Volume II - Appropriations Funds and Related Information
Chapter 01A – VA Journal Vouchers
Questions concerning this policy chapter should be directed to:
- Veterans Health Administration
- Veterans Benefits Administration
- National Cemetery Administration
- Debt Management Center
- Financial Services Center
- Construction and Facilities Management
- All others
0101 Overview
This chapter establishes the Department of Veterans Affairs’ (VA) financial policy for processing journal vouchers (JVs) to enter, adjust, or correct accounting and financial information. Proper preparation of JVs is important to ensure that financial events are accurately recorded and documented. VA will maintain adequate JV documentation to support the event and ensure a detailed audit trail exists.
Key points covered in this chapter:
- JV documentation will provide evidence that others can use to substantiate the need to process a JV and to ensure that the JV was proper and accurate;
- VA will ensure that JVs are reviewed and approved timely by appropriate personnel, and that documentation of JV approval is maintained for audit purposes; and
- Non-routine JVs require the approval of the Administration or Staff Office CFO and FSC prior to entry into VA’s accounting system.
0102 Revisions
| Section | Revision | Requesting Office | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Various | Update approval authority for JVs | FSC | Changes to positions authorized to approve JVs | May 2024 |
| 0105 | Included examples of documentation to be completed and maintained for JVs | VHA | Clarify requirements for JV supporting documentation | September 2023 |
| Appendix I | Added appendix for supporting documentation examples for journal vouchers. | VHA | Clarify requirements for JV supporting documentation | September 2023 |
| Various | Removed Appendix B and added link to sample OF 1017G in 0106 Authorities and References. Adjusted remaining appendices. Updated section 0108. | OFP (047G) | Formatting update | September 2023 |
| 010505 | Require Office of Financial Reporting (OFR) approval prior to processing JV adjustments to closed periods. | OFR | Review adjustments for impact on financial statements | January 2022 |
| 010501 Appendix D | Allowed FSC approval of reporting JVs over $1 billion to occur within seven business days of the transaction | FSC | To accommodate limited instances when both the Executive Director and Deputy Executive Director are unavailable to approve a JV prior to the close of a reporting window | August 2020 |
| Various | Removed JV information from Volume II, Chapter 1 – VA’s Accounting Classification Structure and established a new chapter | OFP (047G) | JV information is more appropriate in a separate policy | June 2020 |
| Various | Reformatted to new policy format and completed five- year update | OFP (047G) | Reorganized chapter layout | June 2020 |
| 0105 Policies | Added pre-approval requirement for non- routine JVs in VA’s accounting system and MinX JVs equal to or greater than $100 million | OFP (047G) | NFR 15-1,Consolidated Financial Reporting | December 2017 |
| 0104 | Assigned roles and responsibilities for pre-approval of non-routine JVs in VA’s accounting system and MinX JVs equal to or greater than $100 million. | OFP (047G) | NFR 15-1,Consolidated Financial Reporting | December 2017 |
| Appendix F | Added the JV Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) to policy | OFP (047G) | Update per CLA recommendation for NFR 16-4 Financial Reporting | March 2017 |
| Appendix F | Updated various sections of JV SOP to reflect current procedures, and added appropriate approvals | OFP (047G) | Update per CLA recommendation for NFR 16-4 Financial Reporting | March 2017 |
0103 Definitions
Expenditure Transfers – The shifting of funds between Treasury Account Symbols (TAS) for transactions related to outlays (e.g., transaction codes EB, ET, and EW in the Financial Management System (FMS)).
Free-form JV – A type of non-routine JV transaction where GL accounts are not predefined. Free-form JVs are used in VA’s Accounting System to adjust GL account balances when a standard transaction is not available.
Journal Voucher (JV) – A written document that serves as an integral part of the audit trail and bears sufficient documentation to explain the purpose and details of the transaction.
Management Information Exchange (MinX) – A Hyperion-based reporting system that automates the preparation of VA’s financial statements. MinX receives data via interface from VA’s accounting system.
Non-routine JVs – Standard financial system transactions in excess of $100 million with the exception of interface, batch and budget funding transactions. Free-form JV transactions, regardless of amount, are always non-routine transactions. Non-routine transactions in excess of $100 million require Administration/Staff Office CFO and FSC approval.
Post-Review Process – A standardized review of the transaction to ensure there were no errors in the posting of the JV, that documentation is clear and sufficient to support the transaction, and that required approvals were obtained. This process is an integral part of VA’s internal controls and was designed to ensure the JV was accurately posted and had the desired accounting effect in the GL.
Reporting JVs – MinX JVs prepared and approved for financial reporting and presentation purposes by select staff at Financial Services Center (FSC), Veterans Benefits Administration (VBA), and Office of Financial Reporting (OFR).
Routine JVs – Standard financial system transactions (including standard vouchers and expenditure transfers) under $100 million; interface transactions; batch transactions from other systems; and standard transaction codes AA, AC, AL, SA, SL, ST, and TA (in FMS) regardless of amount. Non-interfaced transactions require local supervisory approval (i.e., Chief Accountant, Assistant CFO, CFO).
Standard Voucher (SV) – A transaction where the debits and credits are pre-defined (e.g., transaction codes SV and RJ in FMS). SV is used to record non-routine accounting transactions that are not included in any of the other iFAMS modules like accruals, recurring accounting reclassifications, and interfaces.
VA’s Accounting System – serves as the central accounting system for all of VA. The legacy system used by VA is the Financial Management System (FMS), and the modern system used by VA is the integrated financial and acquisition management system (iFAMS).
0104 Roles and Responsibilities
Administration and Staff Office CFOs are responsible for the review and approval of all JVs greater than or equal to $100 million.
Financial Services Center (FSC) is responsible for the entry, review, and authorization of JVs in VA’s accounting system and JVs used in the preparation of Financial Statements (other than those prepared by the Office of Financial Reporting). FSC also performs a variety of roles in the oversight of the agency’s JV processes.
JV Approving Official – Role held by a staff member within the local finance office. The JV Approving Official approves the JV for posting and ensures accuracy and completeness of supporting documentation.
JV Authorizer (FSC only) – Role held by a limited number of FSC staff members with security access to input JVs into VA’s accounting system. The JV Authorizer reviews the final approved JV and posts the JV to the accounting system.
JV Preparer – Role held by a staff member within a local finance office who identifies the need for a JV, collects the necessary supporting documentation, and prepares the JV for review and approval. This role is referred to as the “MinX JV Submitter” for reporting JVs.
Office of Financial Reporting (OFR) – is the Office responsible for preparing, approving, and posting Reporting JVs.
0105 Policies
010501 General Policies
- VA JVs are categorized into the following types:
- Routine: Standard financial system transactions less than $100 million. Interface, batch, and budget funding transactions are considered routine transactions regardless of dollar value;
- Non-routine: Standard financial system transactions in excess of $100 million with the exception of interface, batch and budget funding transactions;
- Free-form JV: Transactions (where GL codes are not predefined), regardless of amount, prepared to adjust general ledger balances when a standard transaction is not available; and
- Reporting: MinX JVs prepared and approved for financial reporting and presentation purposes by select staff at FSC, VBA, and OFR.
- JVs are used to correct or adjust VA general ledger (GL) account balances and the quarterly and annual consolidated financial statements. They are used to record accounting activities such as:
- Expenditure transfers;
- Adjustments;
- Estimates;
- Closing entries; and
- To post accounting events that cannot be accomplished using standard financial system functions.
- At a minimum, the following documentation will be completed and maintained for JVs:
- All JVs and supporting documentation packages must be clearly labeled with the Document ID number (e.g., local log for JVs for identification and tracking purposes). The Document ID number serves as the JV identification number and is referred to as the “Label” in the MinX system.
- A clear description of the purpose of the JV (e.g., the reason for the correction or adjustment) and an adequate detailed explanation supporting why the JV must be processed. An adequate explanation means that additional descriptions or discussions should not be required to understand the purpose of the JV and to verify the accuracy of the posted entry.
- Documents supporting the amounts and GL accounts to be posted (e.g., macro-proforma). This includes schedules (e.g., reconciliations or transaction details), that would enable anyone reviewing the JV to re-perform calculations or verify summarized amounts.
- Sufficient evidence (e.g., a before / after trial balance, financial system verification) proving that the JV was properly posted to appropriate GLs and that the entry had the desired effect on VA’s financial records and statements.
- Documentation that properly identifies the JV Preparer and JV Approving Official by name, title, office symbol (e.g., copy of the completed OF 1017-G to identify the preparer and approver). To satisfy segregation of duties requirements, the JV Preparer and JV Approving Official must be different individuals. The JV Approving Official should have a level of authority above that of the individual preparing the JV.
- The signature of the JV Preparer and JV Approving Official and the date the JV was prepared and approved. A system generated digital signature is acceptable.
- For non-routine JVs that cannot be handled by standard vouchers (i.e., free-form JVs), enter the initials and date of the JV authorizer confirming entry into the accounting system by FSC.
- See Appendix I for supporting documentation examples.
- When one financial organization posts a routine transaction under $100 million that impacts the records for another organization (e.g., one station posts an expenditure transfer to one or more other stations), the JV Approving Official will review and approve (or reject) the JV. Once approved, the JV Preparer will enter the transaction into the financial system and forward a complete and approved copy of the package to the affected finance offices.
- A request for a JV not supported by accurate or proper documentation will be denied by the JV Approving Official and returned with a request for additional information required to process the JV, along with any applicable authoritative guidance to support the need for the JV.
- Before returning the JV package, the finance office being impacted by the JV should contact the JV Preparer for additional information to address questions and concerns. If the JV Preparer cannot provide the requested supporting information, the JV package will be returned, and the initial JV reversed.
- All documentation related to JVs will be retained in accordance with the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) General Records Schedule, Chapter 4 – Budget, Accounting, and Financial Management.
- To ensure proper accounting, JVs greater than $100 million but less than $1 billion require approval by the Administration or Staff Office CFO or designee. This approval should eliminate accounting errors prior to posting transactions in the accounting systems. The Administration or Staff Office CFO may re-delegate this approval within their office only and no lower than the GS-15 level. These JVs also require approval by the FSC Senior Advisor, Chief Accounting Officer (CAO) or Financial Accounting Service (FAS) Director or their designees no lower than the GS-15 level.
- The organization requesting the JV will perform a post-review for all non-routine and reporting JVs to confirm the appropriate updates took place in FMS. This review is designed to ensure that the transaction had the desired effect on the GL and must occur within seven business days.
010502 Routine Journal Vouchers
- Routine JVs are standard financial system transactions less than $100 million. Interface, batch, and budget funding transactions are considered routine JVs regardless of dollar value.
- VA Administrations and Staff Offices are authorized to approve routine JVs less than $100 million. VA may use routine JVs to record accounting activities such as salary accruals or continuation of pay.
010503 Non-Routine Journal Vouchers
- JVs may not be split into multiple entries to circumvent the $100 million additional approval requirement.
- Administration or Staff Office CFO review and approval must ensure that the JV is proper and accurate, and that appropriate documentation exists and is on file for audit purposes.
- Administration or Staff Office CFO approval shall be obtained prior to the JV being recorded in VA’s accounting system. However, if there is insufficient time to route the JV for approval due to reporting deadlines, the entry may be made, and approval obtained as soon as possible after entry. In no instance should approval be later than seven business days after the date of the JV entry.
- Finance Offices will ensure JVs undergo a post-review process to ensure the JV had the desired effect on the GL. Discrepancies found in the post-review process will be brought to the immediate attention of FSC.
- After documenting the Administration or Staff Office CFO’s approval, the JV will be forwarded for review and approval by the FSC Senior Advisor, CAO or FAS Director if the amount of the JV is less than $1 billion. To the extent possible, JVs will be approved by the FSC Senior Advisor, CAO or FAS Director the same day, but no later than seven business days from the date of the transaction.
- If the amount of the JV is equal to or greater than $1 billion, it must be approved by the FSC Executive Director (ED), Deputy Executive Director (DED), or the Senior Advisor the same day, but no later than seven business days from the date of transaction.
- It is the responsibility of the Administration and Staff Office CFOs to ensure their financial information is properly recorded and presented, even if their accounting functions are performed by FSC. The CFOs must ensure they have adequate internal controls in place to oversee the work performed by FSC.
- CFOs will state on their End of Quarter Financial Statement Certification submitted to OFR, “JVs in VA’s accounting system equal to or greater than $100 million have been appropriately reviewed and approved.” Refer to VA Financial Policy Volume VII, Chapter 1 – Financial Statement Reporting, for further information on this certification.
- For station level requests, documentation will be sent via email to the Outlook Mailbox, VAFSCNWAccounting@va.gov. FSC’s mailroom staff will scan all JV documentation into the Document Management System (DMS) for access by all FSC Nationwide Accountants.
010504 Free-Form Journal Vouchers
- FSC-FAS staff will post free-form JVs in VA’s accounting system when an abnormal balance or problem is discovered that cannot be corrected with a routine accounting transaction (e.g., standard voucher). The ability to post free-form JVs in VA’s accounting system is limited to a small group within FSC.
- In the event that a free-form JV with the same purpose and impacting the same GL accounts is required on a recurring basis, FSC will work to develop a standard voucher for that scenario in VA’s accounting system.
- FSC will maintain the series of JV categories/types to standardize the descriptions used for JVs. The JV authorizer who inputs the JV into the accounting system will determine the appropriate standardized description used on the JV.
- All free-form JVs will be reviewed by FSC prior to entry into the accounting system, regardless of dollar amount.
- Free-form JVs over $100 million follow the same review and approval process as other non-routine JVs.
010505 Journal Vouchers Used in Financial Reporting
- VA will utilize the MinX system to create VA’s financial statements and facilitate reporting to Treasury and OMB.
- MinX JVs (referred to as “Reporting JVs”) are used primarily to adjust GL balances for the content and presentation of VA’s financial statements.
- For iFAMS users, reporting JVs are entered in iFAMS and interfaced to MinX daily. iFAMS reporting JVs are generally reversed in the following month. There may be limited situations where the entry will be needed for more than one month.
- FSC-FAS, OFR, and VBA-Accounting Policy and Reporting Division (APRD) staff may post adjusting entries in MinX.
- Administration and Staff Office Reporting JVs over $100 million will be reviewed and approved by the Administration and Staff Office CFO prior to submitting to FSC’s Outlook Mailbox, vafscminxjvpost@va.gov, for approval and processing. To the extent possible, JVs will be approved the same day.
- Administration or Staff Office CFO review and approval must ensure that the JV is proper and accurate, and that appropriate documentation exists and is on file for audit purposes.
- Reporting JVs over $100 million prepared by OFR as part of the financial reporting process will be reviewed and approved by OFR prior to entry into MinX. Transactions may not be split into multiple entries to circumvent this requirement.
- Reporting JVs greater than or equal to $1 billion require approval by the Administration CFO, Staff Office CFO or Director of the Financial Reporting Service. In addition, secondary approval must be obtained from the FSC ED, FSC DED, FSC Senior Advisor or Associate Deputy Assistant Secretary for OFR (ADAS OFR). This review and approval will follow the same process and documentation requirements listed for JVs over $100 million but cannot be delegated to an employee outside the Senior Executive Service (SES) or Senior Leader (SL) series. Review and approval will occur within seven business days after the JV is posted.
- All monthly closing adjustments made by FSC, Administrations, and Staff Offices must be processed in iFAMS and MinX by the cutoff date provided by OFR.
- FSC, Administrations, and Staff Offices will coordinate adjustments to closed periods and obtain the ADAS OFR or OFR Deputy Director approval prior to processing a JV adjustment. FSC, Administrations and Staff Offices will provide adequate supporting information to OFR to determine if the adjustment to the closed period has any impact on the financial statements.
010506 JV Logs
- Field stations will establish and maintain a local log for JVs for identification and tracking purposes. Two separate centralized JV Logs are also maintained – one for non-routine JVs in VA’s accounting system, and one for MinX JVs.
- VA’s accounting system / MinX JV Logs are used in the JV Preparation process, to verify completeness and accuracy of the JV population in the quarterly JV monitoring and testing process, and for other analytic procedures. See Appendix E for detailed information regarding JV logs.
0106 Authorities and References
- 31 U.S.C. §1534, Adjustments between Appropriations
- National Archives and Records Administration, General Records Schedule, Chapter 4, Budget, Accounting, and Financial Management
- OF 1017-G Journal Voucher
- Sample of a properly prepared OF-1017
- USSGL Section IV, USSGL Account Attributes
- VA Financial Policy Volume VII, Chapter 1 – Financial Statement Reporting
0107 Rescissions
Volume II, Chapter 1A – VA Journal Vouchers – September 2023.
Appendix A: JV Preparation and Approval in FMS
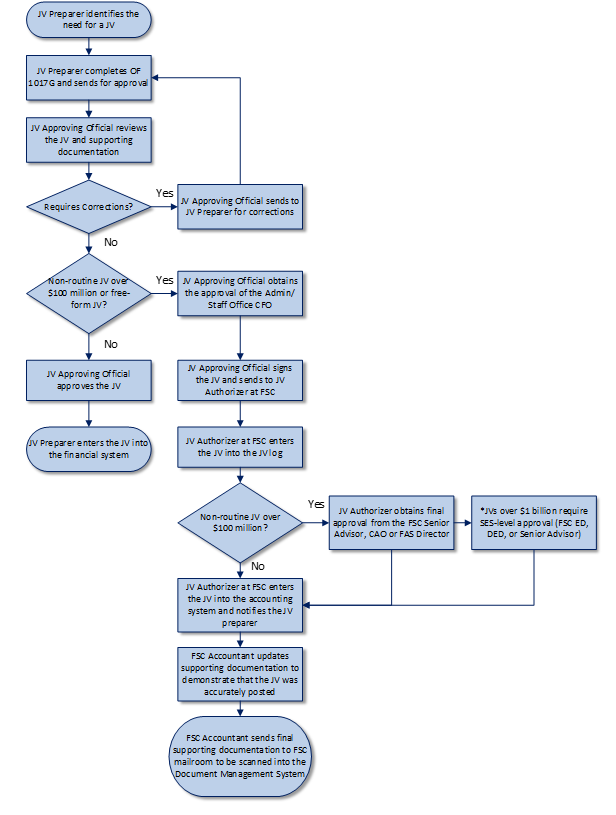
- Procedures for JV preparation in FMS.
- The JV Preparer identifies the need to complete a JV. Before creating a JV, the JV Preparer should consider the following:
- If the intended JV serves more than one purpose, then the JV Preparer should prepare multiple JVs.
- The JV Preparer should work with accountants at FSC to verify that there are no standard accounting system transactions available that can correct the issue.
- If the JV is not on the list of standard adjusting accounting system JV categories, the JV Preparer should consult with the FSC Accountant, JV Approving Official, or JV Authorizer to verify that the JV is necessary.
- The JV Preparer completes the mandatory OF 1017-G JV form and sends it via email or fax with all supporting documentation to the JV Approving Official. A sample of a properly prepared OF 1017-G can be found in 0106 Authorities and References. The OF 1017-G JV form provided by the JV Preparer must include the GL accounts, fund, and budget fiscal year. The following additional fields may also be provided depending on the purpose of the JV:
- Balanced budgetary and balanced proprietary general ledger entries at the individual accounting system fund code level;
- Cost center;
- Fund control point/accounting classification code;
- Budget object code for any expense GL accounts and obligation/expenditure GL accounts;
- Revenue source code for any revenue GL accounts and budgetary reimbursement GL accounts;
- Schedule number and accomplish date for cash entries;
- Vendor code is required for federal GL account entries; and
- Explanation describing what caused the erroneous balance.
- The JV Preparer identifies the need to complete a JV. Before creating a JV, the JV Preparer should consider the following:
- Procedures for JV Approval in FMS.
- The JV Approving Official reviews the JV and supporting documentation for the following:
- The JV resolves the identified problem;
- The description includes adequate detailed explanations supporting why the JV must be processed;
- The JV category and entry descriptions are consistent and complete;
- Supporting documentation stands on its own and fully supports the requested entry; and
- Documentation is complete and attached schedules and calculations tie to the amounts on the JV.
- If the JV requires changes or corrections, the JV Approving Official will notify the JV Preparer of the required updates. The JV Preparer will modify the JV and supporting documentation as required.
- The JV Approving Official signs the hard copy or provides an electronic authorization of the JV to indicate approval. The JV and supporting documentation are then given to the JV Authorizer at FSC for entry into the accounting system.
- For JV’s initiated by a field level-station or Administration, the JV Preparer or JV Approving Official submits the JV and supporting documentation to the FSC-Nationwide Accounting Section through the Outlook Mailbox, VAFSCNWAccounting@va.gov. The FSC Accountant provides secondary review and approval prior to submitting to the JV Authorizer.
- For JV’s initiated within FSC-FAS, all supporting documentation must also be provided to the JV Authorizer within FSC.
- The JV Authorizer at FSC enters the JV into the JV log to obtain a sequential number that is entered into the comments field on the JV header in the accounting system to be used as a cross reference for documentation. The JV authorizer then adds his/her initials and date to the hard copy of the JV, and then enters the approved JV into the accounting system. For non-routine JVs over $100 million, the JV authorizer will obtain final approval from the FSC Senior Advisor, CAO or FAS Director before entering the JV into FMS. If the JV is $1 billion or greater, it requires SES level (FSC ED, DED, or Senior Advisor) approval.
- Once the JV is posted in the accounting system, the JV Preparer or FSC Accountant updates the JV supporting documentation to demonstrate that the JV was accurately posted in the accounting system (e.g., a screenshot of the JV, trial balance or other available report). The final JV supporting documentation should be sent to the FSC mailroom, so that it can be scanned into the Document Management System (DMS).
- The JV Approving Official reviews the JV and supporting documentation for the following:
Appendix B: Free-form JV Preparation and Approval in iFAMS
- Procedures for free-form JV preparation in iFAMS.
- The JV Preparer identifies the need to complete a JV. Before creating a JV, the JV Preparer should consider the following:
- If the intended JV serves more than one purpose, then the JV Preparer should prepare multiple JVs.
- The JV Preparer should work with accountants at FSC to verify that there are no standard accounting system transactions available that can correct the issue.
- If the JV is not on the list of standard adjusting accounting system JV categories, the JV Preparer should consult with the FSC Accountant, JV Approving Official, or JV Authorizer to verify that the JV is necessary.
- The JV Preparer completes the mandatory OF 1017-G JV form and sends it with all supporting documentation to the JV Approving Official. A sample of a properly prepared OF 1017-G can be found in 0106 Authorities and References. The OF 1017-G JV form provided by the JV Preparer must include the GL accounts, fund, and budget fiscal year. The following additional fields may also be provided depending on the purpose of the JV:
- Balanced budgetary and balanced proprietary general ledger entries at the individual accounting system fund code level;
- Cost center;
- Budget object class code for any expense GL accounts and obligation/expenditure GL accounts;
- Revenue source code for any revenue GL accounts and budgetary reimbursement GL accounts;
- Schedule number and accomplish date for cash entries;
- Vendor code is required for federal GL account entries; and
- Explanation describing what caused the erroneous balance.
- The JV Preparer identifies the need to complete a JV. Before creating a JV, the JV Preparer should consider the following:
- Procedures for JV Approval in iFAMS.
- The JV Approving Official reviews the JV and supporting documentation for the following:
- The JV resolves the identified problem;
- The description includes adequate detailed explanations supporting why the JV must be processed;
- The JV category and entry descriptions are consistent and complete;
- Supporting documentation stands on its own and fully supports the requested entry; and
- Documentation is complete and attached schedules and calculations tie to the amounts on the JV.
- If the JV requires changes or corrections, the JV Approving Official will send the JV back to the JV Preparer for the required updates. The JV Preparer will modify the JV and supporting documentation as required.
- The JV Approving Official signs the hard copy or provides an electronic authorization of the JV to indicate approval. The JV and supporting documentation are then given to the JV Authorizer at FSC for entry into the accounting system.
- For JV’s initiated by a field level-station or Administration, the JV Preparer or JV Approving Official submits the JV and supporting documentation to the FSC- Nationwide Accounting Section through the Outlook Mailbox, vafscnwaccounting@va.gov. The FSC Accountant provides secondary review and approval prior to submitting to the JV Authorizer.
- For JV’s initiated within FSC-FAS, all supporting documentation must also be provided to the JV Authorizer within FSC.
- The JV Authorizer at FSC enters the JV into the JV log to obtain a sequential number that is entered into the description field in the accounting system to be used as a cross reference for documentation. The JV Authorizer then enters the JV into the accounting system. After entry is input in iFAMS by the FSC JV Authorizer, an FSC Approving Official must approve the JV in iFAMS. For JVs over $100 million, iFAMS will route the JV to the FSC Senior Advisor, CAO or FAS Director for final approval. If the JV is $1 billion or greater, it requires SES level (FSC ED, DED, or Senior Advisor) approval.
- The JV Approving Official reviews the JV and supporting documentation for the following:
Appendix C: Reporting JV Preparation and Approval in MinX
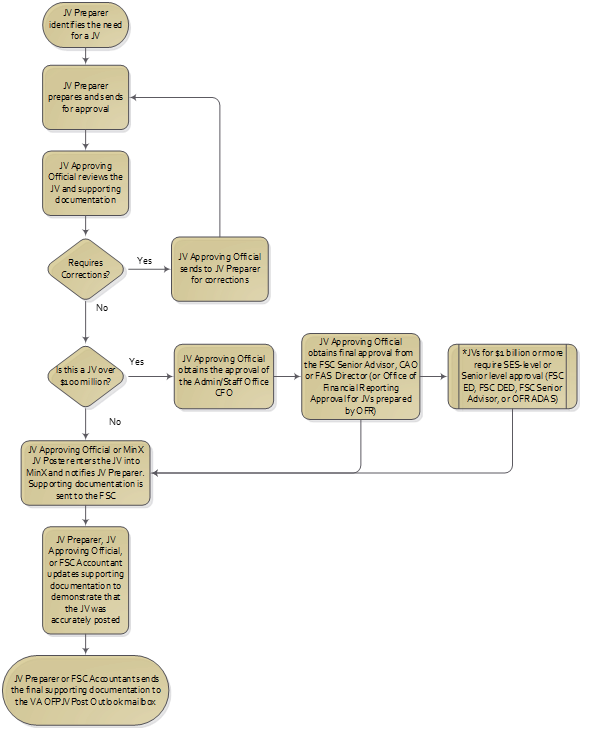
- These procedures apply only to reporting JVs entered in MinX. iFAMS users will enter reporting JVs in the accounting system. Departmental elimination JVs will be entered in MinX regardless of whether the reporting entities are in iFAMS or FMS.
- MinX JV Preparation. On a monthly basis, when the MinX period opens, the JV Preparer (referred to in MinX as the JV Submitter) identifies a need to complete a JV. Before creating a JV, the JV Preparer should consider the following:
- Whether an adjustment can be posted in FMS, rather than in MinX. The JV Preparer should consult with FSC or OFR to make this determination. Once the accounting system period is closed and the MinX period is open, it is too late to enter an adjustment in the accounting system; however, the JV Preparer should consider whether this type of adjustment, if required in the future, can be done in the accounting system, rather than in MinX.
- Whether the JV is on the list of approved recurring JVs. If the JV is not on the list of approved MinX JV purposes, the JV Preparer should consult with the JV Approving Official, OFR, or other official to verify that the JV is necessary.
- At the end of the fiscal year, the JV Preparer will determine whether the JV is required in MinX period 13 or 14.
- MinX period 13 is considered the adjustment period for permanently recording JVs from MinX into the accounting system. It is critical that the JV Preparer select “FMS Adjustment” or “Non-FMS Adjustment” in period 13 so that entries properly transfer to FMS. All entries flagged as “FMS Adjustment,” are recorded in FMS, when period 13 in MinX is closed. During period 13 for a pre-set period of time per the close schedule, MinX is available for JV input. After the period 13 close date, the JV Preparer must request permission from OFR to post adjustments. MinX may be re-opened on a case by case basis. For an alignment of the MinX and accounting system periods, see Appendix G, FMS and MinX Periods.
- When MinX period 14 opens, MinX should be used only for certain types of adjustments such as corrections to the presentation of statements, adjustments that must be made as a result of the audit, entries to re-input rejections from the Period 13 interface, or to re-input non-accounting system transactions from Period 13 that are not carried forward to Period 14.
- Once the need is identified, the JV Preparer will prepare and submit the JV. The JV Preparer either enters data directly into MinX or for large JVs submits data in a pre- established JV template. Both submission methods require the same approval process and documentary evidence (typical support is a JV support workbook). Specific fields are required for all MinX JVs regardless of submission type (direct entry or template). Required data fields are detailed in the table below.
MinX JV Data Field Requirements
| Field | Headings |
|---|---|
| Label (Document ID Number) | This is the JV identification number, also referred to as the Document ID number. Input the JV Name, following the naming convention of – Administration_ Fund_Period Year_Alpha- numeric Character(s) (e.g., A, B, C, D, E). *–Note that VBA uses the Business Line (e.g., HOU, BEN, INS, etc.) in lieu of the Administration, as required for VBA reporting. |
| Balance Type | Select “Balanced” or “Balanced by Entity”, in cases where the JV applies to more than one entity. The field will default to “Balanced.” |
| Year and Period | Select the Year and Period to which the JV applies, at the system POV view. |
| Type | Regular |
| Group | This field is a drop-down menu: Select One of the following MinX JV Categories: 1-Accruals/Payroll 2-Budgetary Adjustments 3-Financial Presentations 4-Timing Differences 5-Other 6-Systems Limitation 7-Audit Adjustments |
| Security Class | This field is populated based on the User ID of the individual submitting the JV and is based on the individual’s Group. |
| Currency | USD |
| Description | Input a description for the JV, relevant to the MinX approved purposes. The description should provide sufficient clarification to stand on its own without further conversation or information and is subject to the field character limits (255 characters). |
| Field | Lines |
|---|---|
| Scenario | “Actual” |
| GL Account | Input the General Ledger account for the JV line. |
| Debit/Credit | Input the amount to be debited / credited from the GL. |
| Entity | Input the Treasury Account Symbol (TAS) / Fund to which the JV applies. |
| Value | Input “Entity Curr Adjs” |
| ICP | Select “[ICP None]” |
| Custom 1 | Select the VA station number associated with the TAS. Select [None] if VA station does not apply. Example: “20_105” for TAS processed mainly at VBA’s Administrative and Loan Accounting Center (ALAC), or “20_201P” for TAS processed mainly at VBA’s Hines office. |
| Custom 2 | Select “GX” for Treasury’s General Fund (trading partner 099 only), “FX” for Federal other than Treasury’s General Fund (all other Federal trading partners), “NX” for Non-Federal, or “[None]” if the attribute does not apply. See USSGL Section IV, USSGL Account Attributes for a list of applicable values for each GL account. *The combination of NX with a trading partner will result in error similar to selecting FX and inputting no trading partner. The system will not prevent illogical Fed/NonFed and Trading Partner combinations at input. They will post as they are submitted but will produce Fed/NonFed anomalies on various reports and the GTAS adjusted trial balance. **In a few circumstances, “ZX” for Federal non-reciprocating is a valid entry. While ZX transactions are Federal, they do not include a trading partner. |
| Custom 3 | Select “FMSAdjustment” for a period 13 adjustment that should be interfaced in the accounting system in period 14, or “NonFMSAdjustment” for a period 13 adjustment that should not be interfaced in the accounting system in period 14. Most adjustments should be “FMSAdjustment”. *The default for this field is “[None]”, which should not be selected, as it will result in incorrect Trial Balance reports. |
| Custom 4 | Select the Budget Object Class (BOC) Code, as appropriate. Enter “[None]” if there is no BOC Code. |
| Trading Partner | Select the Trading Partner / Trading Partner Main Account from the available selections (e.g., “0200550”, “0360150”, etc.). If this is not a Federal transaction, enter “[None]”. The Trading Partner includes the three-digit Trading Partner Agency Identifier (TP AID) followed by the four-digit Trading Partner Main Account (TP Main) code. GTAS reporting requires a valid TP AID and TP Main combination on all Federal bulk file lines. Example: transactions with Treasury’s General Fund include AID “099” and TP Main “0000”, displayed as “0990000”. Transactions between funds in VA include AID “036” and TP Main “XXXX” will be displayed as “036XXXX”. |
| Line description | Description for the individual line. Also used to pass information to the process that loads JVs to the accounting system at year end. The MinX field character limit is 55 characters. For period 13, do not use more than 30 characters because the description will be truncated when posted to the accounting system. |
- Once the JV is submitted in MinX, the JV Preparer provides the JV and all supporting documentation to the JV Approving Official.
- The JV Approving Official reviews the JV and supporting documentation for the following:
- The description includes adequate detailed explanations supporting why the JV must be processed;
- The JV category and entry descriptions are consistent and complete;
- Supporting documentation stands on its own;
- Documentation is complete and attached schedules and calculations tie to the adjustment amounts of the JV.
- If the JV requires changes or modifications, the JV Approving Official will notify the JV Preparer of the required updates.
- The JV Preparer will then un-submit the JV and place the JV in working status in MinX to make updates.
- Once the updates are complete, the JV Preparer will re-submit the JV in MinX and notify the JV Approving Official that the revised JV is ready for approval.
- When all documentation is complete and the MinX JV has been approved, the JV Approving Official may post the JV if the JV Approving Official has posting authority in MinX. If not, the JV Approving Official sends a notification to the MinX JV Poster through the Outlook Mailbox, vafscminxjvpost@va.gov, that the JV is ready to be posted. A designated JV Approving Official at FSC will post the JV and notify the requesting office.
- The JV Approving Official shall notify the JV Preparer that the JV has been approved.
- To verify that a MinX JV has accurately posted in the system, the JV Approving Official should manually trigger the consolidation process using the“Consolidate” function in MinX. For further instructions on the consolidation process, refer to the MinX JV Guide.
- The JV Preparer or JV Approving Official should update the JV supporting documentation to demonstrate that the JV was accurately posted in MinX (e.g., a pre- entry and post-entry consolidation trial balance, screen shot of the JV, or other report).
- The JV Preparer or JV Approving Official must send an email with all supporting documentation and attachments to the Outlook Mailbox, vacoofpjvpost@va.gov. (For VBA, only the JV Approving Official submits the MinX JV workbooks to OFR.) The subject line for the email must be the same as the JV number (label) posted in MinX. The final supporting documentation for the JV should demonstrate that the JV was accurately posted in MinX (e.g., a pre-entry and post-entry consolidation trial balance, screen shot of the JV, or other report).
- The JV Approving Official reviews the JV and supporting documentation for the following:
- MinX JVs Requiring Additional Approvals. JVs over the $100 million threshold must be approved by the Administration or Staff Office CFO prior to submitting to the FSC Senior Advisor, CAO or FAS Director for approval and processing. The Administration or Staff Office CFO may re-delegate this approval no lower than the GS-15 level. Reporting JVs over $100 million prepared by OFR as part of the financial reporting process will be reviewed and approved by OFR prior to entry into MinX. If the JV dollar value is at or above $1 billion the JV must be approved by a Senior Executive (SES) member in the JV Preparer’s organization prior to posting in MinX. This approval may not be delegated to the GS-15 level.
- JVs greater than or equal to $1 billion, should be approved by the FSC ED, FSC DED, FSC Senior Advisor, or ADAS OFR the same day, but no later than seven business days from the posting date.
- The JV Preparer or JV Approving Official must provide the JV and supporting documentation to the Administration or Staff Office CFO either in hard copy or via email. (For VBA, only the JV Approving Official submits the MinX JV workbooks to the APRD Director. The APRD Director provides the workbook to the SES.)
- The Administration or Staff Office CFO reviews and approves the documentation and provides evidence of approval, in either hard copy or electronic format to the JV Preparer or JV Approving Official.
- In situations where the same JV (type, purpose, GL impact) is required periodically throughout the year (e.g., monthly, or quarterly), the SES may provide broad approval for all instances of the JV, in the form of a summary memo or other blanket statement.
- Once the Administration or Staff Office CFO approval and signature is obtained, the JV Approving Official certifies / approves the JV via the “post” command in MinX. (For VBA, once VBA SES approves and provides approval to the APRD Director and JV Approving Official, the JV Approving Official “approves” in MinX and sends the JV workbook to the Outlook Mailbox, vafscminxjvpost@va.gov.)
- The JV Preparer or JV Approving Official verifies that evidence of the Administration or Staff Office CFO approval is retained with the supporting documentation sent to the Outlook Mailbox, vacoofpjvpost@va.gov.
Appendix D: Reporting JV Preparation and Approval for iFAMS Users
- For iFAMS users, reporting JVs are entered in iFAMS and interfaced to MinX daily.
- Specific transaction types are configured as reporting JVs. These transaction types facilitate a reversal that can be triggered in iFAMS in the following month.
- Departmental elimination JVs will be entered in MinX regardless of whether the entities are in iFAMS or FMS. See Appendix C for MinX Reporting JV procedures.
- If the JV is not on the list of approved MinX JV purposes, the JV Preparer should consult with the JV Approving Official, OFR, or other official to verify that the JV is necessary.
Appendix E: JV Log Procedures
- FSC maintains a log of adjusting JVs entered into VA’s Accounting System. The JV Log contains the following fields:
- FSC Assigned Sequential Number – A unique sequential number used to name JVs. The number is selected by the JV Authorizer and must be entered in the JV Header Description field in the accounting system;
- FMS Document ID – A unique document ID created by the JV Preparer using the numbering scheme of the applicable station. Any changes to the FMS Document ID are recorded in the “Notes” column of the JV Log;
- Prepared By – The name of the individual that prepared or requested the JV – which can be an accountant at a field station or Administration, FSC-NAS Accountant, or other accountants within FSC-FAS;
- Approved By – The name of the individual that approved the JV – which can be the station/administration accountant’s supervisor (or CFO for entries over $100 million), the FSC-NAS Accountant’s supervisor, or FSC Executive Director/Deputy Director/Senior Advisor for JVs over $100 million;
- Reviewed and Input By – The name of the individual that completed the final review and input the JV into the accounting system. This role is limited to personnel at FSC, and no more than five personnel typically have access to input JVs;
- Date – The date that the JV was entered into VA’s accounting system;
- Short Description – A short description of the JV category/type based on the current listing of general descriptions. This description is entered into the “JV Line Description” field in the accounting system, which has a character limit; and
- Detailed Explanation – A detailed explanation of the purpose of the JV that expands upon the Short Description.
- The JV log is used for the following purposes:
- To assign a unique sequential number for each JV prepared;
- To verify the completeness of the accounting system JV population;
- To verify that no duplicate accounting system JVs are entered; and
- Completing analytics on the JVs to inform risk analysis and monitoring procedures.
- The MinX system retains a log of all JVs submitted and posted in MinX.
- The MinX JV log, called the “Full Journal Extract”, can be extracted from the system via the application portion of MinX and contains the following fields:
- Account – The GL account(s) to which the JV entry is recorded;
- Label – The JV document identification number is referred to as the header label (unique identification) for the MinX JV. This label must follow the format “Administration_Fund_Period Year_Alpha Character (e.g., A, B, C, D, etc.)”;
- Line Description – A short description of the purpose of the JV based on the current listing of approved purposes. This description is entered into the “Line Description” field in MinX which is subject to a character limit;
- Created By – The name (username) of the JV Preparer;
- Date Created – The date that the JV was entered into MinX;
- Posted By – The name (username) of the JV Approving Official; and
- Amount – The JV debit/credit amount.
- The MinX JV log is used for the following purposes:
- To identify the population of JVs that have been entered into MinX in the current period in circumstances where timing must be considered (e.g., Elimination JVs);
- To verify the completeness of the MinX JV population;
- To verify that no duplicate MinX JVs are entered; and
- Completing analytics on the JVs to inform risk analysis and monitoring procedures.
- The MinX JV log, called the “Full Journal Extract”, can be extracted from the system via the application portion of MinX and contains the following fields:
Appendix F: Common Journal Vouchers in VA’s Accounting System
- Some of the most common JVs are:
- A direct disbursement transaction used to record expenditures for invoices from other Government agencies. Source documentation to identify the charge and obligation should be maintained either in soft or hard copy. Intra-Governmental Payment and Collection (IPAC) System transactions processed as JVs transactions should be properly supported and referenced.
- An advance disbursement transaction used to record advances and advance offsets for invoices from other Government agencies. Source documentation to identify the charge and obligation should be maintained either in soft or hard copy. IPAC transactions processed as JVs should be properly supported and referenced.
- A transfer of accounting activities (assets, liabilities, or expenditures) to record transfers between stations. The finance office processing the transaction affecting another station serviced by a different finance activity will forward a copy of the OF 1017-G and supporting documentation to the respective finance activity in soft or hard copy.
- A transfer of accounting activities to record a transfer within a station. The finance activity processing this transaction will retain the supporting documentation of the transfer.
- A standard JV to record accounting activities such as deferred maintenance, salary accruals, continuation of pay, or capitalizing an asset.
- A transfer transaction to record a transfer of funds from one account to another, such as to transfer funds from a suspense account to an appropriated fund account. The finance activity processing this transaction will retain the supporting documentation of the transfer.
| Type | Description/Example |
|---|---|
| Accrual | This category of JV is used to record accruals that are not recorded by the administrations/stations as routine business transactions in the normal course of business. |
| Adjustment | This category of JV is used for any type of correction or adjustment that is required. Common types of adjustments include the following: Advances, Asset, Balance Sheet, Budget Authority, Closing Accounts, System Issue, Net Position, Payables, SF-133. |
| Cleanup | This category of JV is used for JVs completed to prepare accounting system data for conversion to a new accounting system. |
| Elimination | This category of JV is used for intra and intergovernmental elimination purposes. |
| Interface Issue | This category of JV is used for adjustments that are required due to interface issues between the accounting system and other systems used to process transactions in the normal course of VA business. Common types of interface adjustments include: Adjustment, Balance Sheet, Canteen, Closing Accounts, Outlays, Payables, Trading Partner. |
| Presentation | This category of JV is used for adjustments required for financial statement presentation purposes. |
| Reclassify | This category of JV is used to correct entries where an attribute of the JV was incorrectly recorded. These JVs do not have an impact on the Trial Balance. For example, at year end all MinX JVs interface into the accounting system aligned to a default station and must be reclassified to the appropriate station. Common types of reclassification entries include: General Ledger, Station, Trading Partner. |
| Timing Differences | This category of JV is used to adjust for timing differences. Common types of timing difference entries include: Adjustment, Advances, Balance Sheet, Budget Authority, Credit Reform, System Issue, Foreign Payments, GTAS, Outlays, Payables, Payroll, Treasury CARS, Treasury GTAS. |
| Type | Description/Example | GL Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1-Accruals/Payroll | Adjustments specific to accrued expense methodology and payroll | |
| Annual Leave | Record Annual leave liability – funded and unfunded | Multiple GLs |
| Accrual Adjustments | Record Accrual Adjustments | Multiple GLs |
| 2-Budgetary Adjustments | Adjustments to conform to budgetary documents – for example, SF-132 Schedule of Apportionment | |
| Budgetary Corrections | This entry is used to balance the SF-132; correct budgetary interface issues | Multiple GLs within the 4000 Series |
| 3-Financial Presentation | Adjustments to financial statement line items, for example, eliminations | |
| Financial Reporting Presentation | This entry is to record VA Offsetting Receipts. Collections are credited to general fund, special fund, or trust fund receipt accounts. | 9701 and 9702 |
| This entry is to correct ending balance for incorrect close out of prior year rescission amount. Note: This adjustment is temporary, pending recommended resolution. | 3100 and 3310 | |
| This adjustment is required to conform with Treasury’s reclassified crosswalks to submit into the GTAS closing package for the SNC. | Multiple GLs and 5XXX and 6XXX | |
| Eliminations | This entry is used for Statement of Net Cost eliminations. | Multiple GLs |
| This entry is required for VA SNC elimination and reclassification for intragovernmental activity and presentation. | Multiple GLs | |
| This entry eliminates the intragovernmental receivable balances in supply and franchise funds (re: DeptAdmin) and offsets the elimination against VHA payables. | 1316, 1317 and 211N | |
| This entry is required to reclassify expenses to 036 to offset Franchise Revenue per FMS Table, “IVLT”. | ||
| 4-Timing Differences | Adjustments to account for data not available at month end for example from Treasury, DOL, DOJ | |
| Treasury CARS Cash Adjustments | This entry adjusts FBWT accounts to Treasury CARS balances for suspense / deposit funds and establishes the VA liability. | 1010 and 2400 or 2410 |
| This entry reclassifies the balances from sub 00 to the only active sub (90); and to the other 6 subs to match CARS; and is required to certify GTAS. | 1010, 1023, 2400, 2401 and 2404 | |
| This entry adjusts NonFMS FBWT GL to tie to GTAS FBWT balance and establishing Treasury liability; and is required to certify GTAS. | 1010 and 2985 | |
| This entry adjusts FBWT and/or outlays for open and expired appropriations and funds. | 1010, and multiple GLs | |
| This entry reclassifies accounting system GFR balances and establishes the Treasury liability. | 2985 and 6744 | |
| This entry is required in Period 14 for Cancelling Funds. Accounting system close logic incorrectly posts to cancelling years with TC ‘BL’. | 4350, 480F and 480N | |
| Authoritative Sources (e.g., DOL FECA) | This entry adjusts the prior year Actuarial Expense recorded in the current year. | 2225 and 6850. |
| Judgment Fund | This entry records the Judgment Fund imputed costs and also the accrual related to Legal contingencies. | 5780 and 6734 |
| 5-Other | One-time entries not belonging to the above categories | |
| Other | This entry is used to record adjustments that do not fit into any other category. | |
| 6-System Limitations | Adjustments necessary to account for VA systems limitations, including trading partner corrections | |
| GTAS | This adjustment is required to conform with Treasury’s reclassified crosswalks to submit into the GTAS closing package for the BS. | Multiple GLs, 13XX, 14XX and 2XXX. |
| These entries are required to correct for how MinX calculates net position amounts as a result of how prior year MinX period 14 entries roll forward. | 2650, 2921, 3310 and 6850. | |
| This entry adjusts GTAS TP 999 for SL 5720, | 5720, 5721, and 5723 | |
| Canteen | This entry is used to true-up Canteen Services ledgers for monthly close. Canteen operates on a retail cycle separate from VA’s system, and manual adjustments are necessary to bring VA’s ledgers into alignment with Canteen. | 1010, 1023, 1120, 1190, 1311, 2116, 3310, 5103, 6100 and 9089. Multiple GLs |
| Trading Partner Corrections | This entry is used to properly record transactions with Trading Partners due to inherent accounting system limitations. | Multiple GLs |
| 7- Audit Adjustments | Auditor requested adjustments | |
| Audit Adjustments | This entry is used to record proposed audit adjustments in MinX period 14. | Multiple GLs |
Appendix G: Comparison of FMS and MinX Periods
- Each accounting system period runs from the first day of the month through the last day of the month (where FMS period 01 is October, FMS period 02 is November, etc.). FMS period 00 represents the current years’ beginning balances. FMS period 13 is open on October 1, and FMS period 14 is a single day for all final entries. FMS period 15 is the period when all general ledgers close out in preparation for the next year’s beginning balances.
- MinX periods open when the final accounting system month end date is received, typically around the 3rd day following month end. The close of MinX periods is dependent on whether it is a month or quarter end. MinX period 13 is the adjustment period for permanently recording JVs from MinX into FMS. MinX period 14 is used only for certain types of adjustments, such as audit adjustments. There is no corresponding MinX period for FMS period 15.
| FMS Period | MinX Period |
|---|---|
| FMS 00 | MinX BegBal00 |
| FMS 01 | MinX OCT |
| FMS 02 | MinX NOV |
| FMS 03 | MinX DEC |
| FMS 04 | MinX JAN |
| FMS 05 | MinX FEB |
| FMS 06 | MinX MAR |
| FMS 07 | MinX APR |
| FMS 08 | MinX MAY |
| FMS 09 | MinX JUN |
| FMS 10 | MinX JUL |
| FMS 11 | MinX AUG |
| FMS 12 | MinX SEP |
| FMS 13 | MinX Period 13 |
| FMS 14 | MinX Period 14 |
| FMS 15 |
Appendix H: JV Approval Thresholds
| Dollar Threshold | Routine JV | Non-Routine JV | Reporting JV/MinX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under $100 million | Follow normal procedures | Follow normal procedures | Follow normal procedures |
| $100 million up to $1 billion | N/A | Admin or Staff Office CFO; may be delegated no lower than the GS-15 level and FSC Senior Advisor, CAO or FAS Director | Admin or Staff Office CFO; may be delegated no lower than the GS-15 level and FSC Senior Advisor, CAO or FAS Director |
| $1 billion or greater | N/A | Admin or Staff Office CFO; may not be delegated below SES level and FSC SES or SL series | Admin or Staff Office CFO; may not be delegated below SES level and FSC SES or SL series |
Appendix I: Supporting Documentation Examples for Journal Vouchers
This is a reference guide for common examples of supporting documentation needed to justify journal vouchers. Supporting documentation should validate the reason why the journal voucher was created/authorized (i.e., email), and include screenshots of all applicable financial system screens (before and after). Data can be obtained from multiple different sources such as Financial Reports System (FRS), VHA Support Service Center (SSC), and Snapshot Web.
| Type/Category | Source Documentation Examples | TT/TC |
|---|---|---|
| Appropriation to Appropriation (i.e., A1 to B2) | · FRS or F20D data pull with Line of Accounting to close out 2-year funding. · Before and after FMS screen Table Sub-allowance Spending (SASP) by Accounting Classification Code (ACC) or SALT by Appropriation showing changes in Expended Amounts. · Documents that support the reason the JV was needed. | EW 01 |
| Salary cost transfer | · Personnel and Accounting Integrated Data System (PAID) Database or Human Resources Payroll Application Service (HRPAS) data supporting employees’ hours worked in alternate location. · Program Office agreement/ Memorandum of Understanding (MOU). · Line of accounting of employee as originally charged. · Copy of email that indicates the numbers of hours worked to transfer to a different Salary Fund Control Point (FCP). · Or submit sufficient documentation on why the Transfer of Disbursement Authority (TDA) is not a viable option to the VHA of Finance Resource Management Office (104B). | EW 56 |
| Credit Card Rebate | · FRS Net Expenditure Report or Financial Content Management (FCM) system as a CALM (CSTA) under form name RMCJ. · US Bank Inter-Branch Transfer (IBT) report. · Distribution of rebate per costing data. · FMS screen shot of the UDST table. | TR24 from suspense and TR18 to station |
| Supplies/Materials | Copy of email, OBLH or OBLL table which shows the expended amounts, and invoice showing purchased. supplies/materials for specific intent to be moved to supplemental funding. | EW 01 |
| Manual Salary Accrual | · Macro used to calculate accrual. · Paid data from database. | RJ 51 |
| Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) | · FEPH, and FEQI (1137) or FEQG (1136) report depending on the BOC. · JVLT & ARLT screenshots. · Documents that support the reason the JV was needed. | TR 65 |
| Expendable Donations | Monthly memo from Center for Development and Civic Engagement (CDCE) Service with sub totals of donated values and all supporting documents to support those values. | SV G8 |
| General Post Fund (GPF) Inactive Accounts | · 8180S: Copy of email to 104B notifying of amount transferred from 8180S to 8180G, · Copy of email supporting the donor cannot be contacted. · 8180A – copy of email to 104B that balance moved to undistributed for VHA Central Office to complete TDA. | SV G8 |
| Payment moves within an Obligation | · Copy of email of the awareness of the problem. · Invoice that caused the problem · Before and after FMS screen table DXRF for both obligations. | ET 01 |
| Move payment to a different obligation · Payment posting errors · Direct Disbursement · Advance Disbursement | · An email from a FCP Official, Invoice Payment and Processing System (IPPS) Certifier or Contracting Officer’s Representative (COR) indicating that a payment was certified or applied the payment to the wrong obligation and indicating where the payment should be applied. · IPPS screen shot showing where the invoice was applied if possible. · DXRF screen shot showing the payment on the wrong obligation. | ET 01 |
| Transfer of assets, liabilities, or expenditures between stations | · Copy of the original purchase order and receiving report from the purchasing station; or · OBLL/OBLH which shows the expended amounts, with RT transaction from DXRF or RCHT. · Documents that support the reason the JV was needed. | EB 01 |
| GL Suspense Balances | · Email from oversight requesting the roll forward. · Data showing before and after GL balances at the time of the roll forward. | EW 03 |
| GL Suspense Transactions | · Unapplied Deposit Screen and JVLT · Documents that support the reason the JV was needed. | TR 24/33 |
| Allowance for Bad Debt | Email from FSC. | SV 23/24/27/P3 |


