Volume I - General Accounting
Chapter 11B – Buy/Sell Transactions (G-Invoicing)
Questions concerning this policy chapter should be directed to:
- Veterans Health Administration
- Veterans Benefits Administration
- National Cemetery Administration
- Debt Management Center
- Financial Services Center
- Construction and Facilities Management
- All others
1101 Overview
This chapter establishes the Department of Veterans Affairs’ (VA) financial policies regarding the creation, execution, administration, accounting, and reporting of buy/sell transactions using the G-Invoicing platform.
For information on paper based (manual) buy/sell agreements refer to VA Financial Policy Volume I Chapter 11a, Buy/Sell Transactions (Paper Form).
For information on the accounting and reporting of other types of IGTs, refer to VA Financial Policy Volume I Chapter 11, Intragovernmental Transactions.
For specific assisted acquisition and accounting related requirements refer to VA Acquisitions Manual Subpart M817.5 Interagency Acquisitions for executing Interagency Agreements (IAAs) and Treasury Financial Manual (TFM) Volume I, Part II, Chapter 4700 – Federal Entity Reporting Requirements for the Financial Report of the United States Government for accounting guidance.
Key points covered in this chapter:
- Government invoicing’s (G-Invoicing) replaces the current paper-based reimbursable agreement process with an electronic origination, review, and approval application for IAAs;
- Bureau of Fiscal Service under the authority of 31 U.S.C. § 3512(b) and § 3513, has mandated use of G-Invoicing by federal entities for all Intra-governmental Buy/Sell activity;
- IAAs establish the relationship between the requesting agency (buyer) and the servicing agency (seller) and may be executed between major organizations (31 U.S.C. § 1513) within VA or between VA and another federal entity;
- VA requires an IAA for all buy/sell transactions;
- VA will comply with statutory and regulatory requirements when entering into IAAs;
- VA will adhere to Treasury’s guidance on IAAs;
- VA will not perform work and/or make any payment before the IAA is officially executed in G-Invoicing;
- VA will review, approve, and retain IAAs and related modifications on Treasury G- Invoicing platform;
- VA will record accounting entries for buy/sell activities, perform regular reconciliations, and resolve reconciliation differences in accordance with Treasury’s guidance; and
- VA will close out G-Invoicing IAAs in a timely manner.
1102 Revisions
| Section | Revision | Requesting Office | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110504 | Updated Obligations reference | OFP | Volume and chapter numbers changed | July 2024 |
| 1105 | Department of Treasury removed the G-Invoicing mandated transition date for ‘In-Flight’ order processing on the platform | OFP | Deadline for all VA G-Invoicing platform activity moved to coincide with removal of Buy/Sell data element option for User Interface and Bulk File IPACs | May 2024 |
| 1105 | Removed all VA to VA G-Invoicing delayed exemptions to the G-Invoicing platform | OFP | Internal VA to VA Buy/Sell agreements transitioned to Treasury’s G-Invoicing platform | May 2024 |
| 1105 | Removed reference statement concerning iFAMS IPAC integrations using bulk file processing during an interim period | OFP | IFAMS has been integrated for all new activity | May 2024 |
| Appendix E | Updated FMS internal VA-VA IPAC processing procedures with administrations in IFAMS to include IGT sub-category | OFP | New Fiscal Service data element to ensure accurate categorization of the transaction | May 2024 |
For a complete listing of previous policy revisions, see Appendix A.
1103 Definitions
Advances – Cash outlays made by a federal entity prior to receiving agreed upon goods and/or services.
Agency Location Code – A numeric symbol assigned by Treasury to identify an agency accounting and/or reporting office.
Assisted Acquisition – A type of interagency acquisition where a servicing agency performs acquisition activities on a requesting agency’s behalf, such as awarding and administering a contract, task order, or delivery order.
Buy/sell Transaction – Transactions that occur between two federal entities where goods or services are purchased by one entity from another entity. This arrangement is accomplished through the issuance of a reimbursable agreement (i.e., G-Invoicing platform, or Treasury Form 7600(A)(B)) between the two entities.
Trading partners should have appropriate statutory authority (e.g., Economy Act), prior to engaging in an agreement for buy/sell transactions.
Enabled Direct Agreement G-Invoicing (EDG) – iFAMS document type EDG. Invoicing enabled agreement transaction; updates general ledger and budget.
Enabled Indirect Agreement G-Invoicing (EAG) – iFAMS document type EAG. Invoicing enabled agreement transaction; updated general ledger and budget; uses projects.
Document type EAG.
Federal Intra-governmental Data Standards (FIDS) – Data elements that form the foundation of the Intra-governmental Buy/Sell process.
Freight on Board Point (FOB) – Specifies at what point the Seller transfers ownership of the goods/services to the buyer. This also determines which Performance Transaction Type will initiate fund settlement. (The Seller’s Delivered/Performed or the Buyer’s Received/Accepted.)
- FOB Point : Source – The Buyers Performance transactions are optional unless the Buyer disagrees with the Seller’s Performance Transaction “Delivered/Performed”. Local policy relevant to VA entities may make this a requirement in standard operating procedures.
- FOB Point : Destination/Other – The Buyer’s Performance Transactions are required.
General Terms and Conditions (GT&C) – The section of an IAA that identifies the buyer and seller involved, the authority for the agreement, required actions, period of performance, and type (i.e., single order or multiple order IAA).
- Local GT&C – Completed at the same level as the Order. Access may be limited to only the assigned group.
- Umbrella GT&C – Terms and conditions documented at a higher level in the hierarchy and may cover multiple groups.
G-Invoicing – Treasury’s long-term solution for buy/sell transactions, that will allow federal agencies to initiate payments and to manage the receipt and acceptance of GT&C, orders, and performance.
G-Invoicing Order – Funding section of the IAA that identifies the specific Ordering Agency requirements for the expected delivery of goods and/or services by the Performing Agency,and the corresponding accounting treatment.
- Centralized G-Invoicing Order – A single summarized order that is created and approved at a level higher than where actual goods and services are received. For example, this model would have one 7600B but multiple requestor/buyer obligations and/or servicer/seller agreements in iFAMS or FMS.
- Decentralized G-Invoicing Order – An order model that can be utilized by having separate orders (7600B) or separate order lines to facilitate tracking performance discretely at the level where goods and services are received. For example, there is one requestor/buyer obligation and one servicer/seller agreement.
Inter or Intra-Agency Agreement (IAA) – A written agreement entered between federal agencies (Inter), or organizational units within the same agency (Intra), establishing a relationship between a buyer and seller, which specifies the goods to be furnished or tasks to be accomplished.
Intra-Governmental Payment and Collection (IPAC) – Payment and collection transfer of funds across Federal Program Agencies (FPAs) for goods and services (i.e., buy/sell transactions) fiduciary transfers (i.e., investment and borrowing transactions), federal employee benefits data and check aftermath activity.
Lines/Schedules (G-Invoicing) – Specific details regarding the goods/services the requesting agency is purchasing from the servicing agency are entered as line-item information on Orders placed in G-Invoicing. Each line item will display along with a Schedule Summary. Schedules document accounting information related to the line. There may be multiple schedules for a single line. Required fields for each must be completed prior to approval.
Non-severable Services – Services that represent a single undertaking that, if not completed in full, would not provide the buyer with any value.
Obligation Enabled G-Invoicing (OEG) – iFAMS document type OEG. G-Invoicing enabled Obligation; updates general ledger and budget.
Order – Also known as the ordering instrument, is the funding section of an IAA, which includes the goods and/or services requirements, funding information, and authorized signatures to establish the obligation between the trading partners.
Order Authorization (OAI) – iFAMS document type OAI that links the G-Invoicing Order to the Servicer/Seller agreement or Requestor/Buyer obligation.
Order Originating Partner – The trading partner that first introduces Orders to G- Invoicing under the GT&C agreement. Each GT&C only allows either the Requesting Agency or the Servicing Agency to initiate the corresponding Orders, but not both.
Organization Groups – (also known simply as “Groups”). Groups are organized on a hierarchical agency structure with rules that determine which documents a user may access within the system and also limit the Agency Location Codes (ALCs) and Treasury Account Symbols (TAS) that can be used on a document.
Performance – The exchange of data which indicates that the Intragovernmental Buy/Sell Activitypreviously agreed upon between the Requesting and Servicing Agencies has been completed.
Period of Performance (POP) – The period of time specified by the IAA within which the terms and conditions of an IAA remain in full force and effect. This is also known as the start and stop date of an interagency agreement. Goods and services will not begin being delivered before the start date identified in the POP and will finish being delivered by the end date of the POP.
Reciprocal Category (RC) – Comprised of a set of reclassified financial statement line items that are the reciprocal of each other (for example, accounts payable/accounts receivable). These categories assist in the elimination of federal activity at the government-wide level to prepare the Financial Report.
Requesting Agency – A federal entity that requests goods or services from another federal entity, also referred to as the buyer.
Severable Services – Services of a continuing or recurring nature, which may be funded on a fiscal year or on an incremental basis.
Servicing Agency – A federal entity that is responsible for providing goods or services to another federal entity, also referred to as the seller.
Trading Partner (TP) – A federal entity that is party to IGTs as either the buyer or the seller.
Treasury Account Symbol – An identification code assigned by Treasury, in collaboration with OMB and VA, to an individual appropriation, receipt, or other fund account.
1104 Roles and Responsibilities
Administration and Staff Office Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) are primarily responsible for the appropriate recording and reporting of IAA-related accounting events under their jurisdiction and for reviewing and providing approval for IAAs with amounts greater than or equal to $25 million.
Office of General Counsel (OGC) (Buyer or Seller) is responsible for providing legal review and concurrence on an IAA where applicable.
Financial Services Center (FSC) Leading the VA G-Invoicing implementation effort and will be providing system administration support to VA users after go-live. FSC is responsible for coordinating with program officers and accounting/budget officers to ensure the accuracy of accounting entries, performance of reconciliations, and resolution of reconciliation differences.
G-Invoicing User Administrator – responsible for establishing G-Invoicing Roles as well as managing and initiating access to G-Invoicing. User Administrators will assign user roles based on ‘Least Privilege Principle’, requiring that users be granted the most restrictive set of privileges or access needed for performance of authorized tasks. User Administrators are decentralized and located within each Administration or Staff Office. A listing of User Administrators is posted on the VA IGOV Collaboration page.
1105 Policies
110501 General Policies
- Federal entities will identify a bona fide need for goods and services in daily operations.
- When federal entities are involved in buy/sell activities with each other, they become trading partners (TPs) bound by the terms and conditions contained in an IAA. The federal entity soliciting the goods and services will be referred to as the buyer and the federal entity providing the goods and services will be referred to as the seller.
- VA will comply with statutory and regulatory authorities and only enter an IAA in compliance with the following:
- The Economy Act (31 U.S.C. §§1535,1536) Agency agreements & Crediting Payments between Agencies, and its associated regulation (Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) Subpart 17.5 Interagency Acquisitions) provides guidance for IAAs administered under this Statute. To reduce potential Anti-deficiency Act violations and to be compliant with the Economy Act, buyers and sellers will work together to de-obligate any unused amounts prior to expiration of the appropriation in accordance with the requirements outlined in Section 110503. Buyers must monitor their IAAs regularly to ensure that seller performs agreed-upon tasks timely to avoid any lapse of funding.
- Non-Economy Act
Refers to all statutory authorities other than the Economy Act. Non-Economy Act related statutory authorities include, but are not limited to:- Medical Sharing Agreement, 38 U.S.C § 8153;
- Government Employees Training Act (GETA), 5 U.S.C. § 4104;
- Intergovernmental Personnel Act, 5 U.S.C. § 3371 et seq.;
- Debt Collection Act, 5 U.S.C. § 5514(a)(2);
- VA Supply Fund, 38 U.S.C. § 8121; and
- VA Franchise Fund, Public Law 109-114.
- There are no specific requirements to de-obligate unused amounts associated with Non-Economy Act orders prior to the expiration of the appropriation as long as the buyer has a bona fide need for goods or services and the seller is actively seeking to provide the goods and services.
- VA will utilize G-Invoicing to document all buy/sell activities between organizational units both within and outside of VA.
- All federal Intra-governmental transactions associated with the Buy/Sell IGT category as defined by Treasury Financial Manual (TFM) Volume I, Part II, Chapter 4700, Appendix 3 are identified through RCs 22, 23, and 24.
- VA will continue to leverage credit cards for Buy/Sell activities in line with Treasury guidance and thresholds.
- Grants, cooperative agreements, special purpose agreements and contracts between VA and non-Federal entities are not considered buy/sell transactions and are not processed via an IAA.
- Grants, cooperative agreements, and special purpose agreements are used for special purposes specifically authorized by law and are not for the acquisition of goods or services by the federal government. Refer to P.L. 95-224, 2 C.F.R. § 200.201 – Use of grant agreements (including fixed amount awards), cooperative agreements, and contracts, and 2 C.F.R. § 200.24 – Cooperative agreement for additional details.
- Contracts between VA and non-federal entities, such as state and local Governments for the purchase of goods and services will follow the requirements set forth in the FAR.
- VA will adhere to Treasury Financial Manual (TFM) Volume I, Chapter 4700 to divide the buy/sell process into four distinct phases: IAA initiation and GT&C; Order; Performance Transactions/Receipt and Acceptance; and Funds Settlement/IAA Closeout. Refer to Appendix B for specific business and accounting events that occur in each phase.
- Administrations and Staff Offices will be responsible for processing G-Invoicing activity after go-live. Each Administration and Staff Office will need to:
- Review agreement activity to determine how it will translate to G-Invoicing;
- Review and update standard operating procedures and other guidance documents to incorporate during G-Invoicing implementation;
- Review organizational structures to verify hierarchy location, group structure, agency location codes, and Treasury account symbols;
- Identify User Administrators to be responsible for access to the application; and
- Identify user roles for affected staff as appropriate.
- IAAs will be executed for buy/sell activities between VA and another federal entity or between major organizations within VA.
- Distinguishing between buy/sell transactions or cost sharing/account adjustment expenditure transfers is dependent upon whether or not the office providing the service performs the service as short-term limited assistance or provides that service as a normal part of their business activity. If this is short-term limited assistance a buy/sell agreement is not required, if a normal part of business activity then buy/sell agreement is required. See Appendix G for scenario examples.
110502 G-Invoicing Establishment
- All IGT Buy/Sell activity must be implemented into G-Invoicing by October 1, 2025.
- In the instance that a VA Trading Partner is not ready to implement the use of G-lnvoicing prior to FY26, entities should maintain current processes and procedures to facilitate, maintain, and settle lnteragency Agreements (e.g., 7600A/B forms, IPAC, etc.). These forms are aligned to the FIDS and will assist trading partners in documenting all required data attributes for entry into G-lnvoicing. Refer to VA Financial Policy Volume 1, Chapter 11a, Buy/Sell Transactions (Paper Form) for additional detail.
- VA will not have the ability to initiate an IPAC transaction categorized as Buy/Sell beginning in FY2026. Fiscal Service will remove the Buy/Sell option through the User Interface and Bulk File at this time.
- For those agreements subject to G-Invoicing, VA will follow the IAA establishment process contained in this section to create, document, review, approve, and retain its IAA’s. Each successive stage is contingent upon the successful completion, i.e., approvals, open status, etc. of the previous stage. Facilitation of Intra-governmental Buy/Sell activity in G-Invoicing includes:
- IAA Initiation and GT&C;
- Order;
- Performance Transactions/Receipt and Acceptance; and
- Fund Settlement
- Intragovernmental activity that is not considered Buy/Sell (e.g., Fiduciary, Transfer, and General Fund IGTs) should be excluded from G-Invoicing and VA should continue to facilitate these transactions through current policy, systems, and procedures. Refer to VA Financial Policy Volume 1, Chapter 11, Intragovernmental Transactions for additional detail on IGTs not transitioning to G-Invoicing.
- G-Invoicing does not have built-in segregation of duties controls, so it is the responsibility of supervisors approving platform access via Form 9957 to confirm that user roles do not conflict. Refer to User Admin Resources for Segregation of Duties Matrix for Assigning of G-Invoicing Roles that are not in conflict and VA Financial Policy Vol I, Chapter 5, Management’s Responsibility for Internal Controls. Recertification of user roles will be performed yearly by User Administrators. User Administrator roles will be recertified twice yearly.
- After a determination has been reached that an IAA with another federal entity is in the best interest of the federal government, the buyer’s program officer will work with the potential seller to develop the agreement.
- The buyer’s program officer will obtain a cost estimate from the seller and consult with the buyer’s accounting/budget officer to verify funding availability. Under the constraint of a continuing resolution, the Order can be completed for the full amount of the POP as long as the buyer identifies the funding restriction and denotes it in the IAA. In addition, there are special rules of funds control for different types of services as follows:
- The funds available to pay for services in one fiscal year are not available to pay for services in the following fiscal year unless the services are non-severable or otherwise authorized by law.
- For non-severable services, only the funding available in the fiscal year when the services begin will be used for the duration of the IAA’s POP. Funding available in subsequent fiscal years cannot be used for payment or reimbursement of the services. Refer to VA Financial Policy Volume I, Ch 11a Buy/Sell Transactions (Paper Form) for additional information on non-severable services.
- For severable services, funding may be obligated for up to 12 months and may cross fiscal years (41 U.S.C. § 3902, Severable services contracts for periods crossing fiscal years). Each option period exercised starts a new order and 12- month POP. Refer to VA Financial Policy Volume I, Ch 11a Buy/Sell Transactions (Paper Form) for additional information on severable services and IAAs.
- Either the Requesting Agency (Buyer) or the Servicing Agency (Seller) will begin the G-Invoicing document flow by creating a new GT&C. G-Invoicing will assign a unique agreement number which will be used to track each GT&C from origination through completion or termination.
- The period of performance on a GT&C can be for multi-years. However, it should not exceed five (5) years unless a longer period is specifically authorized by statute or required by the servicing trading partner. At no time, shall the end period of performance of an order exceed the end period of performance established on the GT&C.
- The initiator of the agreement will enter contact information, authorizing officials, agreement scope, roles, and any clauses. Order Originating Partner indicator is determined as part of the GT&C agreement. Each GT&C only allows either the Requesting Agency or the Servicing Agency to initiate the corresponding Orders, but not both. After review, the initiating party will share a draft of the order with the trading partner.
- Trading partners may approve once all data has been entered by both trading partners and submitted for approvals. An order cannot be initiated in G- Invoicing until an agreed upon GT&C has been approved by both the Buyer and the Seller and is in “Open” status. Approvals are required from all parties involved in a buy/sell transaction before any goods or services are received or reimbursements made with another federal entity.
- GT&Cs with a status of ‘open’ may be modified by either trading partner. GT&C modifications are required to be approved by both trading partners.
- Information documented in the GT&C and Order(s) includes data elements that form the foundation of the buy/sell agreement. G-Invoicing required terms conform with Treasury requirements and contain all data elements specified by Treasury to capture the necessary information required for trading partners reliance on proper accounting from initiation through settlement.
- FIDS completed within the Order stage convey a physical stamp of transaction type, period of performance, and other accounting requirements for both agencies. The FIDS within the Order stage effect the accounting treatment of transactions throughout the rest of the buy/sell lifecycle.
- VA will initiate (as the Order Originating Partner) an Order from an open GT&C. Order numbers are auto-generated by G-Invoicing. Product requirements are detailed and accounting terms (Treasury account symbol, accounting string, and obligation number) are entered in the Order. Statutory Authority and supporting data are entered on the respective tabs of the Order draft. A VA Program Official and a Funding Official must approve the Order.
- VA (if not the Order Originating Partner) will review the data entered by its trading partner, complete the required fields for the 2nd agency, and approve the Order prompting the Order to become Open. Performance transactions cannot be initiated in G-Invoicing until an agreed upon Order has been approved by both the Buyer and the Seller and is in an “Open” status.
- Orders that are in an ‘open’ or ‘closed’ status may only be modified by the agency (Buyer or Seller) that created them. Modifications made to an Order will require the Order to be re-approved by both trading partners. If there is performance against an Order, there will be restrictions on what fields can be modified on the Order.
- VA’s Program Official must ensure the appropriate higher-level review and approval (e.g., email or memorandum) of the Order have occurred and are properly documented and attached within G-invoicing, prior to signing the IAA. Below are additional reviews requiring approval attachment within G-Invoicing prior to final Order approval:
- OGC, if applicable (i.e., All Economy Act interagency acquisitions with $250,000 or more in life cycle costs, and all interagency acquisitions with $750,000 or more in life cycle costs, require OGC review and concurrence).
- Other applicable reviews if required (per internal Directives and Handbooks).
- Chief Information Officer (CIO) or designee, if applicable.
- Administration and Staff Office CFOs for amounts ≥ $25M.
- VA’s Funding Official will verify funding information associated with an Order and provide funding approval within G-Invoicing.
- The performance portion of the FIDS enforces the exchange of data which supports accurate and timely accounting entries. Performance transactions provide the key triggers for the recording of accounting entries related to accruals, advances, and liquidations. FIDS recorded within G-Invoicing from which VA will reference for the respective accounting transactions include:
- Capitalization indicator;
- Assisted acquisitions indicator (see definition of assisted acquisition);
- Advance payment indicator;
- FOB point i.e., Source, Destination, Other; and
- Constructive receipt days.
- G-Invoicing online platform will be the central document repository for all signed, executed buy/sell IAAs.
- Any changes to an Order after it has been approved by both buyer and seller must be amended with an approved Order Modification within G-invoicing.
110503 G-Invoicing Administration
From the inception of the buy/sell activity, the buyer and seller will assign their Program Officials or designees to lead the administration process. VA will not perform work and/or make any payments before the IAA is officially executed.
- Upon the execution of the Order:
- The seller will:
- Start working on the ordered goods and services;
- Record an unfilled customer order/undelivered order and anticipated reimbursements; and
- If an advance is utilized, record the advance as a liability.
- The buyer will:
- Obligate the funds based on the IAA. See Appendix D and E for detailed walk-through of G-Invoicing processes in accounting systems.
- If an advance is utilized, record an asset for the advance.
- The seller will:
- During the Performance stage of the IAA:
- The seller will:
- Manage the fulfillment of the IAA, including, but not limited to:
- Overseeing the performance of the seller and/or the contractor;
- Initiating/exchange of performance transaction data;
- Reporting/Recording accruals at a minimum on a quarterly basis;
- Initiating/recording and liquidating advances;
- Monitoring goods and services delivery and receipt status to conform with the POP start and stop date;
- Resolving performance/compliance issues and disputes; and
- Negotiating and signing modifications to the IAA, when necessary.
- Manage the fulfillment of the IAA, including, but not limited to:
- The buyer will:
- Manage the fulfillment of the IAA, including, but not limited to:
- Ensuring contract expectations are being met by the seller and/or the contractor
- Responding/exchange of performance transaction data;
- Recording accruals/amounts based on performance date;
- Recording advance as asset if utilized and reduction of prepayment after receipt and acceptance;
- Monitoring goods and services delivery and receipt status to conform with the POP start and stop date;
- Resolving performance/compliance issues and disputes;
- Negotiating and signing modifications to the IAA, when necessary; and
- Initiating the closeout process.
- Manage the fulfillment of the IAA, including, but not limited to:
- The seller will:
- Reconciliation
- The seller will:
- Reconcile buy/sell transactions to ensure accounting entries are correct in their systems during the POP and as a part of closeout;
- Comply with Treasury’s requirement to reconcile transactions, which include:
- seller’s accounts receivable vs. buyer’s accounts payable;
- seller’s unearned revenue/liability from buyer vs. buyer’s advance to seller; and
- seller’s revenue vs. buyer’s expenses/capitalized purchases;
- Perform reconciliation on a monthly basis;
- VA will resolve reconciliation differences in a timely manner to ensure the accuracy of VA’s quarterly consolidated financial statements, which are certified by the CFOs of the Administrations and Staff Offices; and
- Reconciliation differences will be documented using the IAA agreement number and order number.
- The buyer will:
- Reconcile buy/sell transactions to ensure accounting entries are correct in their systems during the POP and as a part of closeout;
- Comply with Treasury’s requirement to reconcile transactions, which include:
- buyer’s accounts payable vs. seller’s accounts receivable;
- buyer’s advance to seller vs. seller’s unearned revenue/liability frombuyer; and
- buyer’s expenses/capitalized purchases vs. seller’s revenue;
- Perform reconciliation on a monthly basis;
- VA will resolve reconciliation differences in a timely manner to ensure the accuracy of VA’s quarterly consolidated financial statements, which are certified by the CFOs of the Administrations and Staff Offices; and
- Reconciliation differences will be documented using the IAA agreement number and order number.
- As required by Treasury, FSC will communicate with other federal agencies as timely as possible, but no less than quarterly, to address and resolve reconciliation differences.
- If the reconciliation differences with other federal agencies cannot be resolved timely, FSC will comply with Treasury’s requirements for developing Root Cause/Corrective Action Plans (CAP) and the Dispute Resolution Process. Refer to VA Financial Policy Volume I, Chapter 11, Intragovernmental Transactions, for detailed information.
- The seller will:
- Fund settlement occurs upon successful completion of the Performance Transactions. During the fund settlement, G-Invoicing communicates directly with IPAC and sends the performance and settlement confirmations to iFAMS via the G- Invoicing integration, not the IPAC bulk file. VA legacy accounting system (FMS) will not integrate with G-Invoicing. See Appendix D below for FMS fund settlement processes.
110504 Order and Obligations Close Out
- The Requesting Agency is the only agency that can request an Order closure.
- Per Fiscal Service – G-Invoicing Rules of Engagement, an Order cannot be closed until the respective totals of Performance Transactions by the buyer and seller are in agreement. Depending on the Freight On Board (FOB) Point selected, a buyer’s Performance Transaction is optional, unless the buyer disagrees with the seller’s Performance Transaction. Local policy relevant to VA entities may make this a requirement in standard operating procedures.
- Detailed Order Closure Rules for G-Invoicing platform may be found in G-Invoicing User Guide.
- In accordance with TFM 4700, Trading Partners must monitor all Orders as they approach their end date. The Seller will identify Orders that are approaching end date and check the status with the Buyer to confirm that they are ready for closeout.
- Buyer will review the Order status and perform procedures to close out and deobligate the Order if the Statutory Authority for the agreement mandated it.
- Seller will determine during closeout if any third-party supporting contracts are open that need to be deobligated and closed.
- Each Schedule within a G-Invoicing order must either be fully performed, modified down to the amount that was performed (and paid), have a Final Performance Indicator of ‘F’ (final), or cancelled before an Order can be systematically closed.
- VA will run monthly reports to ensure completed Orders are closed.
- All finance offices with open Intragovernmental obligations will perform monthly reviews and reconciliations to ensure that their obligations, to include undelivered orders (UDOs) and delivered unpaid obligations, are valid.
- Intragovernmental obligations with lengthy completion/execution timeframes (e.g., software product development, high-tech medical equipment, or construction design contracts) can be reviewed quarterly. The quarterly review must validate that the obligations have legitimate lengthy periods of inactivity during the period of performance, which would not require an adjustment to the obligation. See Volume III, Chapter 2 – Obligations, for detailed information on review of open and stale obligations.
110505 IAA Related Reporting Requirements
- FSC and Administration/Staff Office CFOs will cooperate to ensure the appropriate recording and reporting for buy/sell-related activities, transactions, and reconciliations in VA’s accounting system. In accordance with OMB Circular A-136 Federal entities must maintain accurate, detailed information on IGT transactions to enable easy identification, rationale, and location of supporting documentation.
- FSC will run monthly control reports reconciling G-Invoicing Order data with obligations in VA’s accounting systems ensuring that obligations were recorded promptly and correctly. When discrepancies are noted, FSC will work with the appropriate VA office to ensure that reconciling items are resolved.
- Office of Business Oversight (OBO) will perform reviews over compliance with G- Invoicing based on risk.
- FSC and Administration/Staff Office CFOs will follow OMB and Treasury’s guidelines for performing reconciliations and reporting. Refer to VA Financial Policy Volume I, Chapter 11, Intragovernmental Transactions for details.
1106 Authorities and References
- 31 U.S.C. § 1513, Officials Controlling Apportionments
- 31 U.S.C. § 1535, Agency Agreements
- 31 U.S.C. § 3512(b) and § 3513, Accounting Requirements, Systems, and Information
- 38 U.S.C § 308, Assistant Secretaries; Deputy Assistant Secretaries
- 41 U.S.C. § 3902, Severable services contracts for periods crossing fiscal years
- FAR 17.5, Interagency Acquisitions
- G-Invoicing User Guide
- Intragovernmental Accounting Division Page
- OMB Circular A-136, Financial Reporting Requirements
- Segregation of Duties Matrix – Assigning G-Invoicing Roles
- TFM Guidance – G-Invoicing Rules of Engagement
- TFM Volume I, Part 2, Chapter 4700, Federal Entity Reporting Requirements for the Financial Report of the United States Government
- TFM Volume I, Part 6, Chapter 4000, Intragovernmental Transaction Applications – Intragovernmental Payment and Collection (IPAC) and Government Invoicing (G- Invoicing)
- Treasury Fiscal Service Data Register
- VA Acquisition Regulation (VAAR)
- VA Acquisition Manual (VAAM)
- VA Acquisitions Manual Subpart M817.5 Interagency Acquisitions
- VA Financial Policy Library
- Volume I, Chapter 5 – Management’s Responsibility for Internal Controls
- Volume I, Chapter 11 – Intragovernmental Transactions
- Volume I, Chapter 11a – Buy/Sell Transactions (Paper Form)
- Volume III, Chapter 2A – Non-Contractual Obligations Policy
- Volume VIII, Chapter 1A – Invoice Review and Certification
- VA Form 9957 Access Request Form
1107 Rescissions
Volume I, Chapter 11B – Buy/Sell Transactions (G-Invoicing), May 2024
Appendix A: Previous Policy Revisions
| Section | Revision | Office | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1101 Overview | Added reference to the Treasury Financial Manual (TFM) Vol I, Part II, Chapter 4700 for additional information related to assisted acquisition and accounting requirements | OFP | OMB Federal Procurement Policy, Improving the Management and Use of Interagency Acquisitions removed as some material updated | November 2022 |
| 1105 Policies | Updated terms for conciseness | OFP | Consistency among terminology usage | November 2022 |
| 110501 General Policies | Added criteria for determination of buy/sell transaction vs cost sharing/account adjustment | OFP | Elements for consideration when determining intragovernmental processing | August 2022 |
| Appendix F | Personnel Cost Scenario Examples added as Appendix F | OFP | Fact patterns to assist with determination of correct transactional process | August 2022 |
| Various | New Chapter | OFP | Implementation of policy for creation, execution and reporting of Buy/Sell transactions using Treasury G-Invoicing platform | July 2022 |
Appendix B: TFM 4700 Buy/Sell IPAC & G-Invoicing Transaction Cycles
The Buy/Sell process model is defined by four distinct phases of activity:
- IAA Initiation and GT&C
- Order
- Performance Transactions/Receipt and Acceptance
- Fund Settlement/IAA Closeout
Each phase is characterized by specific business and accounting event(s) and is governed by a particular set of business rules to guide the decision-making process throughout the Buy/Sell life cycle, as displayed below in Figures 1 and 2.
Figure 1 : Buy/Sell Transactions completed in the IPAC environment
| Phase | Initiation and GT&C | Order | Performance Transaction and Receipt/Acceptance | Fund Settlement and IAA Closeout |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buy/Sell Business Event | -Document statutory authority and bonafide need -Complete Determination & Findings and identify trading partners -Establish GT&C -Officials Approve GT&C | -Complete accounting terms of IAA -Detail product requirements -Document TAS/BETCs -Create fiscal obligation | Goods/services are performed and delivered | -Buyer submits payment -Funds are transferred -Agreement is closed out |
| Accounting Event(s) | -No accounting Events | -Record UCO/UDO -Record advance payments (if necessary) | -Document the exchange of goods/services -Record invoices -Record accruals | -Record payment/collection -Record deobligations (if necessary) |
| Source: TFM Volume 1, Chapter 4700, Appendix 8 | ||||
Figure 2: Buy/Sell Transactions completed in the G-Invoicing environment
| Stage | GT&C | Order | Performance Transaction | Fund Settlement and IAA Closeout |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform | G-Invoicing | G-Invoicing | G-Invoicing | IPAC |
| Buy/Sell Business Event | -Trading partners’ roles & responsibilities are identified -Contact information and authorized officials are established -Agency Officials will Establish & approve GT&C | -Accounting terms of the IAA are completed -Product requirements are detailed -A fiscal obligation is created | -Goods / services are delivered / performed -The exchange of goods / services (Delivered / Received) -Accrual information is exchanged | -IPAC is initiated through the completion of the Performance Transaction -Funds are transferred |
| Source: TFM Volume 1, Chapter 4700, Appendix 8 | ||||
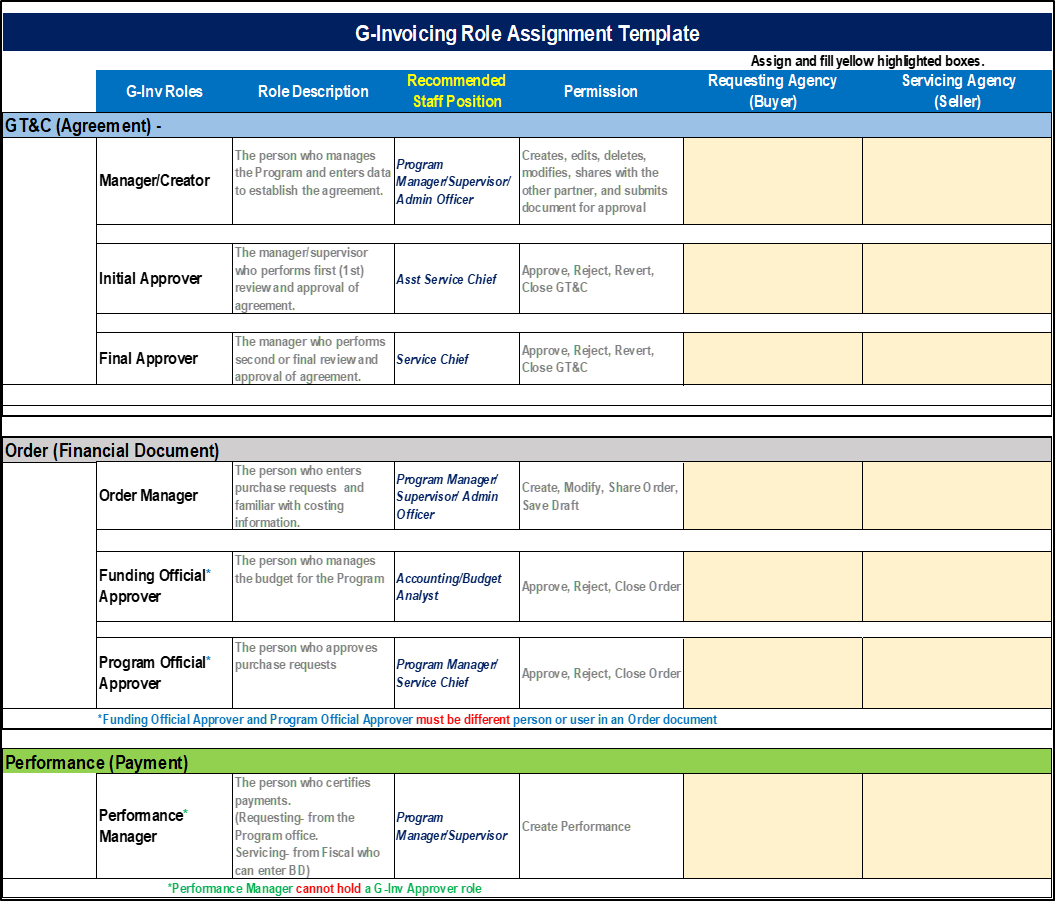
Appendix C: G-Invoicing Role Assignment Template
Key duties and responsibilities will be divided or segregated among different individuals to reduce the risk of error or fraud. This includes separating the responsibilities for authorizing transactions, processing and recording them, reviewing the transactions, and handling any related assets. No one individual will control all key aspects of a transaction or event. For example, a manager authorizing obligations would not be responsible for entering obligations into financial management systems or handling the payment of invoices.
Appendix D: G-Invoicing in Integrated Financial and Acquisition Management System (iFAMS)
- G-Invoicing functionality (including integrations and batch processes) will begin with iFAMS release 7.9 coinciding with Treasury G-Invoicing mandated start date of October 1, 2022. NCA, VBAGOE and OM+ will be the first offices initiated in this process. All other groups will receive training as part of their respective waves into iFAMS.
- G-Invoicing Process for Buyer/Seller in IFAMS entails:
- General Terms & Conditions
- GT&Cs are initiated, modified, and approved in Treasury G-Invoicing.
- Inbound integration will be utilized to pull approved GT&Cs (and their attachments) into iFAMS.
- GT&C refresh batch processing will be utilized to pull approved GT&C updates into iFAMS for modifications made to GT&Cs in Treasury G-Invoicing application.
- No user action other than ‘View’ can be taken in iFAMS.
- A GT&C record is created for each Requestor/Servicer Type in iFAMS.
- No general ledger or budget updates are made by GT&C records integration into iFAMS.
- Orders
- Orders are initiated, modified, and approved in Treasury G-Invoicing.
- Inbound Order Pull integration will be used to retrieve approved Treasury G- Invoicing Orders, Modifications, and Cancellations (and their attachments) into iFAMS.
- Inbound Order integration creates an OAI document type in iFAMS.
- Seller copies forward from OAI record to create agreement document type EDG/EAG in iFAMS. General ledger and Budget are updated.
- Buyer copies forward from OAI record to create obligation document type OEG in iFAMS. General ledger and Budget are updated.
- No user action other than ‘View’ can be taken in iFAMS.
- Performance
- Outbound (push transaction) and inbound (Confirmation) performance integration pushes performance transactions out to G-Invoicing for Settlement (Confirmation).
- Performance transactions are initiated by the Servicer/Seller in iFAMS and pushed out to G-Invoicing via the Performance integration.
- Buyer’s acceptance is pushed to G-Invoicing – this initiates the Settlement.
- IPAC bulk file has no role in transmission of Performance transactions to Treasury.
- Distinct inbound/outbound accrual batch processes create accrual transactions. Revenue accrual created for Servicer/Seller and payable accrual for Requestor/Buyer. Accrual process within iFAMS currently under review. All sellers would need to be onboarded within G-Invoicing.
- Performance activity can be viewed in the iFAMS performance query.
- Settlement
- Inbound integration pulls settled Performance transactions in from G-Invoicing.
- Crosswalk, Reconciliation, and Form Generation batch processes reconcile Settlement transactions to referenced documents and generate the collection or payment transactions.
- Settlement transactions are created automatically via the integration. This includes advance offsets, and prepayment liquidations for Orders with advance schedules.
- Settlement activity can be viewed in the iFAMS Performance query and the Performance Integration query.
- General Terms & Conditions
Appendix E: G-Invoicing in Financial Management System (FMS)
- VA legacy accounting system (FMS) will not integrate with G-Invoicing.
- FMS users will process agreements through G-Invoicing.
- IPACS will be generated by G-Invoicing:
- Incoming IPACS are generated in G-Invoicing and pulled into FASPAC via the IPAC bulk file.
- Outgoing IPACS are generated in G-Invoicing (instead of FASPAC) and then imported into FASPAC with the daily bulk file.
- FASPAC will then integrate with FMS.
- All transactions with users in iFAMS will need to be processed using IPACs. While the core ALC associated with FMS (36001200) will continue to be used for VA Administrations/Offices operating in FMS, a new core ALC for iFAMS organizations was established. ALC 03600104 will be used for iFAMS organizations.
- All IPACS are required to include the appropriate IGT sub-category data element to accurately categorize the transaction. This includes:
- Buy/Sell;
- Expenditure Transfer – Non-Exchange;
- Benefits;
- Custodial Transfer – Non-Exchange;
- Custodial Transfer – Exchange;
- Capital Transfer;
- Investments;
- Borrowings; and
- Other/Miscellaneous
Accounting Transactions
G-Invoicing requires the use of IPAC for settlement, therefore, internal transfer transactions for internal VA to VA Orders should no longer be used. This includes IM transactions and expenditure transfers (EB, EW, ET) for buy/sell activity. For Orders processed in G-Invoicing the following transactions are required:
| FMS | Servicing Agency | Requesting Agency |
|---|---|---|
| At the time of Order approval: | RA 01 | obligation document |
| At the time of billing, before Performance: | BD 06 | —- |
| IFAMS | Servicing Agency | Requesting Agency |
|---|---|---|
| At the time of Order approval: | EDE | OEE/OEX |
| At the time of billing, before Performance: | BME | —- |
IPACs received from G-Invoicing will be processed and recorded in FMS by the IAD IPAC Processing team. Note that G-Invoicing users must site the obligation and billing documents in G-Invoicing for the IPAC Processing team to record the collection/disbursement to the appropriate location. If these transactions are not referenced, the collection will be recorded to suspense and disbursement will be recorded to the default line of accounting.
Appendix F: G-Invoicing Platform Access Request Form 9957
G-Invoicing platform access will only be provisioned by User Administrator after completion (and approval) of Access Request Form 9957. VA Financial Policy Vol III, Chapter 1A – Invoice Review and Certification for segregation of duties information should be applied when approving user roles. The United States Department of Treasury’s Bureau of the Fiscal Service requires agencies to keep documentation regarding each user added to the system.
Appendix G: Personnel Cost Scenario Examples
| Description | Transfer for the Payment of a Good or Service is normal part of Sellers business activity (Buy/Sell) | Does Transfer result in an Obligation or Outlay (Expenditure Transfer) | Policy Guidance | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| An NCA staff member performs a project for the VAMC and VHA wishes to provide a performance award. | No | Yes | Volume II, Chapter 7 – Various Appropriations Law Related Topics Page 7 Volume 1 Chapter 9 – Expenditure Transfers Page 6 | VA will record adjustments to expenditures by transferring expenditures from one VA organization to another (e.g., one of the organizations gives an award to a VA employee who works in another VA organization and the employing organization has already obligated and expended the award to its employee). Subject to award limitation VA may record a transfer of costs associated with an employee’s activity from one organization completed on behalf of another organization, if the costs have already been obligated and expended by the employing organization. |
| A medical center would like to have a person who currently works in the Canteen Service, work for Dietetics on the weekends. This person would help prepare food. They would be filling a gap as there is a shortage of food workers at this medical center. | No | Yes | Volume II, Chapter 7 – Various Appropriations Law Related Topics Page 6/7 Volume 1 Chapter 9 – Expenditure Transfers Page 6 | VA will record adjustments to expenditures to temporarily charge one VA appropriation for an expenditure benefiting another VA appropriation, as long as amounts are available in both appropriations and the accounts are adjusted to reimburse the appropriation initially charged during or as of the close of the fiscal year. VA may record a transfer of costs associated with an employee’s activity from one organization completed on behalf of another organization, if the costs have already been obligated and expended by the employing organization. |
| A VBA contact center representative located on the same campus as a VAMC volunteers to serve on their labor pool for COVID. This would result in overtime. | No | Yes | Volume II, Chapter 7 – Various Appropriations Law Related Topics Pages 6/7 Volume 1 Chapter 9 – Expenditure Transfers Page 6 | VA will record adjustments to expenditures to temporarily charge one VA appropriation for an expenditure benefiting another VA appropriation, as long as amounts are available in both appropriations and the accounts are adjusted to reimburse the appropriation initially charged during or as of the close of the fiscal year. VA may record a transfer of costs associated with an employee’s activity from one organization completed on behalf of another organization, if the costs have already been obligated and expended by the employing organization. |
| Signed 2269 for a salary/payroll agreement between facility A and B, the detail assignment to include 10% of FTE time up to a one-year period. The requesting organization will reimburse the servicing organization for the period of service. | No | Yes | Volume II, Chapter 7 – Various Appropriations Law Related Topics Page 6/7 | VA will record adjustments to expenditures to temporarily charge one VA appropriation for an expenditure benefiting another VA appropriation, as long as amounts are available in both appropriations and the accounts are adjusted to reimburse the appropriation initially charged during or as of the close of the fiscal year. |


