History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 96: Postcard of Veterans Vocational School
In 1918, the government created the first nationwide vocational training system to help disabled Veterans acquire new occupational skills and find meaningful work. Over the next 10 years, more than 100,000 Veterans completed training programs in every field from agriculture and manufacturing to business and photography.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 95: 1840 Census of Pensioners
In a first, the 1840 census collected data on Veterans and widows receiving a pension from the federal government. The government published its findings in a stand-alone volume titled “A Census of Pensioners for Revolutionary or Military Services.”
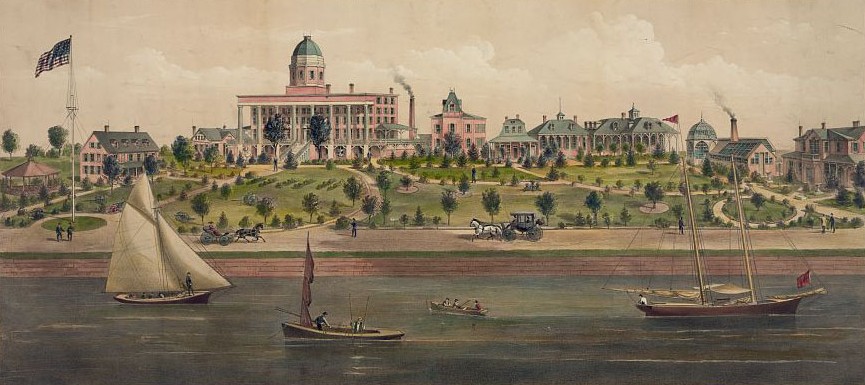
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 94: Southern Branch of the National Home
The Southern Branch of the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers opened in Hampton, Virginia, in late 1870. The circumstances surrounding the purchase of the property, however, prompted an investigation into the first president of the National Home’s Board of Managers, Benjamin Butler.

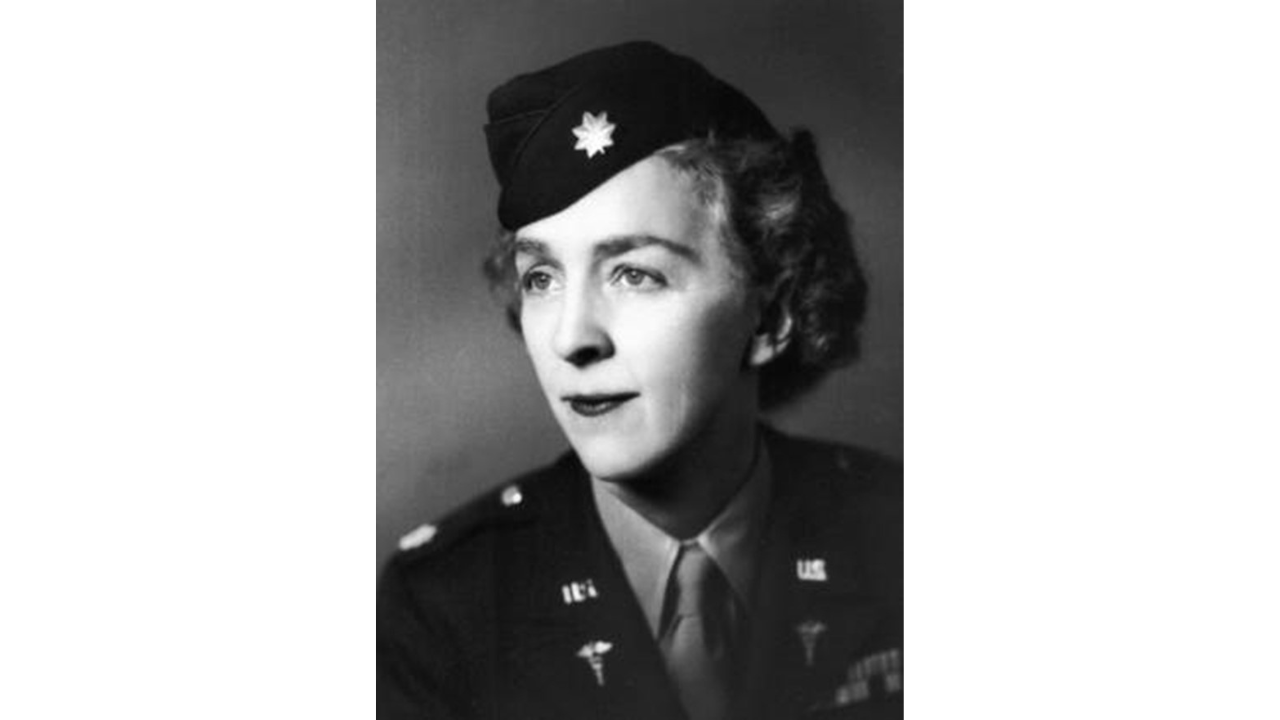
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 91: Hines Scrapbook Dedication
In 1933, VA staff presented agency chief Frank Hines with a scrapbook commemorating his ten years of service to Veterans. Intended as a personal keepsake for Hines, the scrapbook also offers a snapshot of a particular time in VA history.

Featured Stories
History of Former Whipple VA Directors Schmoll And McIntyre
Leadership change is something that happens constantly, whether it’s due to promotion, health, or other circumstances. At the Department of Veterans Affairs’ Northern Arizona Medical Center (formally known as Whipple VA Hospital) in Prescott, Arizona, directors have stayed in their position on average, three to five years. The shortest stint was 22 months, the longest was 16 years and two months. Most former directors moved on and retired elsewhere. However, two former directors, Paul N. Schmoll and Virgil I. McIntyre, either returned to or stayed in Prescott following their retirement. Both men are laid to rest at local cemeteries in the Prescott, Arizona, area.

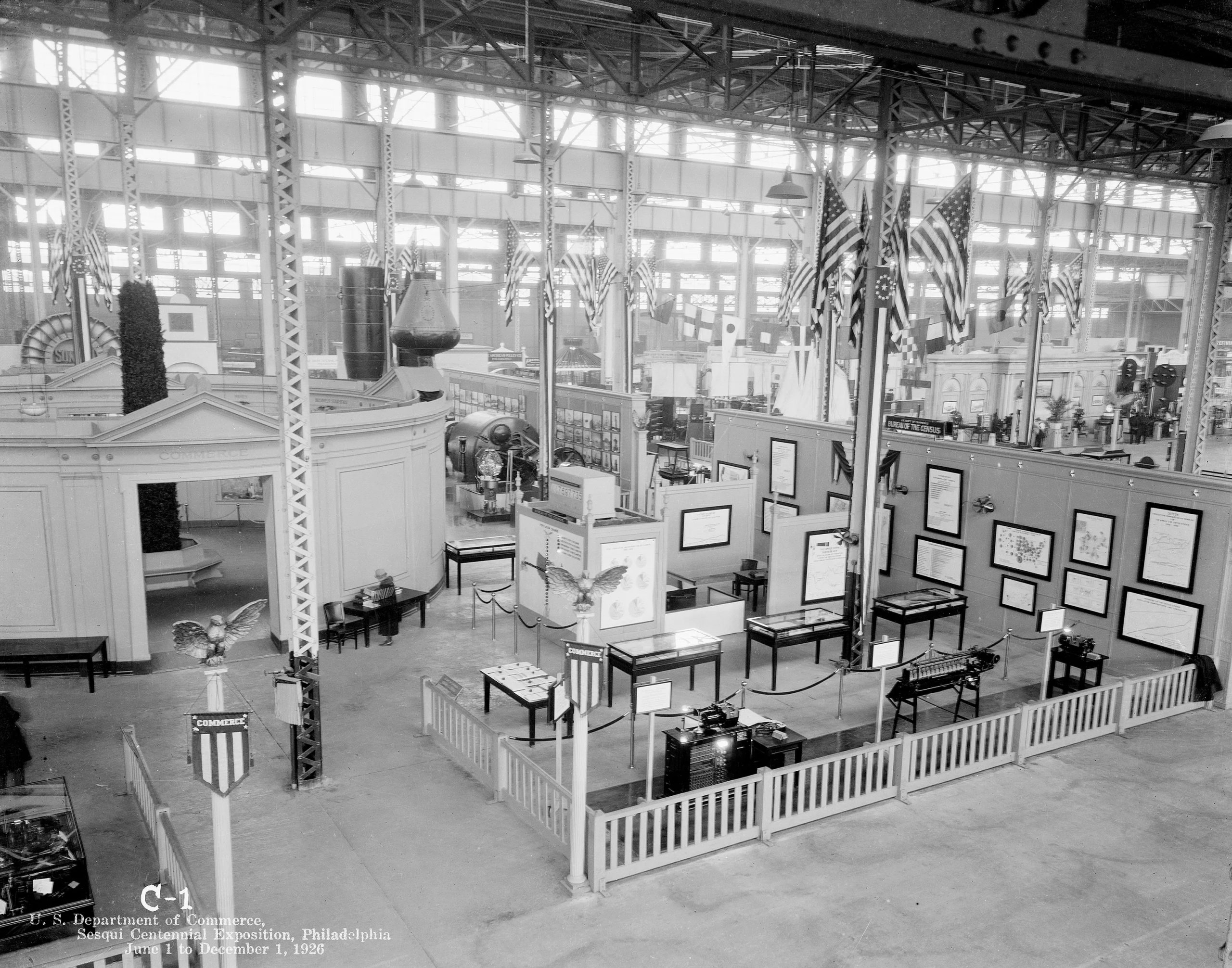
Exhibits
VA Research at 100: A Century of Medical Advancements
In 1925, 100 years ago, the Veterans Bureau initiated the first hospital-based medical research studies to address Veteran-specific issues like mental health, tuberculosis, cancer and toxic exposure. The program has since made significant medical breakthroughs and innovations, impacting the world.

Featured Stories
Happy Birthday America! How VA and Its Predecessors Celebrated the Nation’s Independence at 100, 150, and 200 years
In 2026, the United States will celebrate the 250th anniversary of its independence. While this will be the Department of Veterans Affairs’ first national centennial since becoming a cabinet-level department in 1989, its predecessor organizations, including the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers, the Pension Bureau, the Veterans Bureau, and the Veterans Administration, routinely participated in national centennial commemorations. Each served to honor the contributions of American Veterans in preserving freedom.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 89: VA Film “You Can Lick TB” (1949)
In 1949, VA produced a 19-minute film titled “You Can Lick TB.” The film follows a fictional conversation between a bedridden Veteran with tuberculosis and his VA doctor, dramatizing through brief vignettes the different stages of TB treatment and recovery.
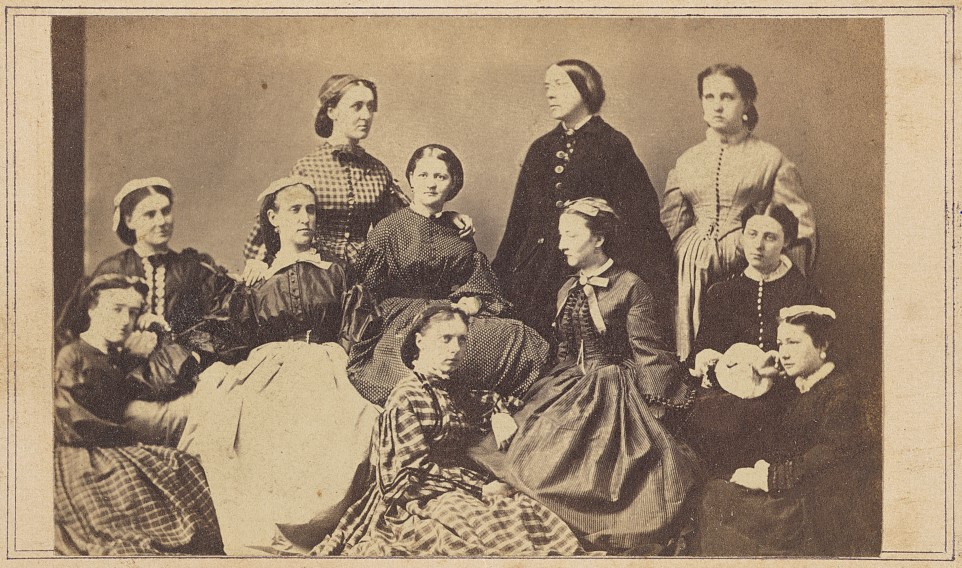

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 88: Civil War Nurses
During the Civil War, thousands of women served as nurses for the Union Army. Most had no prior medical training, but they volunteered out of a desire to support family members and other loved ones fighting in the war. Female nurses cared for soldiers in city infirmaries, on hospital ships, and even on the battlefield, enduring hardships and sometimes putting their own lives in danger to minister to the injured.
Despite the invaluable service they rendered, Union nurses received no federal benefits after the war. Women-led organizations such as the Woman’s Relief Corps spearheaded efforts to compensate former nurses for their service. In 1892, Congress finally acceded to their demands.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 87: Shoulder Patch For Veterans Administration Military Personnel in World War II
For a time during and after World War II, active duty military personnel were assigned to the Veterans Administration.
That assignment was represented by a blue circle with a golden phoenix rising from the ashes. This was the shoulder patch worn by the more than 1,000 physicians, dentists, and other medical professionals serving in the U.S. Army at VA medical centers.
This was the same patch worn by Gen. Omar Bradley during his time as VA administrator after the war concluded.

Featured Stories
The Historic Streets of the VA Medical Center in Prescott, Arizona
Ever wonder where some historic street names come from? That's the question that pops up at the VA Medical Center in Prescott, Arizona. Multiples names are displayed on white signs, such as Holmberg, Allee and Whipple. Who are they? Dive in and find out.



