
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 44: Bureau of War Risk Insurance Occupation of Smithsonian Museum
When World War I erupted in Europe in August 1914, the United States stayed neutral but the nation quickly became a major supplier of industrial and agricultural goods to France and England. To protect this valuable trade, Congress established the Bureau of War Risk Insurance (BWRI) within the Treasury Department to insure American ships and cargo “against loss or damage by the risks of war.”

Featured Stories
Reflections from the Front: A New Podcast from the VA History Office
Women have been a vital part of the nation’s military from the very beginning. Although they were not able to serve in an official capacity until the twentieth century, women have always found ways to assist war efforts. In a new podcast series "Reflections from the Front", VA History Office interns Parker Beverly and Hannah Nelson take interviews from women Veterans and brings to life the stories of incredible resolve and adversity.
Exhibits
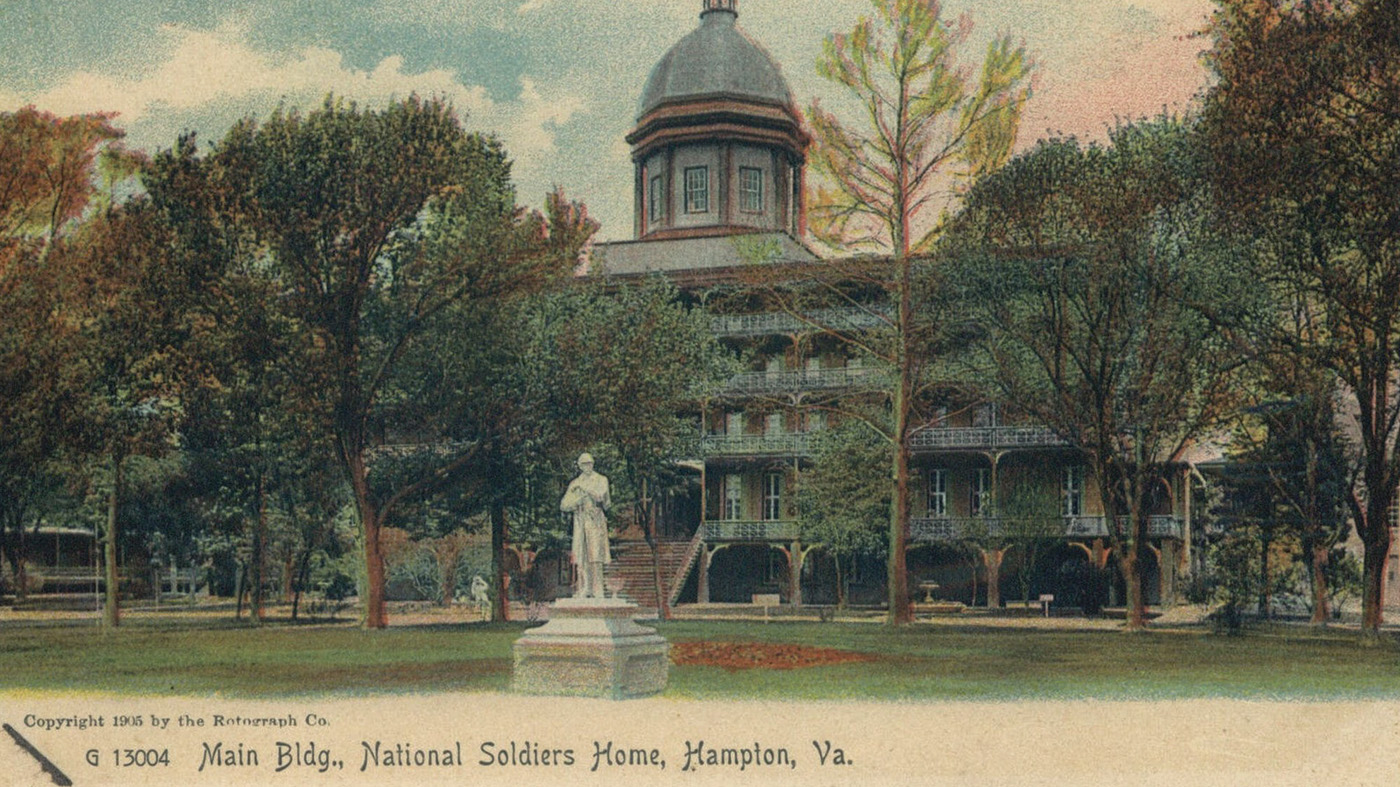
Historic Postcards From the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers Era
VA History Exhibit - Postcards were used frequently in the late 19th and early 20th century to capture Veterans' daily life at the 11 different National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers branches, which were early VA campuses. Check out the artwork and photographs from that era in this exhibit by VA History Office intern Kara Wheeler.

Exhibits
War Girls: California’s Army nurses in World War I
Between April 6, 1917 and November 18, 1918, over 21,000 American women enlisted in the U.S. Army Nurse Corps. This digital exhibit explores and commemorates the lives of California’s Army nurses buried in national cemeteries: Alta Ireland Heron, Vera Marston Rush, Etta Parker, Guilda N. Jones Vicini, and Mayme E. Williamson.
History of VA in 100 Objects
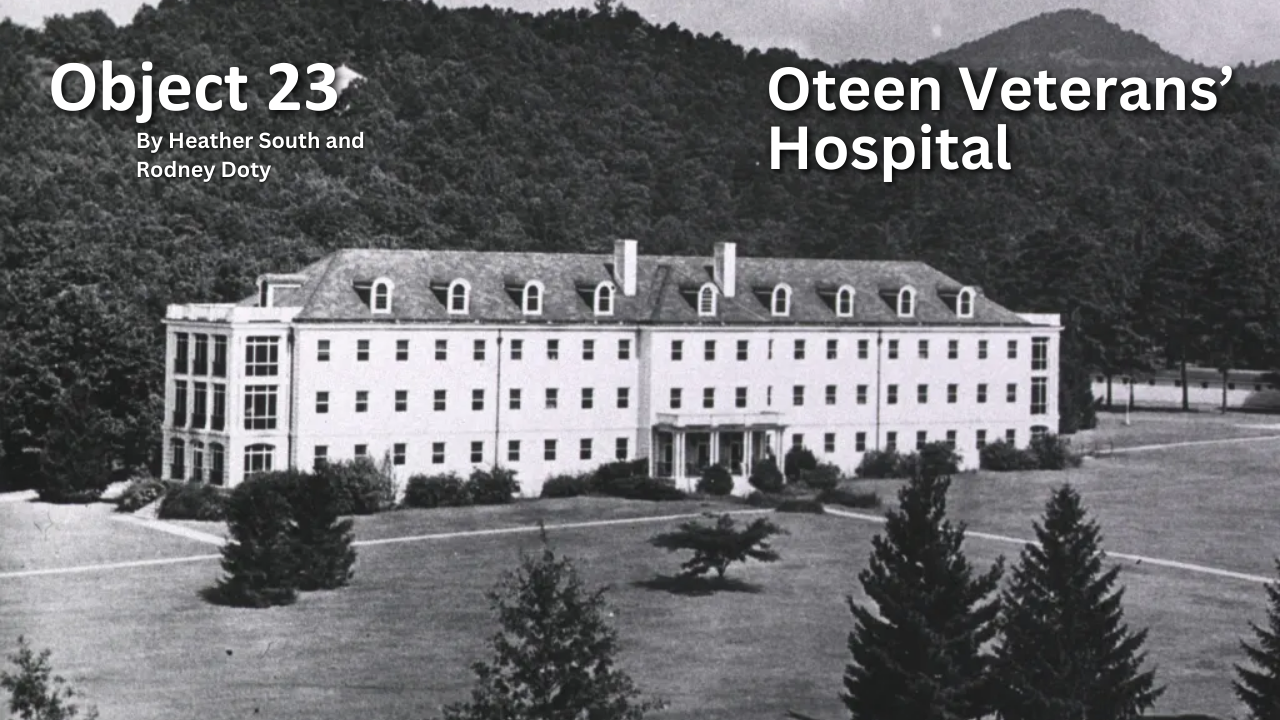
Object 23: Oteen Veterans’ Hospital
After the United States entered World War I in 1917, the government hastily built new facilities both to train Army medical personnel and to provide care for soldiers wounded during the fighting or stricken with disease. Oteen Veterans' Hospital was one of these.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 22: United States Veterans’ Bureau Medical Bulletin
In the space of just a few years following World War I, the U.S. government created an expansive health system for ex-servicemembers under the direction of a new and independent federal agency, the Veterans’ Bureau. A medical bulletin was soon published monthly featuring articles from the healthcare staff.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 21: Bonus Army
After World War I, Americans discharged from military service faced a difficult homecoming. Many struggled to find work in the tight labor market created by a post-war recession. After a deferred payout, the Bonus Act, was passed, many Veterans marched on the capital to voice displeasure. The Bonus Army soon formed.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 13: Veterans’ Administration Seal
On July 21, 1930, President Herbert C. Hoover signed Executive Order 5398 establishing the Veterans’ Administration (VA), the forerunner of today’s Department of Veterans Affairs. Soon Adminstrator Frank Hines had created a new Veterans' Administration seal to go with the new agency.

History of VA in 100 Objects
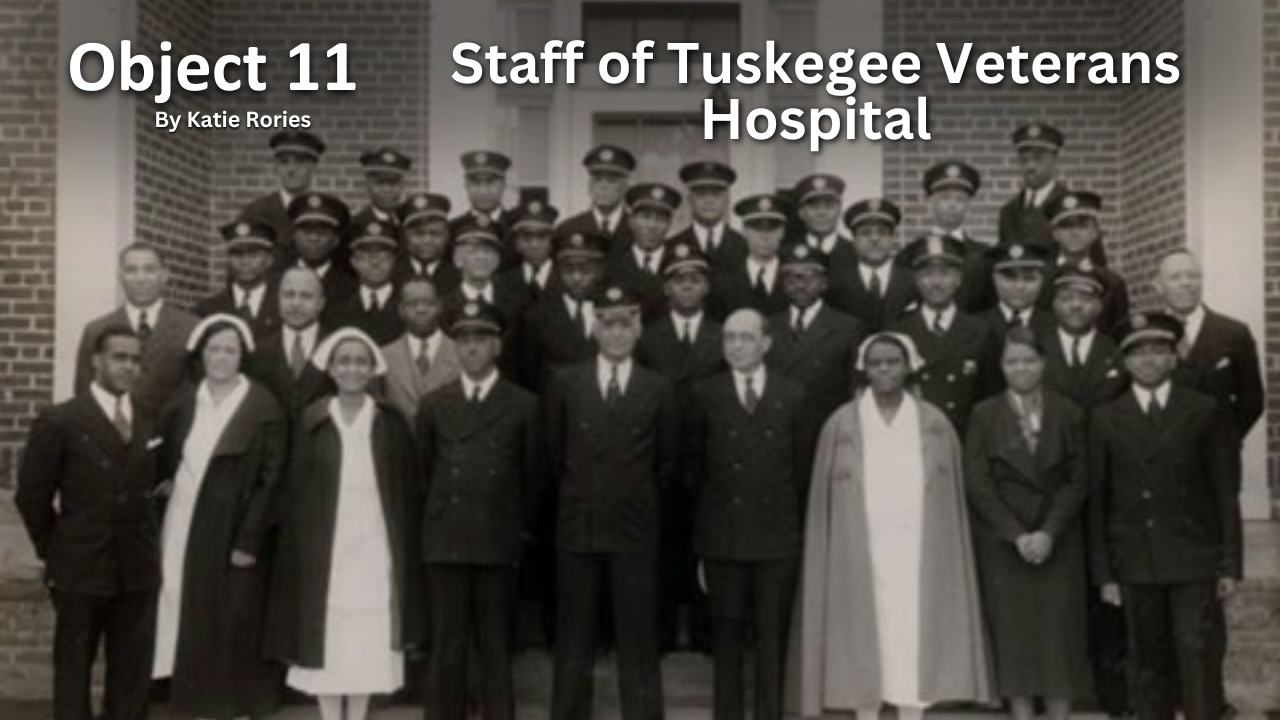
Object 11: Staff of Tuskegee Veterans Hospital
To accommodate the growing number of African American Veterans in the south following World War I, the Veterans Bureau opened the Tuskegee Veterans Hospital in 1923 reserved exclusively for their use. Originally called the “Hospital for Sick and Injured Colored World War Veterans,” the installation was staffed entirely by Black doctors and nurses.





