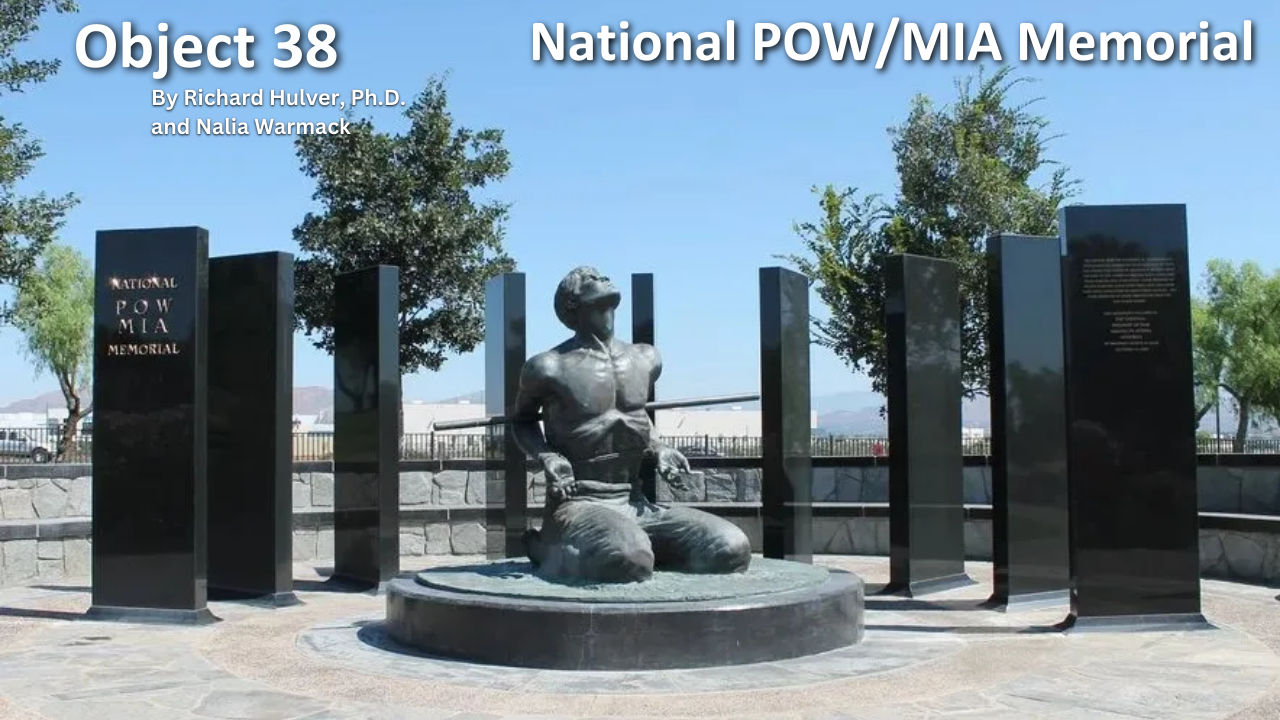
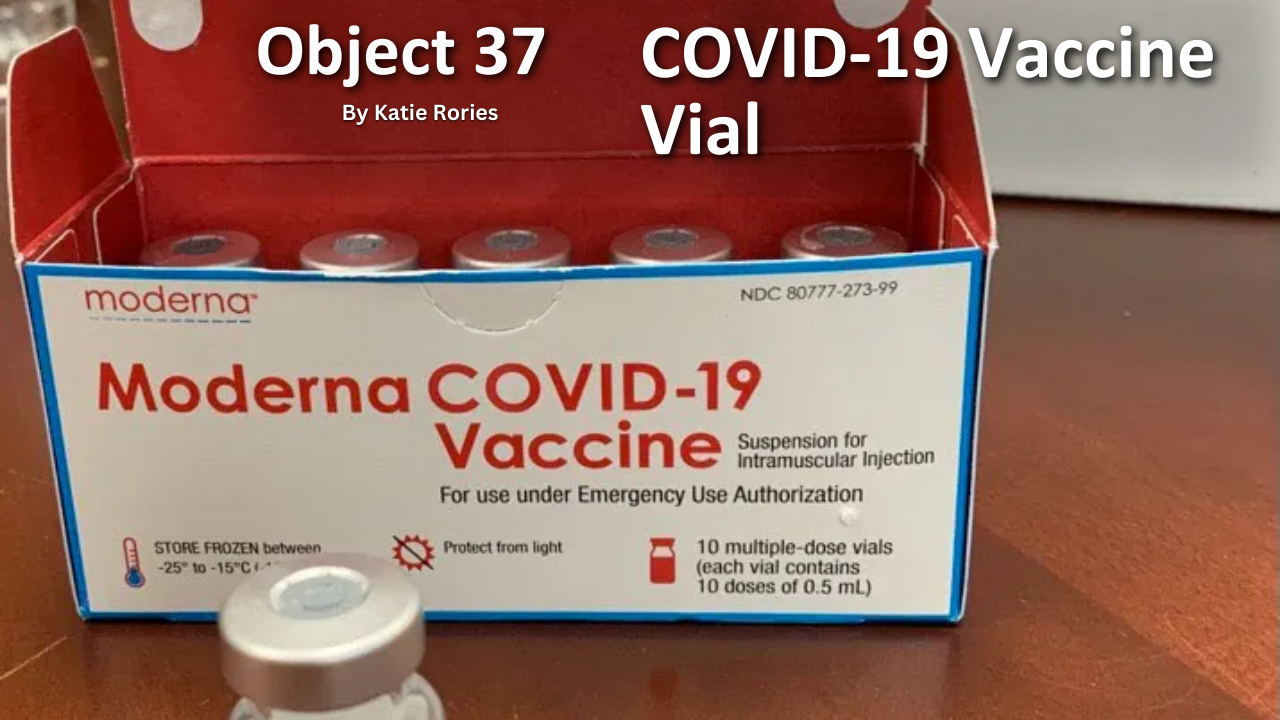
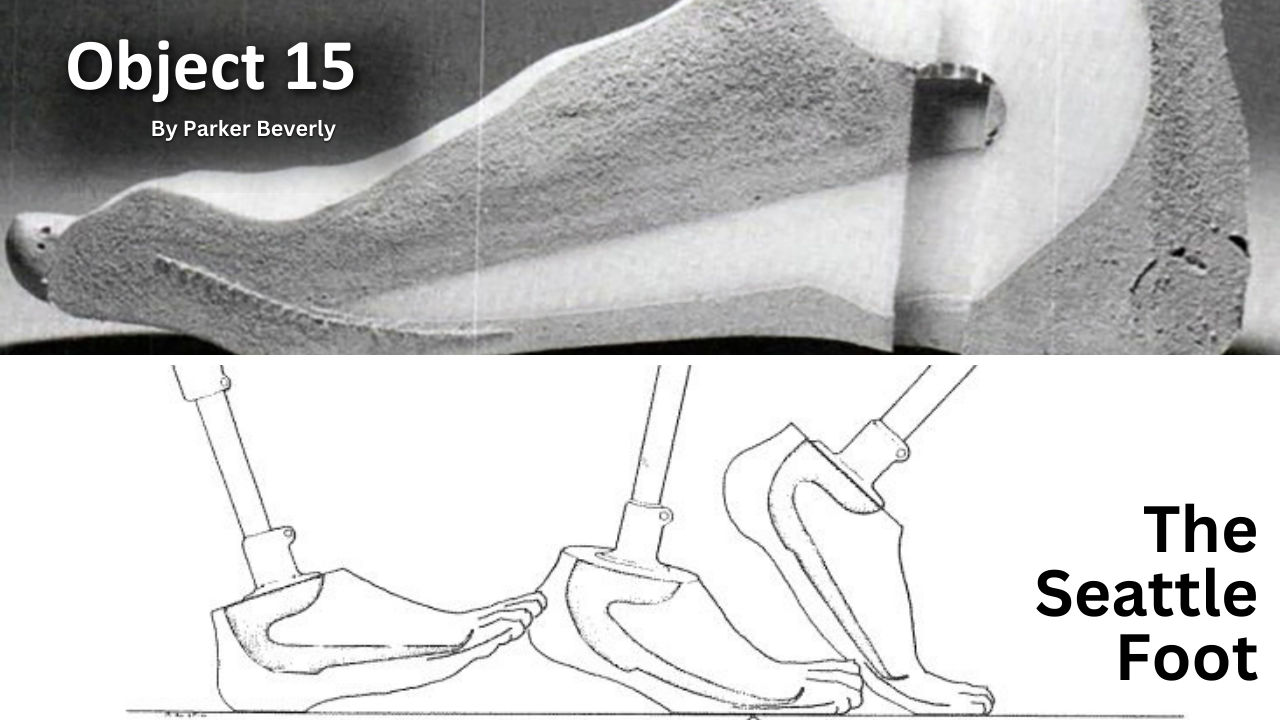
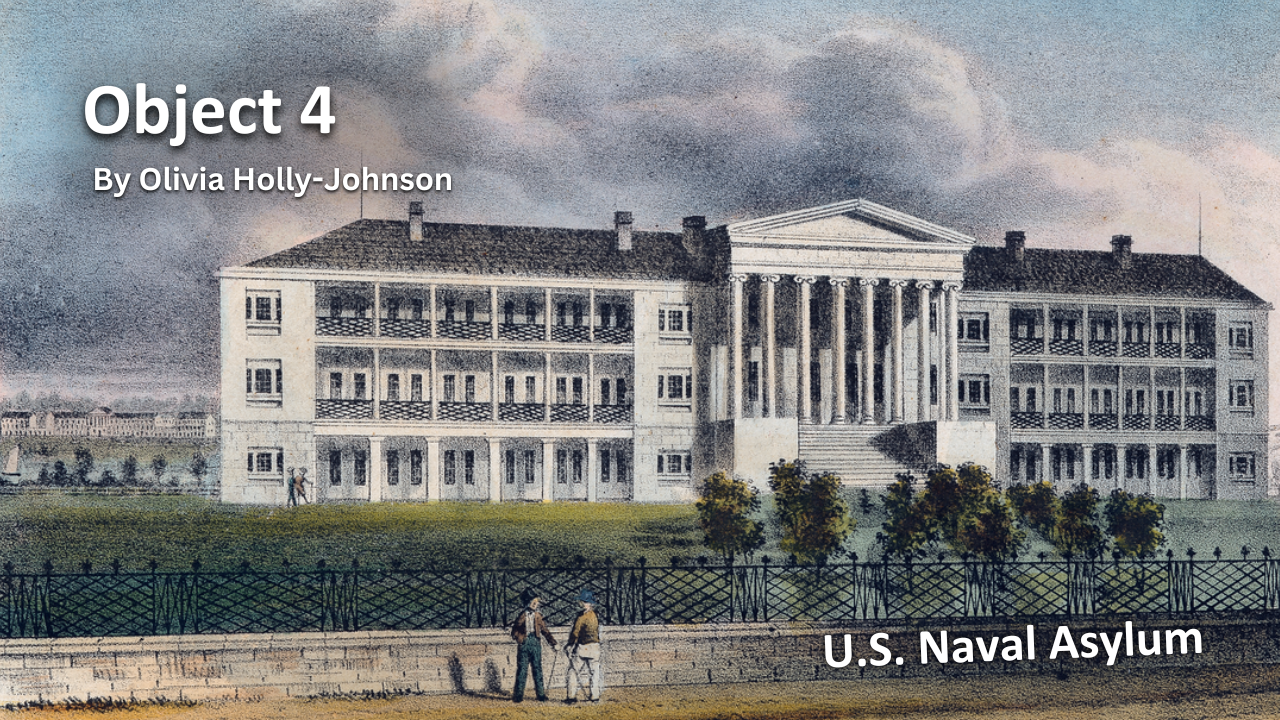
The History of VA in 100 Objects exhibit spotlights the objects that illuminate how the nation has honored and cared for Veterans from 1776 to the present. New entries are added every few weeks as we continue the countdown to the 100th Object. Join the journey through VA’s past, object by object.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 96: Postcard of Veterans Vocational School
In 1918, the government created the first nationwide vocational training system to help disabled Veterans acquire new occupational skills and find meaningful work. Over the next 10 years, more than 100,000 Veterans completed training programs in every field from agriculture and manufacturing to business and photography.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 95: 1840 Census of Pensioners
In a first, the 1840 census collected data on Veterans and widows receiving a pension from the federal government. The government published its findings in a stand-alone volume titled “A Census of Pensioners for Revolutionary or Military Services.”
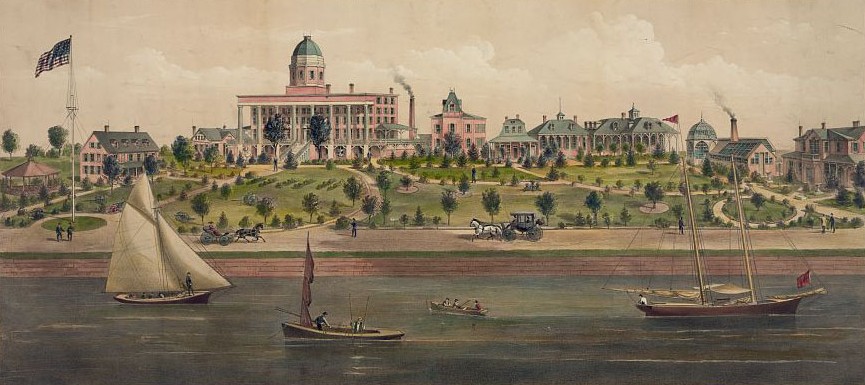
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 94: Southern Branch of the National Home
The Southern Branch of the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers opened in Hampton, Virginia, in late 1870. The circumstances surrounding the purchase of the property, however, prompted an investigation into the first president of the National Home’s Board of Managers, Benjamin Butler.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 93: Occupational Therapy Floor Loom
During World War I and afterwards, the United States committed to rehabilitating sick and wounded soldiers so they could resume productive lives in the civilian workforce. The emerging field of occupational therapy played a crucial role in the rehabilitative process.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 92: Pension Attorney Promotional Pamphlet
The expansion of the Civil War pension system was a cash windfall for pension attorneys. These lawyers used their legal know-how to help Veterans obtain benefits, but they were also accused of exploiting their clients and fleecing the government.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 91: Hines Scrapbook Dedication
In 1933, VA staff presented agency chief Frank Hines with a scrapbook commemorating his ten years of service to Veterans. Intended as a personal keepsake for Hines, the scrapbook also offers a snapshot of a particular time in VA history.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 90: Pearl Harbor Unknowns Marker
Seamen 1st Class Raymond Emory survived the attack on Pearl Harbor. Decades later, his research and advocacy led the government to add ship names to the markers of the Pearl Harbor unknowns interred in the National Cemetery of the Pacific.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 89: VA Film “You Can Lick TB” (1949)
In 1949, VA produced a 19-minute film titled “You Can Lick TB.” The film follows a fictional conversation between a bedridden Veteran with tuberculosis and his VA doctor, dramatizing through brief vignettes the different stages of TB treatment and recovery.
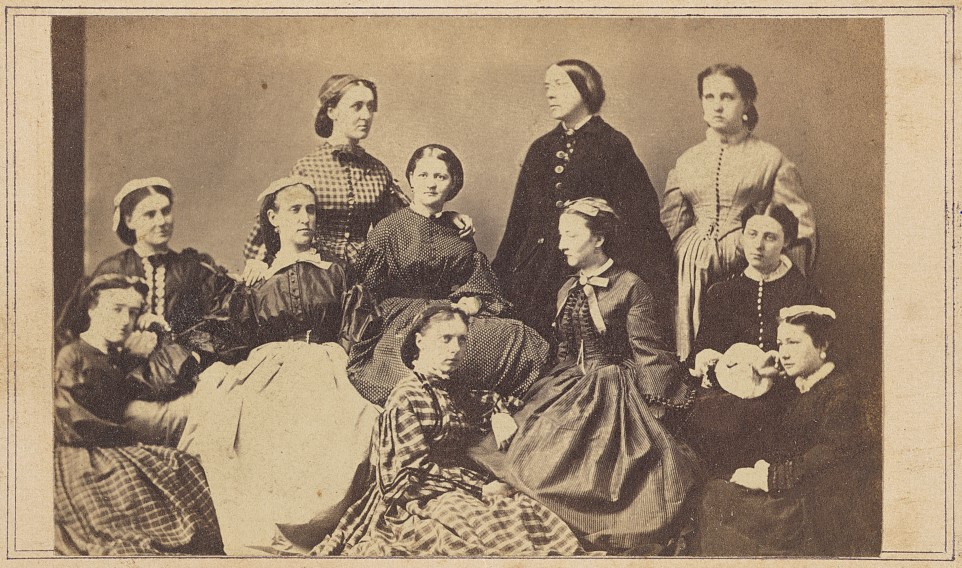

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 88: Civil War Nurses
During the Civil War, thousands of women served as nurses for the Union Army. Most had no prior medical training, but they volunteered out of a desire to support family members and other loved ones fighting in the war. Female nurses cared for soldiers in city infirmaries, on hospital ships, and even on the battlefield, enduring hardships and sometimes putting their own lives in danger to minister to the injured.
Despite the invaluable service they rendered, Union nurses received no federal benefits after the war. Women-led organizations such as the Woman’s Relief Corps spearheaded efforts to compensate former nurses for their service. In 1892, Congress finally acceded to their demands.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 87: Shoulder Patch For Veterans Administration Military Personnel in World War II
For a time during and after World War II, active duty military personnel were assigned to the Veterans Administration.
That assignment was represented by a blue circle with a golden phoenix rising from the ashes. This was the shoulder patch worn by the more than 1,000 physicians, dentists, and other medical professionals serving in the U.S. Army at VA medical centers.
This was the same patch worn by Gen. Omar Bradley during his time as VA administrator after the war concluded.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 86: The Roll of Honor
“The following pages are devoted to the memory of those heroes who have given up their lives upon the altar of their country, in defense of the American Union.”
So opened the preface to the first volume of the Roll of Honor, a compendium of over 300,000 Federal soldiers who died during the Civil War and were interred in national and other cemeteries. The genesis of this 27-volume collection published between 1865 and 1871 can be traced to Quartermaster General Montgomery C. Meigs and the department he oversaw for a remarkable 21 years from 1861 to 1882.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 85: Congressman Claypool’s “$1 Per Day Pension” Ribbon
Founded in 1866 as fraternal organization for Union Veterans, the Grand Army of the Republic (GAR) embraced a new mission in the 1880s: political activism. The GAR formed a pension committee in 1881 for the express purpose of lobbying Congress for more generous pension benefits.
An artifact from the political wrangling over pensions is now part of the permanent collection of the National VA History Center in Dayton, Ohio. The item is a small pension ribbon displaying the message: “I endorse the $1 per day pension as recommended by the Departments of Ohio and Indiana G.A.R.” The button attached to the ribbon features two American flags and the phrase “saved by the boys of ’61-65.” The back of the ribbon bears the signature of Horatio C. Claypool, a Democratic judge who ran for the seat in Ohio’s eleventh Congressional district in the 1910 mid-term elections.
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 84: Gettysburg Address Tablet
President Abraham Lincoln is one of the most revered figures in American history. Rankings of U.S. presidents routinely place him at or near the top of the list. Lincoln is also held in high esteem at VA. His stirring call during his second inaugural address in 1865 to “care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan” embodies the nation’s promise to all who wear the uniform, a promise VA and its predecessor administrations have kept ever since the Civil War.
Ever since Lincoln first uttered those memorable words in November 1863, the Gettysburg Address has been linked to our national cemeteries. In 1908, Congress approved a plan to produce a standard Gettysburg Address tablet to be installed in all national cemeteries in time for the centennial of President Lincoln’s birth on February 12, 1909.
History of VA in 100 Objects
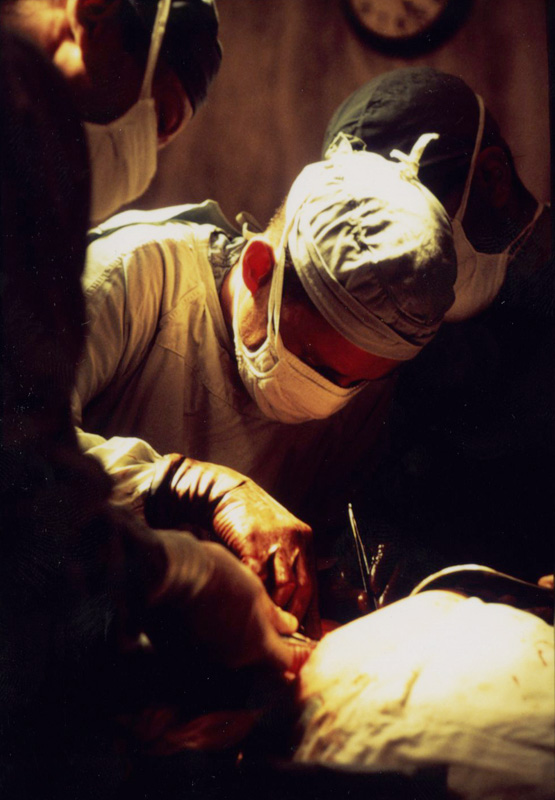
Object 83: First Liver Transplantation at VA Hospital
Prior to the 1960s, liver failure always ended in death. In May 1963, however, Dr. Thomas E. Starzl made medical history at the VA hospital in Denver, Colorado, when he performed the first liver transplantation on a patient who survived the operation.
Starzl's continued to refine his procedure, becoming a leading expert on liver transplants. The success rate for early transplants wasn't optimal, but that didn't stop him from researching new techniques and post-care practices. These innovations, coupled with new medications, improved the effectiveness and life-saving measures of that vital transplant surgery.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 81: World War I Insurance Certificate
An effort to remake the Veteran benefits system during World War I led to the 1917 War Risk Insurance Act that provided insurance benefits to Veterans well beyond their act of service was completed. A $10,000 policy could furnish the beneficiary a monthly income of over $57 in the early 20th Century.
It was a popular benefit, with 4 million applications before the end of the war. This program greatly impacted VA's future insurance efforts.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 80: LUKE/DEKA Prosthetic Arm
In the 19th century, the federal government left the manufacture and distribution of prosthetic limbs for disabled Veterans to private enterprise. The experience of fighting two world wars in the first half of the 20th century led to a reversal in this policy.
In the interwar era, first the Veterans Bureau and then the Veterans Administration assumed responsibility for providing replacement limbs and medical care to Veterans.
In recent decades, another federal agency, the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA), has joined VA as a supporter of cutting-edge research into artificial limb technology. DARPA’s efforts were spurred by the spike in traumatic injuries resulting from the emergence of improvised explosive devices as the insurgent’s weapon of choice in Iraq in 2003-04.
Out of that effort came the LUKE/DEKA prosthetic limb, named after the main character from "Star Wars."

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 79: VA Study of Former Prisoners of War
American prisoners of war from World War II, Korea, and Vietnam faced starvation, torture, forced labor, and other abuses at the hands of their captors. For those that returned home, their experiences in captivity often had long-lasting impacts on their physical and mental health. Over the decades, the U.S. government sought to address their specific needs through legislation conferring special benefits on former prisoners of war.
In 1978, five years after the United States withdrew the last of its combat troops from South Vietnam, Congress mandated VA carry out a thorough study of the disability and medical needs of former prisoners of war. In consultation with the Secretary of Defense, VA completed the study in 14 months and published its findings in early 1980. Like previous investigations in the 1950s, the study confirmed that former prisoners of war had higher rates of service-connected disabilities.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 78: French Cross at Cypress Hills National Cemetery in Brooklyn
In the waning days of World War I, French sailors from three visiting allied warships marched through New York in a Liberty Loan Parade. The timing was unfortunate as the second wave of the influenza pandemic was spreading in the U.S. By January, 25 of French sailors died from the virus.
These men were later buried at the Cypress Hills National Cemetery and later a 12-foot granite cross monument, the French Cross, was dedicated in 1920 on Armistice Day. This event later influenced changes to burial laws that opened up availability of allied service members and U.S. citizens who served in foreign armies in the war against Germany and Austrian empires.
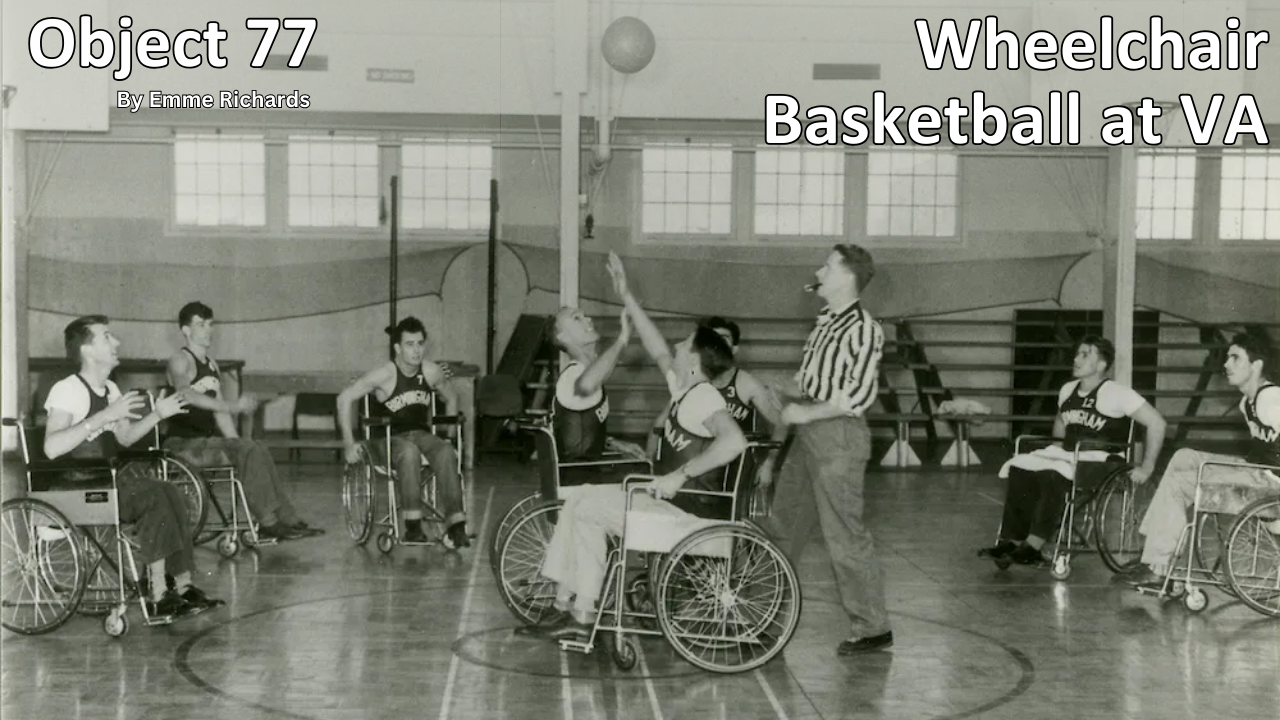
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 77: Wheelchair Basketball at VA
Basketball is one of the most popular sports in the nation. However, for paraplegic Veterans after World War II it was impossible with the current equipment and wheelchairs at the time. While VA offered these Veterans a healthy dose of physical and occupational therapy as well as vocational training, patients craved something more. They wanted to return to the sports, like basketball, that they had grown up playing. Their wheelchairs, which were incredibly bulky and commonly weighed over 100 pounds limited play.
However, the revolutionary wheelchair design created in the late 1930s solved that problem. Their chairs featured lightweight aircraft tubing, rear wheels that were easy to propel, and front casters for pivoting. Weighing in at around 45 pounds, the sleek wheelchairs were ideal for sports, especially basketball with its smooth and flat playing surface. The mobility of paraplegic Veterans drastically increased as they mastered the use of the chair, and they soon began to roll themselves into VA hospital gyms to shoot baskets and play pickup games.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 76: Senate Speech Proposing First Presumptive Conditions For Great War Veterans
After World War I, claims for disability from discharged soldiers poured into the offices of the Bureau of War Risk Insurance, the federal agency responsible for evaluating them. By mid-1921, the bureau had awarded some amount of compensation to 337,000 Veterans. But another 258,000 had been denied benefits. Some of the men turned away were suffering from tuberculosis or neuropsychiatric disorders. These Veterans were often rebuffed not because bureau officials doubted the validity or seriousness of their ailments, but for a different reason: they could not prove their conditions were service connected.
Due to the delayed nature of the diseases, which could appear after service was completed, Massachusetts Senator David Walsh and VSOs pursued legislation to assist Veterans with their claims. Eventually this led to the first presumptive conditions for Veteran benefits.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 75: “Bivouac of the Dead” Tablet
The mounted plaque stands in front of the headstones at Mobile National Cemetery in Alabama. The dark, cast-aluminum tablet draws a stark contrast to the sea of pearly marble beyond. Across its face in white lettering runs the sorrowful first stanza of Theodore O’Hara’ elegiac poem, “Bivouac of the Dead,” beginning with the verse “The muffled drum’s sad roll has beat / The Soldier’s last tattoo; / No more on life's parade shall meet / That brave and fallen few.” Tablets bearing passages from O’Hara’s poem can be found in dozens of VA national cemeteries across the country. Originally written to honor the Kentucky volunteers who died in the Mexican War (1846-48), the poem now serves as a literary memorial to all lives lost in service to the nation.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 74: Photo Spread on Veterans Canteen Service
When U.S. Army General Omar N. Bradley became head of VA at the end of World War II, he was determined to improve the quality of care across the agency’s hospital system. His commitment to providing better patient services extended to the stores and canteen service found in VA hospitals. Veterans and advocacy organizations complained that the concessions operated by third-party vendors often charged inflated prices and delivered substandard services.
After VA conducted an internal investigation that validated Veterans’ concerns, Bradley took the issue to Congress. His desire to find a better solution for Veterans led to the establishment of the Veterans Canteen Service.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 73: Presidential Memorial Certificate
Just after New Year’s Day in 1962, World War II Army Veteran Benjamin B. Belfer sent a letter to his U.S. Senator, Hubert Humphrey of Minnesota, suggesting a simple yet powerful way for the government to honor deceased service members. The tradition was for family members to receive the folded American flag that had been draped over the Veteran’s casket during the funeral service. Belfer proposed presenting the next of kin with a memorial certificate signed by the president of the United States in addition to the burial flag. The certificate, he wrote, would be “a keepsake that will never be forgotten by the family and relatives and friends of the departed Veteran.”
After receiving Belfer’s letter Humphrey wasted no time in sharing his idea with the head of the Veterans Administration, John S. Gleason, Jr. Gleason also saw the value in the proposal and in mid-February his staff worked on creating a design for the certificate and wording. On March 6, the certificate was shown to President John F. Kennedy, Jr.. The following day, Kennedy sent Gleason a short note expressing his wholehearted approval. “I think it is an excellent idea, and I believe that the certificate is tastefully and appropriately done,” he wrote, adding that the issuing of certificates should begin “as quickly as possible.”

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 72: Central Blind Rehabilitation Center’s First Chief Welcomes First Trainee
On July 4, 1948, the Central Blind Rehabilitation Center at the Edward Hines, Jr., VA Hospital in Illinois admitted its first trainee. The Hines Center ushered in a new era of care for blinded Veterans. Yet, its opening was nearly three decades in the making.
Formalized federal care for blinded Veterans dates back to 1917, with the opening of Army General Hospital #7. Later the need to provide rehabilitative services to vision-impaired Veterans returned after World War II.
In 1948, VA opened the Central Blind Rehabilitation Center at the Hines VA Hospital outside of Chicago, Illinois. It's location was chosen because of the large Medical Rehabilitation department already in place was well-suited to provide oversight.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 71: Dade Pyramids And Monument
On the south side of Florida’s St. Augustine National Cemetery, three squat pyramids and a single taller obelisk rise from the ground above the other nearby markers and headstones. The Dade Pyramids and Monument, as they are known, mark the resting place of the U.S. soldiers who died in the opening engagement of the Second Seminole War (1835-42). The memorial honors lives lost while also serving as a grim reminder of the brutal conflict that erupted when the Federal government tried to evict the Seminole people from their tribal lands in Florida.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 70: VA Director Max Cleland at The 1980 Opening of The Atlanta Vet Center
After the Vietnam War, the nation was eager to put the divisive and unpopular conflict behind it. However, the 3.4 million Veterans who served in the Vietnam theater did not have that luxury. One of those Veterans was Max Cleland who lost his legs in the war. He made it a mission to advocate for his fellow Veterans, who struggled with the aftereffects of the war. Eventually, this led to Cleland turning to politics and at 34 being appointed as the youngest Administrator for the Veterans Administration.
During his tenure at VA, Cleland delivered on his goal of providing readily accessible mental health and readjustment counseling designed expressly for Vietnam Veterans. In 1979, VA launched an initiative called Operation Outreach to establish community-based Vet Centers across the country. In one year there were 91 Vet Centers. Today there are over 300.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 69: Stereograph of Landscaped Grounds at Dayton National Home
The federal government in the Civil War arranged to care for returning soldiers too weakened by their wounds, the lingering effects of disease, or the hardships of military life. In the decades after the war, the government established the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers.
The Board of Managers for the National Home added such amenities as chapels, libraries, theaters, and playing fields. Great care also went into the shaping of the physical environment. The board employed landscaping architects to design the grounds of each branch to create an attractive, idyllic setting for residents and visitors alike. Influenced by the picturesque landscape movement, they adorned the National Home campuses with man-made ponds and lakes, ornate flower gardens, elaborate plantings of shrubs and trees, winding trails, and other features to beautify the properties.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 68: Miller Cottage
At the VA Medical Center in Dayton, Ohio, Miller Cottage stands as a mostly forgotten reminder of women’s fight for inclusion in the benefits and health care system for Veterans. This long, multi-story brick building with a white-columned portico originated as a barracks built specifically to house female Veterans on the grounds of what was then called the Central Branch of the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers (NHDVS). The establishment of the residence represented a rare victory for the female Veterans of the First World War in their quest to obtain government support for all uniformed women who served and sacrificed during that conflict.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 67: USS Bennington Monument And Grave Plot
On July 21, 1905, one of the USS Bennington's boilers exploded, killing 49 sailors. Almost immediately after the accident, surviving crew and fellow sailors donated funds to build a monument at the grave site for their fallen comrades. This burial ground would later become Fort Rosecrans National Cemetery.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 66: Frank Lloyd Wright House for Disabled World War II Veteran
When the GI Bill became law in 1944, it included a home loan program for Veterans. After several changes to update the law to reflect current market prices and challenges, one area still needed addressed: support for Veterans who were dependent on wheelchairs for mobility. The answer was the Specially Adapted Housing program, and one of the earliest homes built with the grant money was designed by acclaimed builder Frank Lloyd Wright.

History of VA in 100 Objects
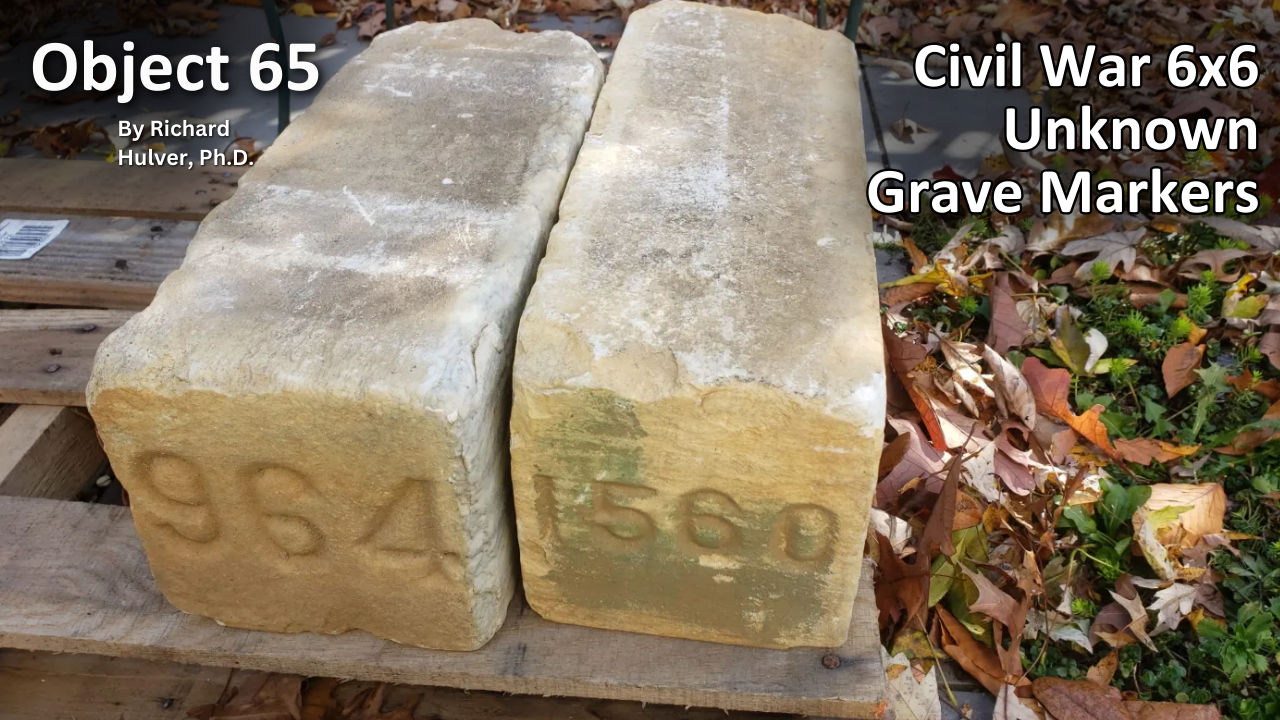
Object 65: Civil War 6×6 Unknown Grave Markers
Graves of unknown soldiers in the national cemeteries are commonplace and marked in many different ways. While the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in the Army’s Arlington National Cemetery is the most culturally recognizable unknown grave, VA national cemeteries also have less grand examples of unknown burials that span the early 19th century through the Korean War. The most common form of unknown marker, however, is the simple 6x6-inch stone that adorns the graves of thousands of Civil War soldiers.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 64: U.S. Public Health Service Hospital #50
U.S. participation in the First World War produced a shift away from relying on long-term institutional care for Veterans in need to a model of Veteran welfare centered around short-term hospitalization. During the war, the War Department assumed responsibility for tending to the sick and wounded. Afterwards, when the Army dismantled its hospital system, the U.S. Public Health Service (PHS) stepped in to fill the breach, acquiring numerous facilities the Army and Navy no longer wanted as well as other properties that could be used for medical purposes.
History of VA in 100 Objects
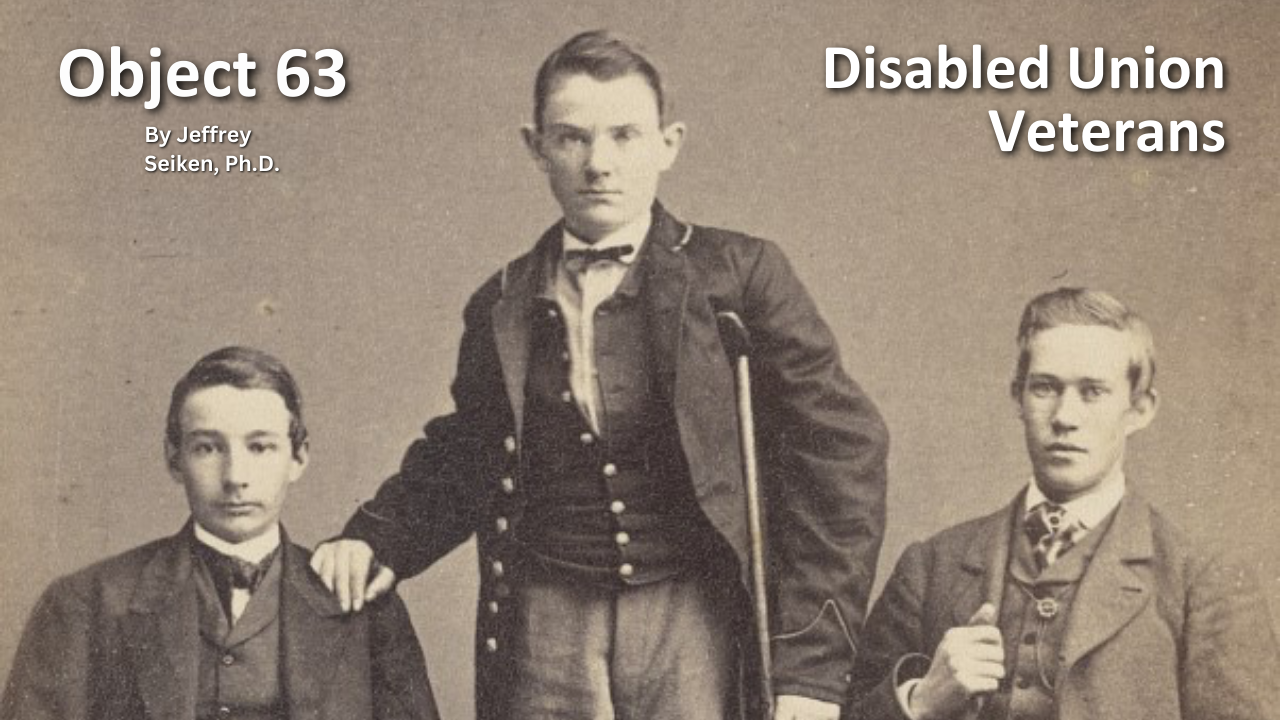
Object 63: Disabled Union Veterans
The North’s victory in the Civil War came at an enormous cost to the more than two million men who fought for the Union cause. Over 350,000 lost their lives due to battle or disease. Almost as many were wounded in action. According to Northern medical records, Union surgeons performed just under 30,000 amputations during the war. For these disabled Union Veterans, Congress made provisions to provide monetary compensation. In July 1861, lawmakers hastily passed a law for Union recruits making them eligible for the same pension allowances as soldiers in the Regular Army. Later in 1862, for the first time, a pension law explicitly granted benefits not just for men wounded in battle but also to those suffering from “disease contracted while in the service of the United States.”

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 62: 1956 “Clues to Suicide” Study
While suicide takes a toll on lives in every segment of society, Veterans in the post 9-11 era have statistically been more at risk than adults in the general population. VA’s efforts to combat the scourge of Veteran suicide owe a significant debt to the foundational research studies conducted by two VA psychologists in the 1950s. The work of Drs. Edwin S. Shneidman and Norman J. Farberow led to some of the earliest crisis intervention programs at VA and elsewhere and the establishment of the nation’s first dedicated Suicide Prevention Center in Los Angeles, California.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 61: Edmund Whitman’s 1869 Report on Reburying Union Dead in National Cemeteries
The U.S. Army’s plan for the recovery of Union dead across the South after the Civil War came about through the labors of a remarkable if little known officer, Edmund Whitman. He spent four years overseeing the collection of thousands of remains and creating “mortuary records” of reburials in new national cemeteries. After completing his “Harvest of Death,” to use his phrase, he produced in 1869 an extraordinary report that recounted the breadth, sequence, and challenges of his reinternment mission.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 60: VA Medal of Honor Recipients Wall Display
The Congressional Medal of Honor is the nation’s highest decoration for valor in the military. More than 1,000 have been awarded, and 98 of those recipients worked at VA. A wall display outside VA's Under Secretary for Benefits in Washington, D.C. pays tribute to each of those individuals, whose stories are tied to the legacy of Veterans serving Veterans.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 59: The Veterans Legacy Memorial
In 2019, VA’s National Cemetery Administration (NCA) launched the Veterans Legacy Memorial (VLM), an innovative, interactive web site with memorial pages for more than 4.5 million Veterans. VLM utilizes the millions of records contained within NCA’s Burial Operations Support System database. Each Veteran’s memorial page is populated with information about his or her military service and place of burial.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 58: Congressional Cemetery Cenotaphs
Congressional Cemetery occupies 35 acres of land in the southeast section of Washington, DC, and has served as the final resting place for scores of elected officials and notable Washingtonians. The more than 60,000 gravesites include 806 maintained by VA. Some 168 of the VA sites are adorned with one of the most distinctive markers to be found in the cemetery—the iconic cenotaphs designed by Benjamin H. Latrobe, the nation’s first professional architect.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 57: Omaha VA Hospital Nuclear Reactor
In August 1945, the United States detonated atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, ending World War II and ushering in the dawn of the Atomic Age. Two years later, the Veterans Administrations started harnessing this technology for a very different purpose—to conduct medical research by installing a small nuclear reactor at the VA hospital in Omaha, Nebraska.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 56: Life Magazine Story on The WAACs
The creation of the Women's Army Auxiliary Corps in 1942 allowed women for the first time to serve with the Army in non-nursing roles. Life Magazine reported on the first group of WAAC officer candidates and auxiliaries going through training in a lengthy photo essay that highlighted the women's professionalism and patriotism.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 55: Dorothea Dix’s Monument to Union Soldiers
On May 12, 1868, Dorothea L. Dix at last had the satisfaction of transferring to the Army ownership of the monument she helped finance and shepherd to completion. Dedicated to “Union Soldiers who perished in the War of the Rebellion,” Dorothea Dix's monument was a 65-foot-tall granite obelisk erected in Hampton National Cemetery in Virginia near the large Civil War hospital at Fort Monroe.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 53: Funeral Ceremony For Vietnam Unknown
After a 26 year journey from the Vietnam Unknown memorial to St. Louis, Missouri, a casket containing the remains of 1st Lt. Michael Blassie was interred in Jefferson Barracks National Cemetery in his hometown on July 11, 1998.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 52: Native American Recruits
At the start of the Great War in 1914, only about half of the 300,000 Native Americans in the United States were citizens. Although the Fourteenth Amendment granted citizenship to all “persons born or naturalized in the United States,” it did not apply to Native Americans because they fell under the jurisdiction of tribal authorities rather than the U.S. government

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 51: VA Telehealth Cart
Long before high-speed internet networks made it fast and easy to transfer information, access services, and communicate with others the world over, VA had experimented with ways to deliver health care at a distance, such as with telehealth carts.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 50: Commissioner of Pensions Annual Report
In 1832, the federal government found itself with a pension problem largely of its own making. In June, Congress passed a law granting a pension to all surviving Revolutionary War Veterans who had served for at least six months, but the increased applications overwhelmed the staff handling claims. A Commissioner of Pensions was then appointed to address the issues.
History of VA in 100 Objects
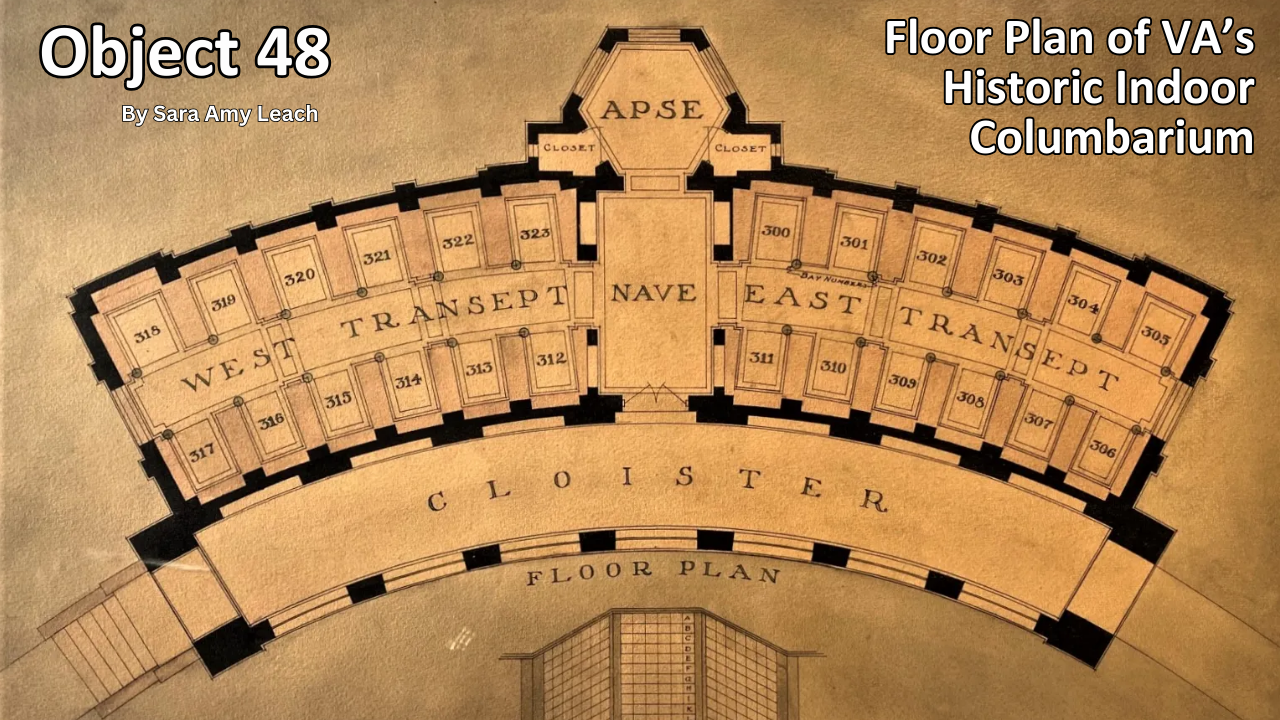
Object 48: Floor Plan of VA’s Historic Indoor Columbarium
In June 1941, Charles Ray Smith—aviation mechanic, Army Veteran, and past commander of the American Legion post in Gridley, California—died suddenly after a surgical procedure at age 52. His brothers and young son had the body cremated at the new columbarium at what is now Los Angeles National Cemetery.

History of VA in 100 Objects
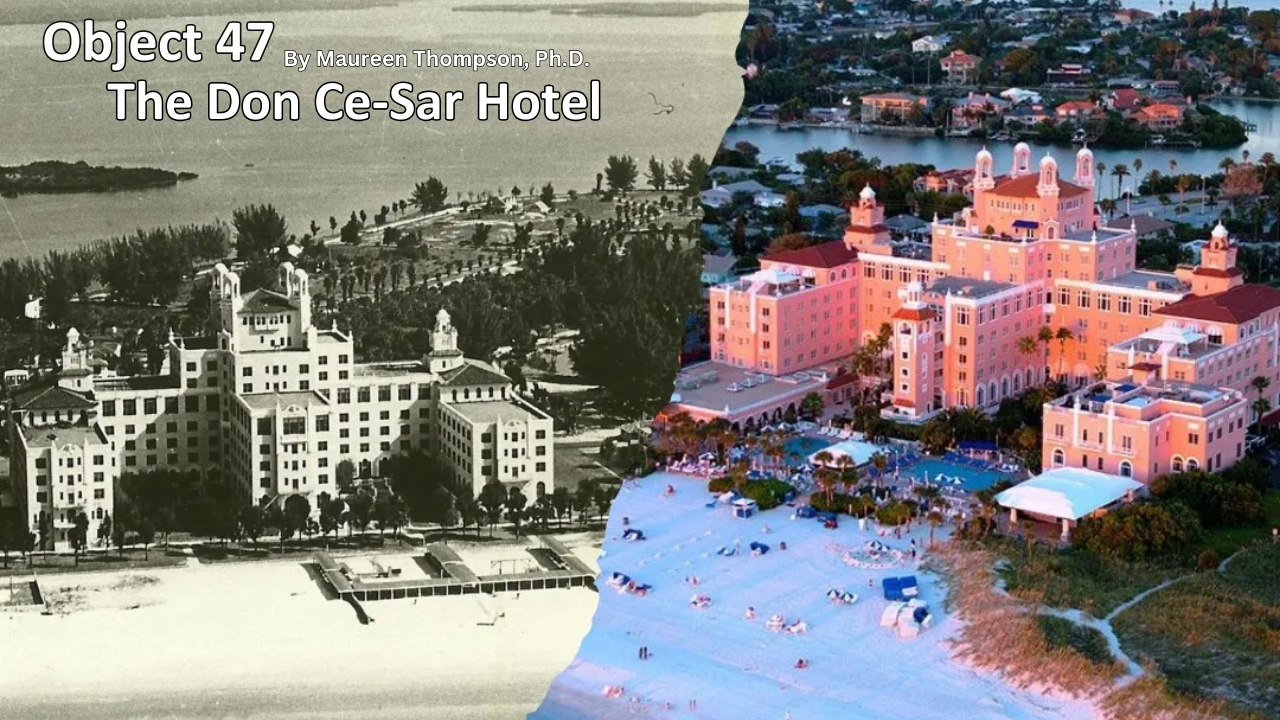
Object 47: The Don Ce-Sar Hotel
The Don Ce-Sar Hotel has graced the Gulf of Mexico beachfront in St. Petersburg, Florida, for almost a century. Known as the Pink Palace for its rosy hue and castle-like appearance, the property was a playground for the rich and famous during its heyday in the 1930s.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 46: Harry Colmery’s Handwritten Draft of GI Bill
The massive mobilization of industry and manpower with the United States’ entry into World War II lifted the nation out of the Great Depression. But even as the country enjoyed new heights of economic prosperity, American leaders worried about what would happen after the war. In 1942, Roosevelt formed two separate committees to focus specifically on programs to assist returning Veterans and one produced the GI Bill of Rights.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 45: National Cemetery Superintendent’s Disability Certificate
The 1867 “Act to establish and to protect National Cemeteries” directed the Secretary of War to appoint a superintendent for each cemetery who was to reside in a lodge at the main entrance of the property. The superintendent’s principal duties involved greeting visitors, answering their questions, and taking care of the grounds. The Army provided superintendents with printed disability certificates affirming that the recipient had “been found a meritorious and trustworthy person, disabled in the service of the United States.”

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 44: Bureau of War Risk Insurance Occupation of Smithsonian Museum
When World War I erupted in Europe in August 1914, the United States stayed neutral but the nation quickly became a major supplier of industrial and agricultural goods to France and England. To protect this valuable trade, Congress established the Bureau of War Risk Insurance (BWRI) within the Treasury Department to insure American ships and cargo “against loss or damage by the risks of war.”
History of VA in 100 Objects
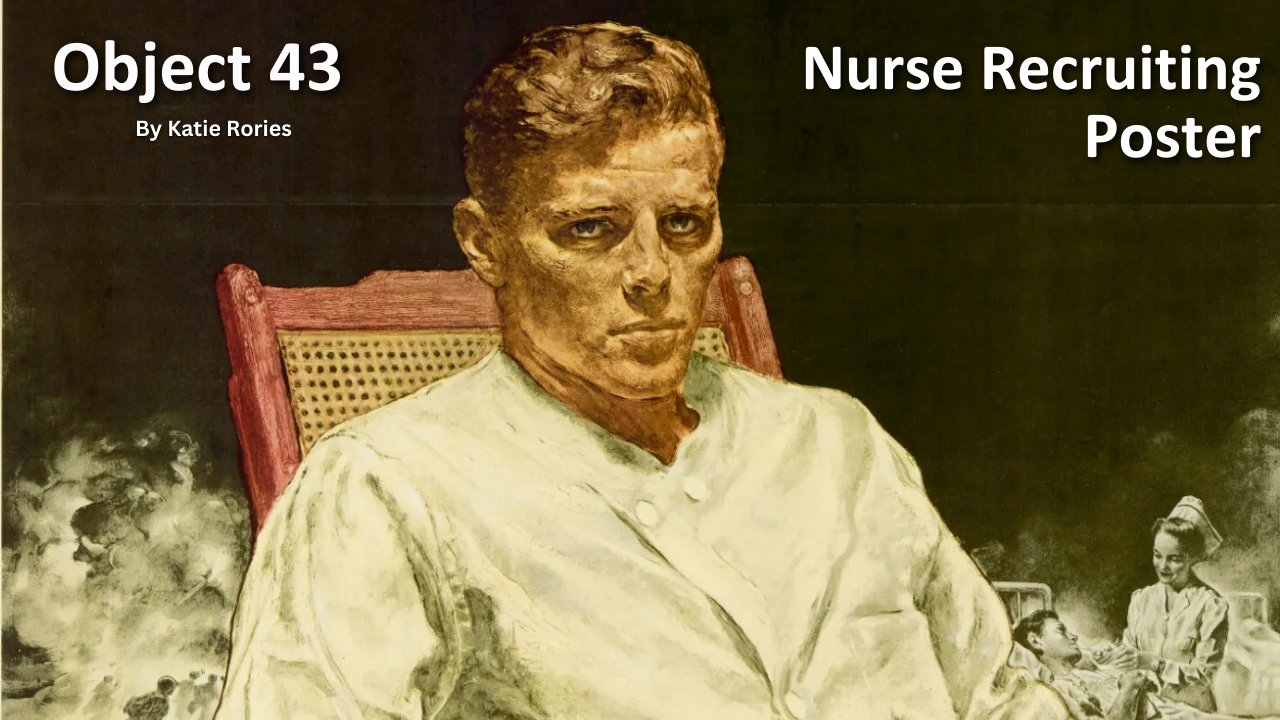
Object 43: Nurse Recruiting Poster
After World War II, the Veterans Administration faced a dire shortage of nurses. During the war, thousands of nurses and doctors left their positions in VA hospitals to join the armed forces. In early 1944 VA Administrator General Frank T. Hines reported a shortfall of roughly 1,000 nurses in 88 of the VA’s 94 hospitals.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 42: Pension Bureau Special Examiners
The pension system expanded enormously after the Civil War. The number of Union Veterans, widows, and dependents drawing a pension from the federal government rose from 15,000 in 1863 to over 200,000 in 1871. The soaring size and costs of the pension system raised concerns about the prevalence of fraud, which the Pension Bureau aimed to stop with special examiners.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 41: Creating the Department of Veterans Affairs
On November 10, 1987, President Ronald W. Reagan declared he would support legislation elevating the Veterans Administration to a cabinet department, creating the Department of Veterans Affairs. The news caught his advisors off-guard.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 40: Dayton’s Tunnel – “Underground Path of Death”
The Civil War Veterans who resided in the barracks or entered the hospital at the Central Branch of the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers (NHDVS) in Dayton, Ohio, knew that the home cemetery was most likely going to be their final resting place. a Veteran’s last journey, reported the Cincinnati Enquirer, followed a literal “underground path of death." Dayton's Tunnel terminated at a gated portal on the edge of what is now Dayton National Cemetery.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 39: “Here’s To Veterans” Vinyl Records
As World War II ended and millions of service members returned home, the Veterans Administration faced the major challenge of not just delivering benefits and medical care, but also ensuring broad public awareness of these programs. The VA Public Relations office in Washington took on that challenge. And, so, Here’s To Veterans was born.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 36: President Clinton’s Fiftieth Anniversary of V-J Day Speech at The National Memorial Cemetery of The Pacific
The scarcity of presidential appearances at VA cemeteries makes President Clinton’s speech at the National Memorial Cemetery of the Pacific, more popularly known as the Punchbowl, on September 2, 1995, particularly noteworthy.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 34: President Zachary Taylor’s Well-Traveled Remains
Three burial vaults, two funeral processions a thousand miles apart, and a daytrip to quash an assertion of foul play–the remains of Zachary Taylor, the only U.S. president laid to rest in a VA national cemetery, have taken an especially tortuous path to their resting place in Louisville, Kentucky.
History of VA in 100 Objects
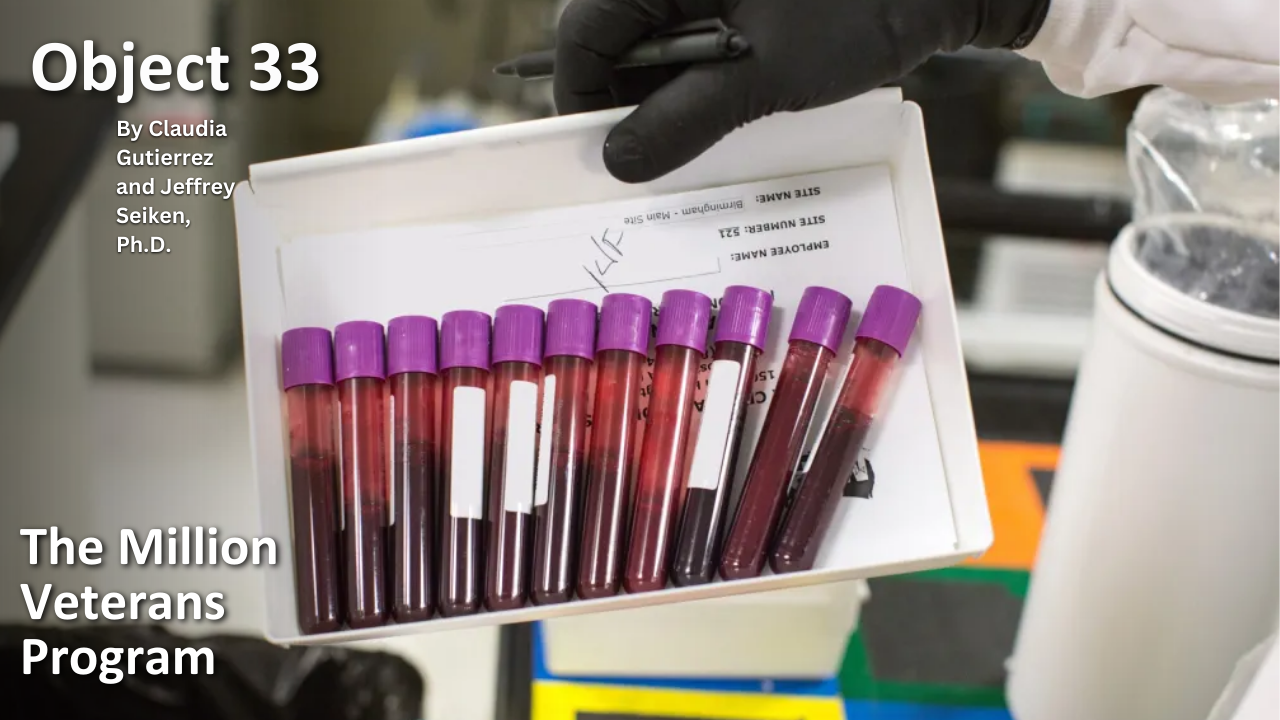
Object 33: The Million Veteran Program
In May 2009, twelve VA doctors and scientists gathered in a small conference room in Rockville, Maryland, to brainstorm about the design of VA’s first-ever large-scale genetic research program, the Million Veteran Program. They wanted to collect medical information from Veterans along with blood samples to extract DNA, with the goal of creating a genomic biobank or database for researchers to explore how genes affect health and disease

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 32: U.S. Colored Troops Burial Petition
Just after Christmas in 1864, African American soldiers recuperating at the United States Colored Troops (USCT) L ‘Overture General Hospital in Alexandria, Virginia, submitted a petition for the right to burial alongside their White counterparts in the city’s Soldiers' Cemetery, one of the first national cemeteries established by the U.S. government during the Civil War.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 30: President Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address
On March 4, 1865, as the Civil War entered its final weeks, President Abraham Lincoln second inaugural address was delivered from the East Portico of the U.S. Capitol. Four years earlier, he had stood in the same spot when he spoke to the crowd that had assembled for his swearing in as the sixteenth President of the United States.
This time, his speech focused on the task ahead for the country, a stirring call for healing and reconciliation. A significant section of his speech was a solemn promise to those who had fought to restore the Union: "...let us strive on to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation’s wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle, and for his widow, and his orphan—to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and a lasting peace, among ourselves, and with all nations."

History of VA in 100 Objects
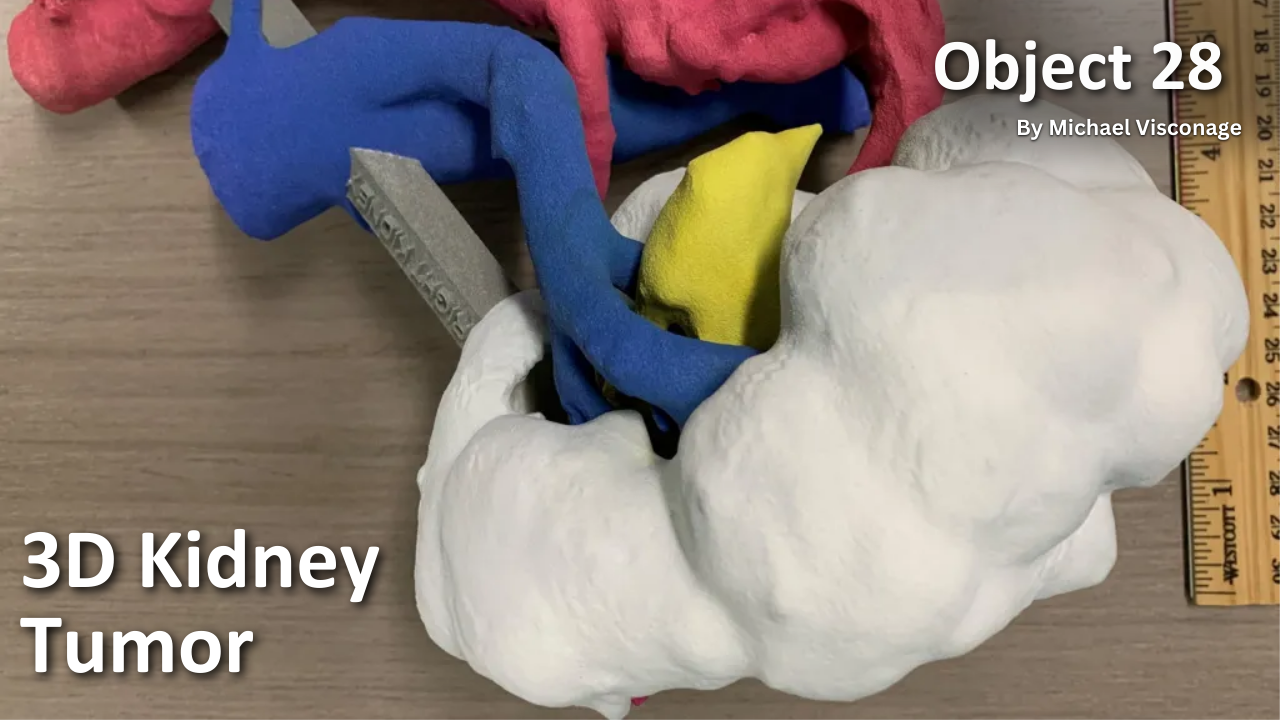
Object 28: 3D Kidney Tumor
In early 2019, the VA Medical Center (VAMC) in Seattle, Washington, made a breakthrough - creating a 3D kidney tumor model to address a medical issue. A pending surgical procedure called for the removal of a tumor from a Veteran’s kidney, complicated by a unique congenital configuration of the veins and arteries.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 24: Calverton Casket Flag
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020 transformed ordinary life for most Americans. Within VA, the National Cemetery Administration made the difficult decision to suspend funeral services to protect visitors and staff. Calverton National Cemetery in New York—an early pandemic epicenter—held a special service. On July 8, 2021, the cemetery presented a casket flag during a single solemn ceremony in which 849 Veterans belatedly received military honors.
History of VA in 100 Objects
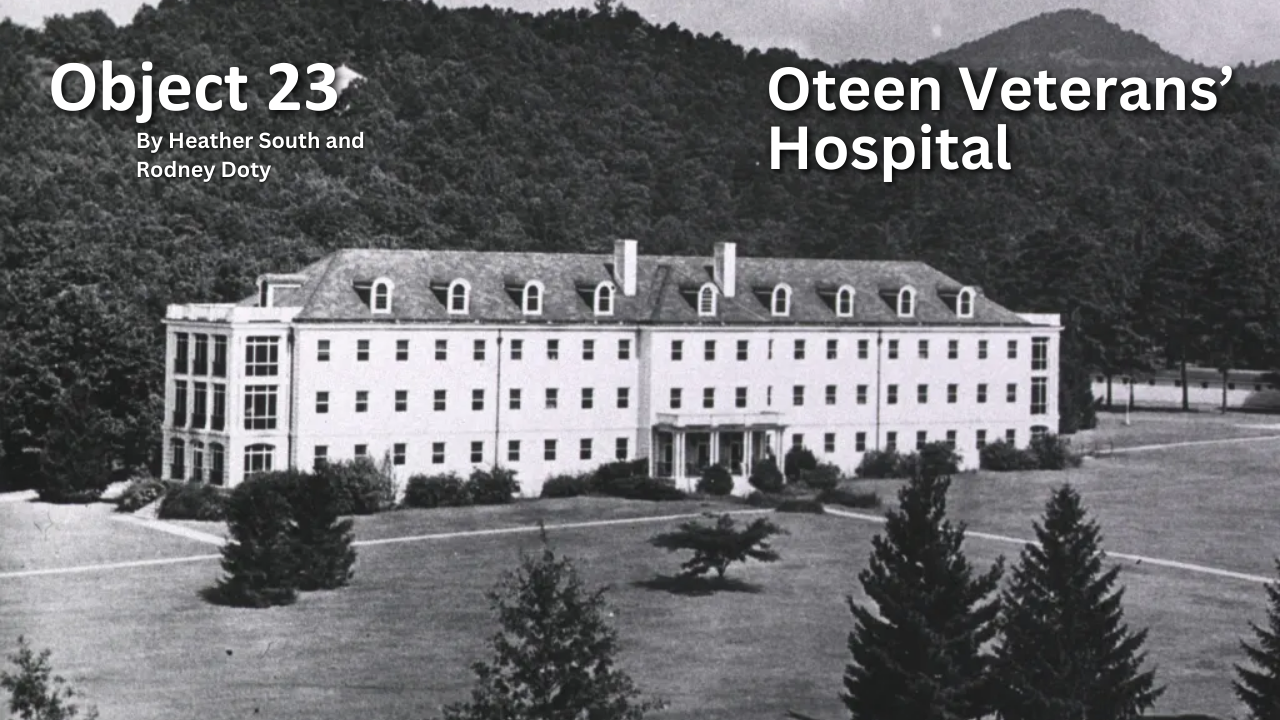
Object 23: Oteen Veterans’ Hospital
After the United States entered World War I in 1917, the government hastily built new facilities both to train Army medical personnel and to provide care for soldiers wounded during the fighting or stricken with disease. Oteen Veterans' Hospital was one of these.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 22: United States Veterans’ Bureau Medical Bulletin
In the space of just a few years following World War I, the U.S. government created an expansive health system for ex-servicemembers under the direction of a new and independent federal agency, the Veterans’ Bureau. A medical bulletin was soon published monthly featuring articles from the healthcare staff.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 21: Bonus Army
After World War I, Americans discharged from military service faced a difficult homecoming. Many struggled to find work in the tight labor market created by a post-war recession. After a deferred payout, the Bonus Act, was passed, many Veterans marched on the capital to voice displeasure. The Bonus Army soon formed.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 20: The Washington Arsenal Monument
The National Cemetery Administration serves as the steward for government and military lots at select private cemeteries nationwide. The Congressional Cemetery in Washington, D.C., is home to the Washington Arsenal Monument, which honors the women who died in an explosion at the arsenal during the Civil War.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 19: The Best Years of Our Lives Movie Poster
In 1946, Americans were adjusting to life in the immediate aftermath of World War II. Post-war concerns were varied. On November 21, 1946, "The Best Years of Our Lives" opened in movie theaters. The film was praised for its frank portrayal of the transition from military service to Veteran status as seen through the eyes of its three main characters returning to their hometown after the war. The movie poster displayed the cast in their roles.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 17: The “Meigs Plan” Lodges
National cemeteries originated out of necessity during the American Civil War. In the summer of 1862, as casualties mounted at an alarming rate, Congress empowered President Abraham Lincoln to purchase and enclose burial plots as national cemeteries to inter the growing number of Union dead. These cemeteries were managed by superintendents, some disabled Civil War Veterans. To house them, Brig. Gen. Montgomery Meigs came up with what was later named the "Meigs Plan," the design for permanent lodges to house the superintendents.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 14: Fleet Admiral Chester W. Nimitz Burial Plot at Golden Gate National Cemetery
Nine individuals in U.S. history have obtained the five-star general officer rank, all but one directly on account of their World War II service. Only one of this select group, Fleet Admiral Chester W. Nimitz, is interred in a VA national cemetery.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 13: Veterans’ Administration Seal
On July 21, 1930, President Herbert C. Hoover signed Executive Order 5398 establishing the Veterans’ Administration (VA), the forerunner of today’s Department of Veterans Affairs. Soon Adminstrator Frank Hines had created a new Veterans' Administration seal to go with the new agency.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 12: Pension Bureau Building
In 1882, the Pension Bureau hired 770 new clerks, doubling the size of its work force. The additional manpower was necessary to keep up with the explosive growth of the pension system after the Civil War. Work soon began on constructing a new Pension Bureau building to serve as the headquarters and home for the enlarged work force.

History of VA in 100 Objects
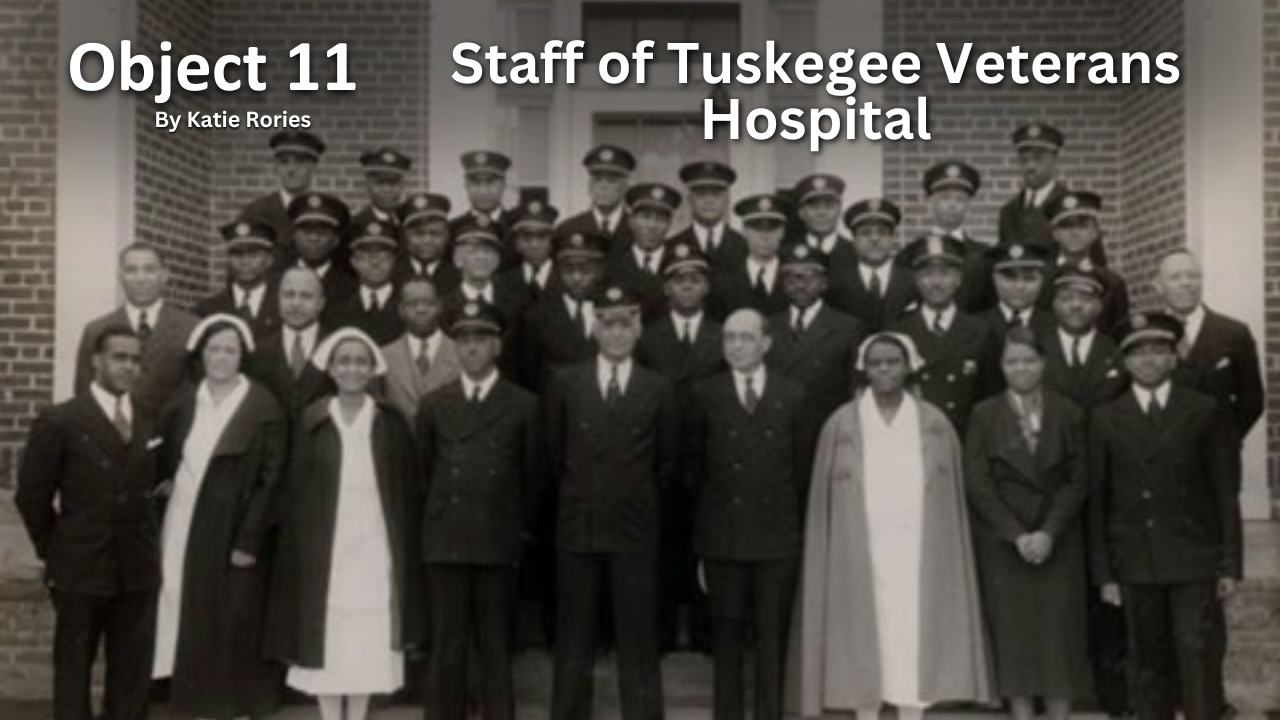
Object 11: Staff of Tuskegee Veterans Hospital
To accommodate the growing number of African American Veterans in the south following World War I, the Veterans Bureau opened the Tuskegee Veterans Hospital in 1923 reserved exclusively for their use. Originally called the “Hospital for Sick and Injured Colored World War Veterans,” the installation was staffed entirely by Black doctors and nurses.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 9: National Home Beer Token
Beer halls and beer gardens were familiar to Civil War Veterans who resided at branches of the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers (NHDVS). The administrators limited consumption in these beer halls by selling beer tokens or tickets that were exchanged for beer. The compromise was welcomed by administrators and Veterans alike.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 8: Public Law 79-293, The Department of Medicine And Surgery Act, 1946
On January 3, 1946, President Harry Truman established the forerunner of today’s Veterans Health Administration when he signed Public Law 79-293, creating the Department of Medicine and Surgery within the Veterans Administration.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 7: Portrait of Revolutionary War Veteran Joseph Winter
More than 15,000 Revolutionary War Veterans qualified for a pension. Veteran Joseph Winter was one of the unlucky few who did not. Winter lived in a settlement near Bethlehem, Pennsylvania before the war, where he supported his family as a weaver. As he grew older, his vision deteriorated and he could no longer perform the work required by his chosen trade. With no pension, Winter became homeless.
History of VA in 100 Objects
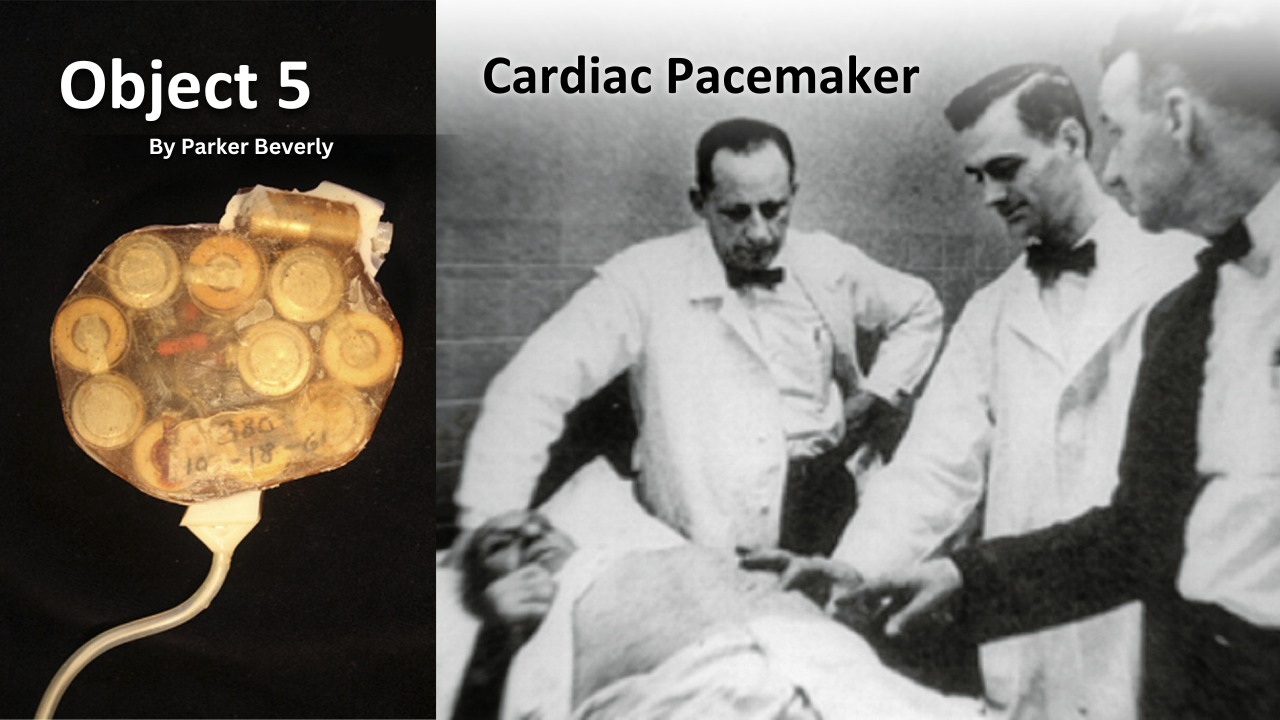
Object 5: Cardiac Pacemaker
In 1960, a VA research team led by surgeon William Chardack inserted what he described as a “battery-operated gadget about twice as big as a spool of Scotch tape and much the same shape” under the skin of a patient suffering from a complete heart block. The gadget was the first cardiac pacemaker.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 3: Civil War National Cemetery Bronze Shield Plaque
The first permanent informational plaques placed in national cemeteries after the Civil War were affixed to upright cannons to brand these sites as a shrine to Union dead. These bronze shield plaques were installed after a 1872 report and served as early monuments to Union dead from the Civil War at national cemeteries.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 2: Bounty Land Warrant
For a nation with limited financial resources, bounty land warrants were an appealing tool to encourage military enlistments. The promise of free 160 acres was the country's second benefit authorized for Veterans. However, the measure had devastating effect on the Indian nations that were dispossessed from the land.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 1: Fort Scott National Cemetery Visitors Register With Susan B. Anthony Signature, 1895
On July 13, 1895, renowned suffragist and social activist Susan B. Anthony visited Fort Scott National Cemetery, Kansas. Sitting on a table within the cemetery superintendent's lodge was a leather-bound visitor register, which she signed.