Volume VII - Financial Reporting
Chapter 02 – Financial Statement Analytics
Questions concerning this policy chapter should be directed to:
0201 Overview
This chapter establishes the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) financial policies regarding financial statement analytics. Financial statement analytics provide management with a tool to assess variances that could be the result of changes in business processes, the establishment of new programs, or the effect of errors or irregularities in financial data presented on the financial statements.
The Office of Financial Policy (OFP) performs five types of analytics to decrease risk of material misstatements on the financial statements, the analytics are:
- Budgetary to proprietary and other account relationship;
- Abnormal balances;
- Financial statement edit checks;
- Fluctuation analysis; and
- Management’s Discussion and Analysis (MD&A) as part of the Agency Financial Report (AFR).
Key points covered in this chapter:
- VA will comply with the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the U.S. Department of the Treasury (Treasury) reporting requirements;
- VA will submit significant variances analysis for interim and year-end financial statement; and
- VA will present highlights of its financial statement analysis in the MD&A section of the AFR.
0202 Revisions
| Section | Revision | Office | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | New Chapter | OFP (047G) | Provide policy on Financial Statement Analytics | October 2018 |
0203 Definitions
Abnormal Balances – A general ledger account balance is abnormal when the reported balance does not comply with the normal debit or credit position assigned to the account by the United States Standard General Ledger (USSGL).
Adjusted Trial Balance (ATB) – A listing of all the account titles and balances contained in the general ledger after adjusting entries for an accounting period have been posted to the accounts.
Agency Financial Report – The Agency’s end of fiscal year financial report that contains various information about the Department as well as the financial statements, notes to the financial statements, the external financial auditor’s opinion, and other supplementary information.
Budgetary Accounts – A series of accounts that reflect the execution of budgetary authority.
Budgetary to Proprietary Relationship – A comparison of certain budgetary and proprietary accounts, where the balances of the budgetary accounts should equal the balances of related proprietary accounts.
Financial Statements Edit Checks – A series of edits used to verify the accuracy of the financial statements by cross-referencing financial line items between statements to ensure they agree. The edit checks are established in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles promulgated by the Federal Accounting Standards Advisory Board and USSGL.
Fluctuation/Flux Analysis – A type of financial statement variance analysis performed to examine balances and/or comparative percentage differences over time.
Governmentwide Treasury Account Symbol Adjusted Trial Balance System (GTAS) – A Treasury operated Governmentwide accounting web-based system used by Federal agencies to submit both budgetary and proprietary financial data.
Management Information Exchange (MinX) System – A hyperion-based reporting system that automates the preparation of VA’s financial statements. MinX receives data via interface from VA’s accounting system.
MAX or OMB MAX – A portfolio of software applications sponsored by OMB including an agency portal used to submit data to OMB, a suite of analytical tools, and collaboration tools for agencies to share and work together with other community members towards common federal goals.
Proprietary Accounts – A series of accounts that are used to record the financial activity of an entity. These accounts include categories such as assets, liabilities, fund balances, revenues, and expenditures. They do not include budgetary accounts.
U.S. Standard General Ledger – Provides a uniform chart of accounts and technical guidance for standardizing federal agency accounting.
0204 Roles and Responsibilities
Administration Fiscal Staff and Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) are responsible for reviewing the abnormal balances and significant variances; researching and identifying underlying causes and key factors; providing sufficient and comprehensive explanations; proposing corrective actions to fix accounting irregularities and errors within their jurisdictions; and assisting with tasks related to Department-wide reporting.
Office of Financial Policy is primarily responsible for the completeness, reasonableness, and accuracy of financial statement analytics as well as for preparing, submitting, and publishing the AFR.
0205 Policies
- VA will comply with guidance from OMB Circular A -136 and Treasury Financial Manual (TFM) Volume I Part 2 Chapter 4700 when submitting interim and year-end significant variance analysis with explanations to OMB and Treasury.
- VA will perform an analysis of variations in the financial statements as part of VA’s internal controls over financial reporting. Financial statement analytics will consist of the following five types of analyses:
- Abnormal Balances Analysis;
- Budgetary to Proprietary and Other Accounts Relationship Analyses;
- Financial Statements Edit Checks;
- Fluctuation/Flux Analysis; and
- Analysis of Entity’s Financial Statements included in MD&A.
020501 Budgetary to Proprietary and Other Accounts Relationship Analyses
Tie-Points highlight the relationship between budgetary and proprietary accounts; and are included in Governmentwide Treasury Account Symbol Adjusted Trial Balance System (GTAS) Edits and Validations.
- VA will use the Tie-Points analysis to facilitate the validation of adjusted trial balance (ATB) data, mitigate potential out of balance conditions, and enhance the integrity of reported data.
- A monthly Tie-Points report will be generated from VA’s financial reporting system and out of balance items will be reviewed on a timely basis.
- VA will research out of balance conditions to identify the underlying causes of imbalances, and when appropriate prepare corrective action plans. OFP will consult with Administrations and the Financial Services Center (FSC) to ensure appropriate corrective actions are taken.
020502 Monthly Abnormal Balances Analysis
The abnormal balances analysis is designed to identify balances in the United States Standard General Ledger (USSGL) level accounts that do not adhere to the normal account balance designations (i.e., normal debit or credit balance).
- VA will perform an abnormal balance analysis monthly.
- Monthly, OFP will distribute a call memorandum via email and the monthly abnormal balance reports to Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs designated point of contacts (POCs) for review and explanation of balances.
- will use the call memorandum as the guide for their abnormal balance analysis. Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs will run updated reports for their analyses if any changes have occurred after the initial reports.
- Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs will research abnormal balances to identify the underlying causes, and when appropriate prepare corrective action plans. OFP will consult with Administrations and FSC to ensure appropriate corrective actions are taken.
- Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs will provide explanations of all abnormal balances on USSGL accounts within their jurisdictions and submit the analysis along with explanations to OFP for review.
- OFP will conduct a review of the analysis and explanations received from the Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs. OFP will follow up with Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs for additional information when needed to ensure the completeness, accuracy, and adequacy of the analysis and to prevent the misstatement of financial information.
020503 Quarterly Financial Statements Edit Checks
Financial statements edit checks analysis can facilitate the detection of reporting errors.
- VA will use financial statement edit checks to uncover accounting anomalies and identify the underlying cause of variances, so that errors can be corrected.
- VA will perform three levels of financial statements edits checks. The three levels are fund level, Administration level, and Department-wide consolidated level.
- OFP, and any additional Administration-specific designated offices, will run validation reports from Management Information Exchange (MinX) Systemto perform fund level edit checks. The Administration-specific designated offices will work on the funds within their Administration’s jurisdiction and OFP will handle the funds for the rest of the Department.
- OFP, and any additional Administration-specific designated offices, will research the root causes of variances, provide explanations, and propose corrections for any accounting errors at fund level.
- OFP will review the final explanations of the unresolved variances at the fund level to ensure that these variances are truly unresolved and the explanations are satisfactory.
- OFP will perform edit checks at the Administration level and Department-wide consolidated level, after variances at the fund level have been either resolved or adequately explained.
- OFP’s Master Edit Check Signature Form, see Appendix A for an example, will be signed off after all reviews are complete.
020504 Quarterly Fluctuation/Flux Analysis
Fluctuation analysis assists in the discovery of unusual balances via comparison of the current reporting period and the same reporting period in comparable prior periods. The analysis focuses on line items of the principal financial statements.
- OFP will run quarterly fluctuation reports from MinX and review the completeness and accuracy of the report.
- OFP will distribute a call memorandum via email and the quarterly fluctuation reports to Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs POCs for quarterly flux analysis.
- Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs will use the call memorandum as the guide for their flux analysis. Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs will run updated reports for their analyses if any changes occur after the initial reports were created.
- Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs will perform thorough research of the key factors causing significant variances on individual line items on the principal financial statements and provide explanations for those variances.
- Administration Fiscal Staff and CFOs will sign the OFP Financial Statement Analytics Sign-Off Sheet indicating that their analysis is complete and submit the sheet along with the analysis to OFP.
- OFP will conduct a review of the analysis performed by the Administration’s Fiscal Staff and CFOs to ensure the completeness, accuracy, and adequacy of the flux analysis.
- At fiscal year-end, OFP will compile and edit analyses provided by Administrations; and create a further five-year analysis. The five-year financial statement analytics will be used as a basis for the analysis component of MD&A.
- A review panel, including OFP staff, Deputy Director of OFP, and Associate Deputy Assistant Secretary of Financial Policy, will review the quarterly and fiscal year-end significant variances analysis and associated explanations.
- Panel reviewers will sign off on the OFP Financial Statement Review Signature Form when the panel determines that the most relevant variances are adequately explained. For an example of the form, see Appendix B, Example of OFP Financial Statement Review Signature Form.
- OFP will submit the required interim and year-end financial statements with notes, required supplementary stewardship information (RSSI), required supplementary information (RSI), and analysis of significant variances with explanations to external financial auditors and OMB through the OMB MAX portal.
020505 Analysis of Entity’s Financial Statements in MD&A
MD&A provides an overview of VA’s financial and performance results for a fiscal year and accentuates VA’s most significant issues in a concise manner.
- VA will analyze its year-end financial statements to highlight its annual financial position, financial performance, and relevant trends.
- VA will provide explanations for significant variances of key items within the MD&A. The analysis may be presented as narratives, illustrative tables, and/or data visualizations for key measures.
- OFP will develop data visualizations for the key measures that depict important financial factors and changes in the current year, and significant changes in the principle financial statements over the five-year period. For an example of the data visualizations, see Appendix C, Example of Chart of Analysis of VA’s Financial Statements.
0206 Authorities and References
- Chief Financial Officers Act of 1990, Public Law 101-576
- Government Performance and Results Modernization Act of 2010, Public Law 111-352
- OMB Circular A-123, Management’s Responsibility for Enterprise Risk Management and Internal Control
- OMB Circular A-136, Financial Reporting Requirements – Revised
- TFM Volume I Part 2 Chapter 4700 Agency Reporting Requirements for the Financial Report of the United States Government
- TFM Volume I Supplement – USSGL
- Statement of Federal Financial Accounting Concepts (SFFAC) 3: Management’s Discussion and Analysis
- Statement of Federal Financial Accounting Standards (SFFAS) 15: Management’s Discussion and Analysis
- Treasury GTAS Edits and Validations Information Portal
0207 Rescissions
None
0208 Questions
Questions concerning these financial policies and procedures should be directed as follows:
- VHA VHA 10A3A Accounting Policy (Outlook)
- VBA VAVBAWAS/CO/FINREP (Outlook)
- NCA NCA Financial Policy Group (Outlook)
- All Others OFP Accounting Policy (Outlook)
Appendix A: Example of the OFP Master Edit Check Signature Form
Link to example of OFP Master Edit Check Signature Form

Appendix B: Example of OFP Financial Statement Review Signature Review Form
Link to example of OFP Financial Statement Review Signature Review Form
Appendix C: Example of Chart of Analysis of VA’s Financial Statements
Comparative Budgetary Resources, FY 2013 – FY 2017
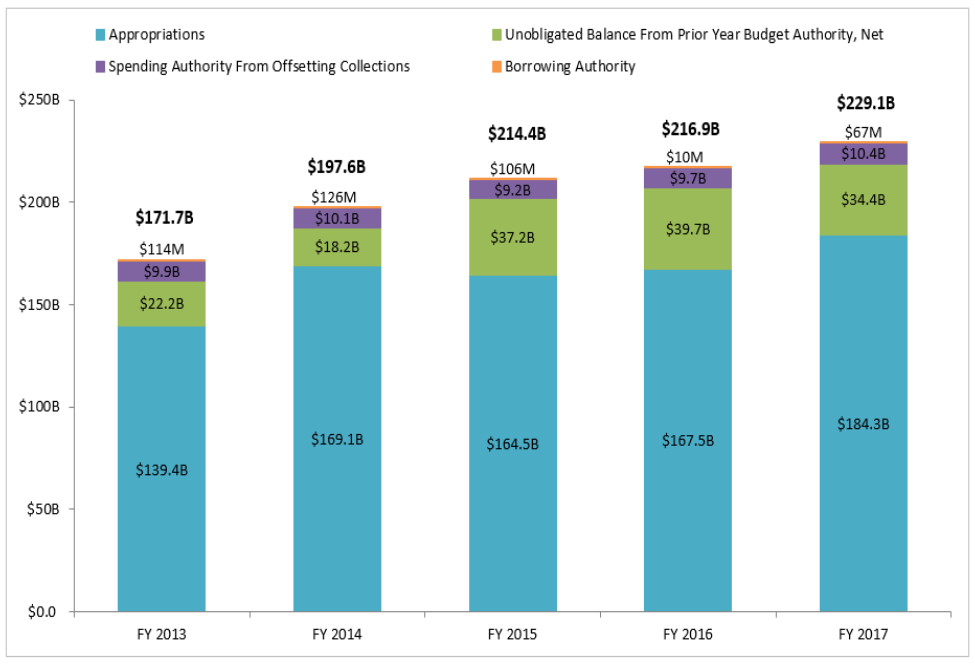
Budgetary Resources
The increase in overall budgetary resources between FY 2016 and FY 2017 is reflective of:
- Growth in medical services benefits provided due to an increase in the number of Veterans receiving care from 6.9 million to 7.1 million in FY 2016 and FY 2017, respectively.
- The VA Choice and Quality Employment Act of 2017 provided additional funding authorization for the Veterans Choice Program (VCP) to ensure Veterans receive the right care, at the right time, from the right provider.
- Higher C&P payments as a result of increases in the number of beneficiaries accessing and receiving these benefits.


