, Marketing Centers, CHAMPVA, Inspector General Offices, National Cemetery Memorial Service Networks (MSNs), National Cemetery Field Support Facilities, Canteen Service Field Offices, Prosthetics Center, National Railroad Retirement Board*, National Personnel Records Center* (military records), Army Reserve Personnel Center*), Office of Resolution Management Field Offices, Consolidated Patient Account Centers (CPAC), National Patient Safety |
| 800-999 | National Cemeteries, Manila Outpatient Clinic (964) Western Area Office (999) |
| *These non-VA activities require station numbers to access the Beneficiary Identification and Records Locator Subsystem (BIRLS). | |
- Types of Station Number Requests. Station numbering requests, to include substation requests, require a memorandum to be sent to the FSC email distribution, VAFSCStationIdentificationOfficer@va.gov, at least 90 days prior to the effective date of the assignment. Requests will be sent through the Administration or Staff Office Chief Financial Officer (for VHA, VBA and NCA). VA Central Office requests will be sent through the FSC. The information is necessary to allow automated information system (AIS) managers time to incorporate changes in the appropriate AIS.
- Types of Station Number Requests.
- Administrative Correction;
- Reservation or Extension;
- Assignment and Activation;
- Name Change;
- Facility Relocation; and
- Retirement
- Each memorandum request will identify the type of station, name, location of the station, the effective date of the assignment, and the point of contact that will serve as the station number liaison on all station number matters affecting proposed changes to their field facilities. The request will include:
- Type of request;
- Date the requested action will take place;
- Facility and Telephone Number;
- Station number(s) affected, when already established;
- Point of contact (POC) name, telephone, and e-mail; and
- Parent Station if request relates to a suffix number.
- Note: Requests to update the facility telephone number may be submitted in an e-mail to the FSC; these do not require a memorandum or change request form. The telephone numbers are used when generating information that may be released to Veterans and providers.
- Types of Station Number Requests.
- Additional Considerations for Station Number Requests.
- Any information that is not known at the time of the station reservation request must be provided to the VA Station Identification Officer by e-mail at VAFSCStationIdentificationOfficer@va.gov within a reasonable timeframe of the memorandum, not to exceed one year from the date of the memorandum notification generated by the VA Station Identification Officer. The e-mail received by the facility must provide a POC or designee. The FSC will contact the POC or designee listed in the e-mail notifying if information is needed or an extension of the reservation is required. The reserved station or suffix number will not be activated until all required information is provided to the VA Station Identification Officer. If the missing information or no request for activation or extension of reserved status is received within one year, a reserved station number that has not been activated or extended will be cancelled.
- VA facilities are generally named for the geographical location where they are located. VA facilities may be named in honor of individuals only when authorized by congressional mandate or Executive Order of the President. Parts of facilities, such as individual buildings, wings of buildings, patient treatment wards, and auditoriums, may be named in honor of individuals, if approved by the Secretary of Veterans Affairs. A copy of the congressional mandate or Executive Order will be attached to the station request.
- VA may assign a new station number to a replacement facility when the replacement facility is built at a location different from the original facility that it replaces. These requests will contain a statement specifying that the new facility will be situated at a different location different than the current facility.
- Several stations may share the same location, but under the leadership of individual directors. In these cases, a separate station number may be assigned to each station.
- When a station is closed, the station number will be retired and will not be reassigned.
- When a VHA regional office activity and a medical center are combined to form a new facility, a new station number will be assigned.
- To facilitate the exchange of data between two or more systems and maintain consistency, program managers will request a substation (suffix modifier) when it is necessary to uniquely identify:
- A medical center or domiciliary division of a complex station;
- A facility separate from the parent station; or
- A non-VA facility where reports are generated either by or through a VA station. The suffix modifier is appended to the VA station number that represents the data on behalf of the non-VA station. For example, a private medical facility treating VA patients would be identified by using the station number of the VHA medical center that authorizes treatment, with a suffix modifier.
- Within a reporting structure, a specific suffix modifier will be uniformly applied to identify a specific function as listed in the Station Suffix Modifiers table.
- Components of medical and regional office centers or medical center complexes that are not stations will not be identified by separate station numbers. When the need arises for these components to be uniquely identified, and such identification is not provided for by other means, a suffix modifier will be assigned to the basic station number.
- Suffix modifiers will not be used to identify routine activities of typical stations.
- FSC review and approval are required prior to requesting changes to Station Suffix Modifiers.
- Stations will forward all change requests to the VAFSC Accounting System’s Oversight VA Station Identification Officer by e-mail at VAFSCStationIdentificationOfficer@va.gov.
- Subsequent to review and approval, the FSC will forward each approved request to OFP for policy update.
| Substation Type | Abbreviation | Suffix Modifier or Classification Range |
|---|---|---|
| VBA Substation | VBASUB | AA – AZ |
| * VA Medical Center | VAMC | A4-A9 |
| *VA Clinic (Includes: VA Health Care Center (HCC), Community-Based Outpatient Clinic (CBOC), both Primary Care CBOC & Multi-Specialty CBOC, and VA Other Outpatient Service Sites (OOS Sites)- to include Mobile Clinics) | HCC CBOC OOS | HCC Classification: BY-BZ CBOC Classification: GA- GZ; G1-G9; JA-JZ; J1-J9 OOS Classification: QA-QZ |
| *VA Community Living Center | CLC | 9AA-9AE; 9BA-9BE |
| Community Nursing Home | CNH | 9AK-9AZ |
| State Veterans Home – Nursing Home | STNH | 9AF-9AJ |
| State Veterans Home – Domiciliary | STHOME | DT-DZ; EA-ES |
| *VA Domiciliary and other Mental Health Residential Rehabilitation Treatment Programs or Residential Care Site (excluding Compensated Work Therapy- Transitional Residence) | VADOM PRRTP | BT-BX |
| Non-VA Hospital (Army) | NVAHA | CN – CS |
| Non-VA Hospital (Navy) | NVAHN | CT – CY |
| Non-VA Hospital (Air Force) | NVAHAF | C0-C4; CZ |
| Non-VA Hospital (Public Health Service) | NVAHPHS | C5-C9; DA |
| Non-VA Hospital (Other Federal) | NVAHOF | DB – DG |
| Non-VA Hospital (Public) | NVAHP | DH – DM |
| Non-VA Hospital (Civil) | NVAHC | DN – DS |
| Employee Education System | EES | D2-D9; E2-E9; F2-F9 |
| History File Construction | HFC | FA-FS |
| Integrated Disability Evaluation System | IDES | MA – MZ |
| *Compensated Work Therapy-Transitional Residence | CWT/TR | PA-PN |
| National Suicide Hotline Call Center | NSHCC | SH1 – SH9 |
Appendix C: VA Organization Codes (iFAMS)
- iFAMS Organization Codes are nine-digit alphanumeric codes where the first character identifies the Administration. The table below lists the leading digits currently defined with an Organization Code example.
| Element | Field Purpose | Format | iFAMS Field Name | Admin | Example Code | Example Code Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organization Code | Represents the organization | 9 alphanumeric characters | Organization Code | NCA | C09310000 | Sarasota National Cemetery |
| Organization Code | Represents the organization | 9 alphanumeric characters | Organization Code | VBA | B30700224 | ES – State Approving Agency Team |
| Roll-Up Values | ||||||
| Organization Category | Represents a higher grouping of similar organizations within an Administration. | 6 alphanumeric characters | Organization Category | The coding for Organization Category will be determined. | ||
| Organization Class | Represents a grouping of similar organizations within an Administration. Examples include CEM000 – Cemeteries, providing the ability to report on all Cemeteries. | 6 alphanumeric characters | Org Class | NCA | CEM000 | Cemeteries |
| Organization Class | Represents a grouping of similar organizations within an Administration. Examples include CEM000 – Cemeteries, providing the ability to report on all Cemeteries. | 6 alphanumeric characters | Org Class | VBA | 307000 | Education Service |
| Organization Group | Represents the VA District and VISN. | 2 alphanumeric characters | District/VISN | NCA | O2 | Southeast District |
| Organization Group | Represents the VA District and VISN. | 2 alphanumeric characters | District/VISN | VBA | HQ | Headquarters |
| Organization Type | Represents a grouping of similar organizations within an Administration. | 6 alphanumeric characters | Organization Type | The coding for Organization Type will be determined. | ||
Appendix D: Agency Location Codes
- An ALC can be in the form of three digits for Regional Financial Centers, four digits for Non-Treasury Disbursing Offices, or eight digits for reporting entities. In most cases, the first two digits of an eight-digit ALC identify the department or agency, the next two digits identify the bureau, and the last four digits identify the specific agency account section within the bureau. The department / agency identifier for most of VA’s ALCs are two digits (36). Treasury began using a three-digit ALC for the department / agency identifier. Newly established VA ALCs will reflect the three-digit code (036). Treasury will not retroactively apply the three-digit convention to existing ALCs.
- This appendix provides procedures for the maintenance of the ALCs, to include requests for establishing, changing, or canceling an ALC. The following steps list the procedures for maintaining the ALC. These procedures are not performed within VA’s accounting system (FMS or iFAMS). This is the process for maintaining VA’s official list of ALCs with Treasury. It is external to financial systems, which are already assigned their core ALCs.
- New Request. A new request should only be made when a new major system or program is created and requires separate Treasury tracking, reconciliation and reporting from an existing system or program (e.g., replacement corporate financial system). VA will limit the number of ALCs to the extent possible.
- A request for a new ALC will be submitted in a memorandum to the FSC Transaction Review mail group. The FSC Transaction Review group will assign the request to an FSC-Financial Accounting Service (FAS) accountant. The ALC request will contain the following information:
- ALC – Proposed ALC number;
- Location – Agency address requesting ALC;
- Program – Name of program;
- Contact;
- Contact phone number;
- Official –Director name, title, and phone number; and
- Detailed justification
- The FAS accountant will verify the memorandum request to determine its propriety and whether the proposed ALC number is available and within the correct numbering sequence. All VA ALCs begin with 3600 or 0360 and are an eight-digit number. The last four digits are assigned based on the following station number sequence:
- Staff Offices: 100/200 series;
- VBA: 300 series;
- VHA: 400 – 600 series;
- VHA and NCA: 700 – 800 series;
- NCA: 800 – 900 series;
- Canteen: 785; and
- Manila Exception: ALCs are 14 digits–the 1st 4 are the agency locator code, 5th and 6th are the bureau code, 7th-10th are the ALC for Global Financial Service, 11th–14th are the Disbursement Office.
- Once the information is verified, the FAS accountant forwards the request to the FAS Director with their recommendation. If approved, FAS will send a letter to Treasury-Fiscal Service containing the above information from an official Government email address to CashAnalysisSection.CARD- FAO@fiscal.treasury.gov, or by mail addressed to the below address.
Cash Accounting Branch (ALC Request)
Department of the Treasury – Bureau of Fiscal Service
200 Third Street Bldg
Parkersburg, WV 26101
Telephone: 304-480-6705
Once the ALC is established, the FAS accountant will inform the requester and the Chief of the FSC FAS Accounting Reconciliation and Report Division.
- A request for a new ALC will be submitted in a memorandum to the FSC Transaction Review mail group. The FSC Transaction Review group will assign the request to an FSC-Financial Accounting Service (FAS) accountant. The ALC request will contain the following information:
- Cancel ALC Request.
- A request to cancel an ALC will be submitted in a memorandum to the FSC Transaction Review mail group. The FSC Transaction Review group will assign the request to an FAS accountant. The request should only be sent after the ALC is reconciled and no activity to the ALC has been posted for the past year. The ALC request will contain the following information:
- ALC – cancellation;
- Location – Agency address;
- Program – Name of program;
- Contact;
- Contact phone number;
- Official –Director name, title, and phone number; and
- Detailed Justification – Include where activity should be reported if any occurs in the future.
- The FAS accountant will verify the memorandum request and forward it to the FAS Director with a recommendation. If approved, FAS will send a letter to Treasury-FMS containing the above information and addressed to:
Cash Accounting Division (ALC Request)
Department of the Treasury – Bureau of Fiscal Service
200 Third Street Bldg
Parkersburg, WV 26101
Telephone: 304-480-6705 - Once Treasury Fiscal Service has canceled the ALC and notified FAS, the FAS accountant will inform the requester and the Chief of the FSC FAS Accounting Reconciliation and Report Division. The FAS accountant also notifies the Office of Financial Policy to update the ALC and Contact table.
- A request to cancel an ALC will be submitted in a memorandum to the FSC Transaction Review mail group. The FSC Transaction Review group will assign the request to an FAS accountant. The request should only be sent after the ALC is reconciled and no activity to the ALC has been posted for the past year. The ALC request will contain the following information:
Active VA ALCs and Contacts
| ALC | Location | Program | Phone | Responsible Office |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36000102 | VA FSC Customers FAS (0474) 1615 Woodward Street Austin, TX 78772 | OGA Medical Claims Payments (Franchise Fund) | 737-294-2539 512-460-5195 512-460-5484 | Chief Accounting Officer 512-820-7733 |
| 36000103 | VBA Central Office (241B) Office of Budget & Finance 810 Vermont Ave., NW Washington, DC 20420 | VBA Life Insurance & Housing Investments | 302-375-6388 202-461-8441 202-460-9974 202-618-0604 | Director, VBA APRS 202-461-9355 |
| 03600104 | Department of Veterans Affairs Financial Services Center FAS (0474) P.O. Box 149975 Austin, TX 78714-9575 | iFAMS | 737-294-2539 512-460-5254 | Chief Accounting Officer 512-820-7733 |
| 36000200 | Financial Services Center FAS (0474) P.O. Box 149975 Austin, TX 78714-9575 | Payroll Adjustments (All appropriations and funds with salary expenses) | 737-294-2539 512-460-5485 512-460-5195 | Chief Accounting Officer 512-820-7733 |
| 36000201 | Department of Veterans Affairs Hines Finance Center (201/241) P.O. Box 7001 Hines, IL 60141-7001 | Benefits Payments (VBA benefits appropriations and funds) | 708-483-5417 708-483-5438 | VBAFC Director 708-681-6650 |
| 36000310 | Department of Veterans Affairs Regional Office & Insurance Center P.O. Box 42954 Philadelphia, PA 19101 | VBA Life Insurance | 215-842-2000 ext: 4279 ext: 4587 ext. 4535 | Chief of Accounting 215-842-2000 ext: 4287 |
| 36000785 | Department of Veterans Affairs 1 Jefferson Barracks Rd., Bldg. 1 St. Louis, MO 63125-4194 | VHA Veterans Canteen Service | 314-845-1300 314-845-1305 314-845-1336 314-845-1361 | Director 314-845-1207 |
| 36001200 | Financial Services Center FAS (0474) P.O. Box 149975 Austin, TX 78714-9575 | VA Legacy Financial System (All appropriations and funds other than VBA Life Insurance, NCA, and GOE) | 737-294-2539 512-460-5254 | Chief Accounting Officer 512-820-7733 |
| 36-02- 8768-0390 | Department of Veterans Affairs – Manila DPO AP 96515 RO Manila | Manila Regional Office/OPC- GOE, Med Svcs, Med Admin, Med Facilities, Suspense | 011-632-8550-3845 011-632-8396-3766 011-632-8550-3902 011-632-8396-3773 011-632-8550-3915 | Acting Chief Support Svs Div 011-632-550- 3928 |
| 36-03- 8768-0390 | Department of Veterans Affairs – Manila DPO AP 96515 RO Manila | Manila Regional Office – Insurance Collections | 011-632-8550-3928 011-632-8396-3766 011-632-8550-3902 011-632-8396-3773 011-632-8550-3915 | Acting Chief Support Svs Div 011-632-550- 3845 |
Appendix E: VA’s Revenue Source Codes (FMS)
A comparison table of FMS to iFAMS Revenue Source Code fields is contained in the FMBT ACS document.
| Used by | Leading Characters | FMS Category Name |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | A | Enhanced Sharing Assets |
| ALL | E | Enhanced-Use Lease Assets |
| VBA | L | VBA Loan Guarantee Programs |
| VACO (Denver Distribution Center) | SF | Supply Fund |
| VACO (Denver Distribution Center) | SM | Supply Fund |
| VACO (Denver Distribution Center) | SR | Supply Fund |
| ALL | U | Out-Lease Assets |
| VBA | V | Education and Insurance |
| VHA | 80 | Non-Medical Care Collection Fund (Non-MCCF) – VHA |
| VHA | 81 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 82 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 83 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 84 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 85 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 86 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 87 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 88 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| VHA | 89 | Medical Care Collection Fund (MCCF) or 8A through 8P – VHA |
| NCA, VHA (ALL) | 9 | VHA General Post Fund and NCA National Cemetery Gift Fund |
| Staff Offices (ALL) | 1000 | Miscellaneous Revenue |
| Staff Offices (ALL) | 1001 | Miscellaneous Revenue – CO |
| Staff Offices (ALL) | 1010 | Interest Revenue |
| VBA (ALL) | 3010 | GOE Admin Support |
| ALL | ANCL | Misc Receipt-Annual Close |
| ALL | AR12 | AR-Conversion |
| ALL | ARRV | Revenue-AR |
| ALL | BFPR | Profit-Burial Flags |
| ALL | CANT | Canteen Interface |
| ALL | CNV1 | Conversion-Act Reimb |
| ALL | CONV | Conversion |
| VHA-Policy/VACO- iFAMS | DD01 | Commodities Cost |
| VHA-Policy/VACO- iFAMS | DD02 | Commodities Markup |
| VHA-Policy/VACO- iFAMS | DD03 | Custom Hearing Costs |
| VHA-Policy/VACO- iFAMS | DD04 | Custom Hear Markup |
| VHA-Policy/VACO- iFAMS | DD05 | Hearing Aid Repairs |
| VHA-Policy/VACO- iFAMS | DD06 | Telehealth Svc Fees |
| ALL | DD99 | Misc Revenue |
| VHA | DDPR | Profit Dir Del |
| VBA | DMAC | LGY GIF Debt-Admin Cost |
| VBA | DMIT | LGY GIF Debt-Interest |
| VBA | DMPO | LGY GIF Debt Coll-Susp Trnsfr |
| VBA | DMPR | LGY GIF Debt Collection |
| VBA | DMTR | LGY GIF Debt |
| ALL | IT01 | Recycling Incom – OI&T |
| ALL | JURY | Jury Fees Collected |
| VBA | OFHE | Reimb-OFHEO |
| ALL | PAID | PAID-Interface SV |
| VACO (Denver Distribution Center) | SDDC | Supply Fund – DDC |
| SE16 | National Security Agency | |
| SE17 | Selective Service System | |
| TH01 | Transitional Housing Interest |
Appendix F: VA’s Revenue Source Codes (iFAMS)
A comparison table of FMS to iFAMS Revenue Source Code fields is contained in the FMBT ACS document.
| Used by | iFAMS Category | iFAMS Category Name |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | A00000 | Agreements Revenue – Enhanced Space |
| ALL | E00000 | Agreements Revenue – EU Lease |
| VBA | L00000 | Loan Guarantee Programs |
| VACO (Denver Distribution Center) | SF0000 | Supply Fund Commodities Revenue |
| VACO (Denver Distribution Center) | SM0000 | Supply Fund Mark Up Revenue |
| VACO (Denver Distribution Center) | SR0000 | Supply Fund Fee Revenue |
| ALL | U00000 | Outlease – License – Permit |
| VBA | V00000 | Education and Insurance Revenue |
| VHA | 800000 | Non-MCCF Revenues and Reimbursable Activities |
| VHA | 810000 | Medical Care Revenue |
| VHA | 811000 | Unbilled Revenue |
| VHA | 820000 | Pharmacy-Related Revenue |
| VHA | 830000 | Ineligible Revenues and Reimbursable Activities |
| VHA | 840000 | Third Party Billings |
| VHA | 841000 | Accident-Related Medical Care Revenue |
| VHA | 850000 | Insurance Billing and Revenue |
| VHA | 851000 | Tricare Insurance Billing and Revenue |
| VHA | 860000 | Long Term Care Revenue |
| VHA | 880000 | Humanitarian Billings |
| VHA | 890000 | First Party Billings |
| ALL | 8R0000 | Garage and Parking Revenue |
| ALL | 900000 | General Post Fund |
| ALL | 910000 | Sale of Property and Investments |
| ALL | 920000 | Other Revenue |
| VBA | 920001 | VBA Other Revenue |
| ALL | 930000 | Donations |
| ALL | 940000 | Interface and Conversion |
Appendix G: Updating Elements in VA’s Accounting System (FMS)
- The Accounting Entries Definition Table (ACED) and Accounting Entries Table (ACEN) will be used to make changes in accounting transactions in FMS.
- The process to make changes to ACEN/ACED table are as follows:
- The ACED and ACEN requests will be routed via CRM Self-Service Portal.
- Requesters will complete the request form on the CRM Self-Service Portal ensuring that all applicable fields are populated.
- A supervisor will review and approve the request form in the CRM Self-Service Portal. The approved request will be routed to FSCTransactionReview@va.gov mail group.
- The FSC Transaction Review group will review, research, and verify the transaction.
- The FSC reviewer will work with the requester to resolve any questionable issues to ensure the transaction is established/updated correctly in FMS.
- When FSC approves the request it will be routed to VACOAlertOFP@va.gov mail group.
- OFP will review, research and verify the transaction.
- OFP will work with the FSC reviewer and the requester to resolve any questionable issues.
- OFP will electronically sign/approve the request and forward the request to FMS Services via the VACO047E7@va.gov mail group.
- When FMS Services receives the approved form, the requested transaction will be entered into FMS.
- Once entered into the system, FMS Services will notify the requester, supervisor, FSC Transaction Review Group, and OFP that the transaction is available for use.
- If there is an issue with processing the request in FMS, FMS Services will work with FSC and OFP to resolve the issue.
ACED ACEN (FMS) System Accounting Transaction Request Form instructions
- Requesters will need to complete applicable fields on the ACED and ACEN request prior to submitting a ticket through the CRM Self-Service Portal.
- Required fields for the ACED and ACEN accounting transaction requests include:
- Name of Person Making Request – Last Name, First Name, Initial.
- Requester E-Mail Address.
- Requester Work Phone Number.
- Date of Request.
- Station #.
- Type of Request – New, Update, or Delete.
- Administration – The administration this request belongs to.
- Reason for Entry or Change – Enter information to explain why the transaction is needed.
- Area – Select from drop down, Production or Test. If the transaction is for Test, then provide the Region.
- TC – List Transaction Code that will be assigned to the transaction.
- TT – List the Transaction Type that will be assigned to the transaction.
- VC – List the Vendor Category that will be assigned to the transaction if applicable.
- BOCT – List the BOC that will be assigned to the transaction if applicable – Check the BOCT table to see if the BOC needs to be posted as indicated by the BOC POST FLAG. If no BOC is needed, then that field should be left blank. Note: RSCs are not posted on the ACED/ACEN table. If the transaction requires an RSC, the requester needs to ensure the RSC exists on the RSRC table in FMS. If it does not exist, a ticket should be submitted via UniCenter requesting the action.
- FCAT – List the Fund Cat that will be assigned to the transaction.
- Entry – Accounting Entry ID – If an entry for the GLs and ACEV already exist, list that entry and add an * behind the Entry ID. If one does not exist, leave it blank – FMS Services will assign an Entry ID to the transaction.
- ACEV – List the ACEV entry that will be assigned to the transaction.
- Description – List a description that identifies the action the transaction performs.
- DR/CR – List the debits and credits that the transaction will hit. Notes – VA lists their debits and credit in the following order – Proprietary, Budgetary, and Subsidiary.
- PP – Prompt Pay indicator. Type in “Y” or “N” in the box if prompt pay is applicable.
- Name of Supervisor/Title – Type in the supervisor’s name and their email address.
- Comments/Notes – Any additional information may be added to the NOTE section.
The ACED and ACED pdf form will only be used if the CRM Self-Service Portal is down and there is an urgent request that will need to be processed.
Appendix H: Updating Elements in VA’s Accounting System (iFAMS)
- iFAMS ACS requests must be submitted through the ACS Governance tool, a component of the FSC CRM application. iFAMS ACS requests include, but are not limited to the following:
- Adding a new account;
- Updating or changing account titles;
- External reporting tables;
- Dimensional values;
- iFAMS Accounting Templates; and
- Concur Interface Accounting templates.
- ACS requests will be submitted as follows:
- Requester will ensure all applicable fields are populated and will route the form for supervisory approval.
- The requester’s supervisor will review and either approve or reject the request.
- When an ACS request is approved, it will be routed to FSC Financial Accounting Service (FAS).
- FSC FAS will review and validate the ACS request (i.e., compare the request against authoritative guidance (e.g., USSGL guidance)).
- Once FSC FAS is satisfied the request is in line with authoritative guidance it will route the change request form to determine system impacts.
- ACS SME in FMBT will review the request to determine impact to FMBT ACS.
- If there is an issue with the request, FSC FAS will work with the customer to resolve.
- When an ACS request is approved by FSC FAS, it will be routed to the Data Owner.
- The Data Owner (e.g., staff member at the FSC, VACO Budget Office, another Administration or Staff Office based upon the data element) will review the ACS request form to validate the data element addition, change or end date, while checking for possible impacts, such as hierarchy changes, flex posting updates, relationship edit modifications, and reporting configuration.
- When the request is approved by the Data Owner, it will be sent to FSC Accounting Systems Oversight Section (ASOS) for required testing and production implementation.
- When a request has been configured in iFAMS, FSC ASOS will send out a notification to all the appropriate POCs that are on the request form.
- When the ACS request has been successfully uploaded into iFAMS, the ACS Governance Tool will automatically generate an email notification to other applicable system owners of the addition, modification, or end date of the iFAMS ACS data elements.
- The CRM guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to submit iFAMS ACS and template requests on the CRM portal. For additional information on submitting ACS requests, refer to the Accounting Classification Structure and Accounting Template User Guide.
- Overview of the submission, review, and approval process within the CRM Self-Service portal.
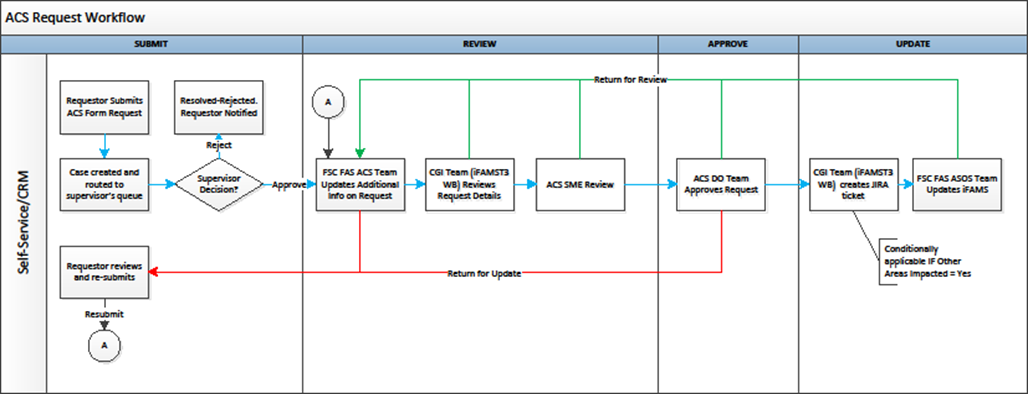
Appendix I: General Ledger Request Process (FMS and MinX)
- The process to make changes to GLAC table are as follows:
- Requestor completes a General Ledger Account Request PDF Form (FMS & MinX) ensuring that applicable fields are populated (including the requester’s digital signature).
- The requester will forward the form to their supervisor for review and approval.
- The supervisor will review and electronically sign, approving the form.
- Supervisory approved forms are forward to FSCTransactionReview@va.gov mail group.
- The FSC Transaction Review group will review, research, and verify the form complies with existing standards and guidance (e.g., USSGL). If additional information is needed the FSC reviewer will work with the requester.
- FSC approved requests, FSC will be electronically signed and routed to the VACOAlertOFP@va.gov mail group.
- OFP will review, research, and verify the request form complies with existing standards (e.g., FASAB) and guidance (e.g., USSGL). If additional information/clarification is needed, for approval, OFP will work with FSC to resolve.
- OFP approved requests are electronically signed and sent to FMS Services at VACO047E7@va.gov mail group.
- FMS Services will process approved GLAC requests in FMS and MinX.
- If there are any issue with processing the request in FMS and MinX, FMS Services will work with FSC and OFP to resolve the issue.
- FMS Services will notify the requester, supervisor, FSC Transaction Review group, and OFP group via e-mail once the transaction has been updated in FMS.
- The latest version (Version 8 – JAN 2015) of the GLAC request form must be used.
- To fill out this form correctly, requestors should utilize the Treasury USSGL website and the GLAC table in FMS.
General Ledger Account Request Form (FMS & MinX)
- Requester will complete all required fields.
- Required fields on the GLAC request form include:
- Name of Person Making Request – Last Name, First Name, Initial.
- Requester E-Mail Address – Requester’s VA e-mail address.
- Requester Work Phone Number.
- Date of Request.
- Type of Request – Place an “X” in the appropriate box – New, Update, Deactivate, Delete.
- Reason for Account or Change – Enter applicable information to help explain why the new account or change is needed.
- FMS Account – Enter the account number.
- Account Name – Enter the account name – Note this field allows 30 characters.
- Short Name – Enter an abbreviated version of the account name – Note this field allows 12 characters.
- Normal Balance – Enter either Credit or Debit – depending on what the normal balance should be.
- SGL Acct – This is an “FMS” field and is the same as the “Roll Up” account. This field allows 6 characters.
- Mirror Acct – If the GL being requested should mirror an existing account, list the account it should mirror. Please take note of the message under this field on the form. This field allows 6 characters.
- Fiscal Year – Enter the fiscal year of the account.
- MinX Account – Enter the account number.
- ICP – Inter Company Partner – Place an “X” if the GL is tied to an ICP.
- Acct Name – Enter the account name – Note this field allows 30 characters.
- Short Name – Enter an abbreviated version of the account name – Note this field allows 12 characters.
- Normal Balance – Enter either Credit or Debit – depending on what the normal balance should be.
- USSGL Acct – Enter the USSGL Acct number found on Treasury’s website. This field allows 6 characters.
- Mirror Acct – If the GL being requested should mirror an existing account, list the account it should mirror. – Please take note of the message under this field on the form. This field allows 6 characters.
- Fiscal Year – Enter the fiscal year of the account.
- Trading Partner – Enter the number assigned to the Trading Partner – Treasury USSGL website has a list that can be researched.
- Will impact MinX Treasury Report on Receivables (TROR) – Place an “X” if the request will make changes in TROR.
- Financial Statements – Indicate what financial statement/s the GL should be included in. The Treasury USSGL website contains this information – check under Crosswalk when querying the GL.
- Name of Supervisor/Title – Type in the supervisor’s name and title. The supervisor should fill in this information when the request has been received from the requester.
- Signature of Supervisor – Type in the supervisor’s name. The supervisor should fill in this information when the request has been received from the requester.
- Dated Signed – Type in the date. The supervisor should fill in this information when the request has been received from the requester.
- Requester Digital Signature – Include the requester digital signature – then forward the document to the supervisor for their digital signature. If digital signature is missing, the request form will be returned.
- Supervisor Digital Signature – Once the supervisor reviews and verifies the request, they should include their digital signature and send the form to the mail groups listed above.
- Additional information may be added to the Note section.


