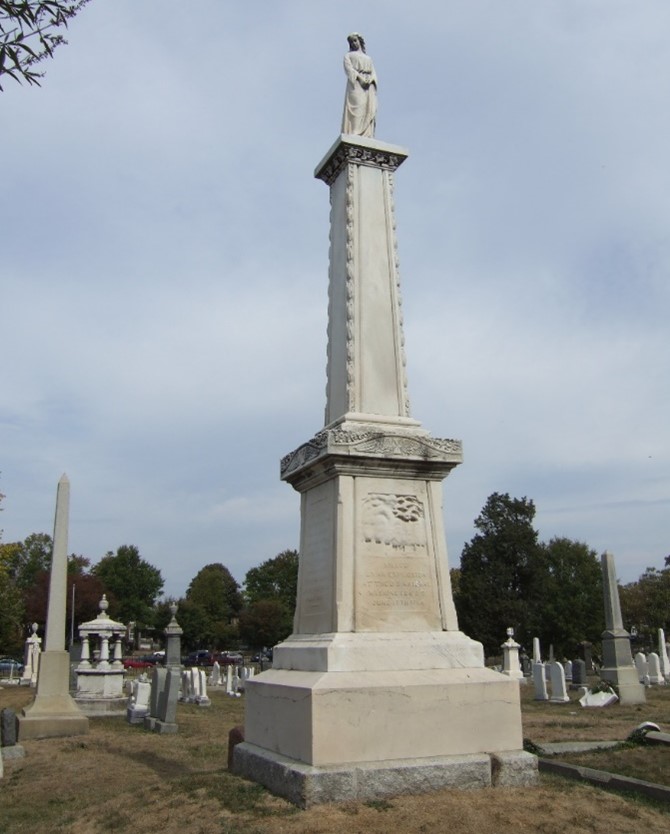
The National Cemetery Administration (NCA) serves as the steward for government and military lots at select private cemeteries nationwide. The Congressional Cemetery in Washington, D.C., is home to several of these lots containing more than 800 burial sites in locations scattered across the 35-acre grounds. Interred within are members of Congress, prisoners of war, a U.S. vice president, Native American dignitaries, and government employees. Their graves are marked by headstones that come in a variety of shapes and sizes. One of the largest markers is the monument honoring the women who died in an explosion at the Washington Arsenal during the Civil War.
On June 17, 1864, female workers—many of whom were young, Irish immigrants—were busy assembling ammunition cartridges at the Washington Arsenal, a U.S. Army installation (now Fort McNair) at the confluence of the Potomac and Anacostia Rivers. The weather that day was sweltering, with temperatures approaching 100 degrees. Just before noon, red and white star pellets used in fireworks that were drying on metal trays outside the women’s workspace ignited in the heat. The pyrotechnics flew into the air and one pellet entered a window left open for ventilation. It skidded across the worktable, igniting the cartridges being assembled, and landed in a barrel of gunpowder. The ensuing explosion blew the roof off the building and fire engulfed the women wearing highly flammable cotton shirts and hoopskirts. The building was consumed in minutes and twenty-one women died.
The local community was devastated by the explosion. Secretary of War Edwin Stanton ordered the War Department to pay for all funeral expenses. A large crowd of people attended the funeral at the arsenal and thousands more turned out for the burial procession to Congressional Cemetery. President Abraham Lincoln joined the events as the “mourner in chief.” A few days later, arsenal employees took up a collection to donate a day’s wages to establish a monument to honor the victims of the tragedy.
Irish-American sculptor Lot Flannery was commissioned to design and carve a memorial to place at the gravesite of the fifteen women buried in one of the cemetery’s government lots. The other six were interred in family plots at the cemetery or elsewhere. Flannery completed the 25-foot-tall marble shaft on a granite base before the anniversary of the explosion at a cost of just over $3,000. He topped the monument with a female figure symbolizing grief that is visible well beyond the cemetery’s walls.
The front face of the monument shaft features a carving of the arsenal explosion; the east and west faces are inscribed with the names of all twenty-one women who died in the accident. In 2008, NCA treated the monument to slow the erosion of the marble and inscriptions. In 2014, a granite marker engraved with the victims’ names was placed in front of the monument as those on the shaft had faded. The following year, on the sesquicentennial of the monument’s completion, it was rededicated.
By Nalia Warmack
Virtual Student Federal Service Intern, National Cemetery Administration
Share this story
Related Stories

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 96: Postcard of Veterans Vocational School
In 1918, the government created the first nationwide vocational training system to help disabled Veterans acquire new occupational skills and find meaningful work. Over the next 10 years, more than 100,000 Veterans completed training programs in every field from agriculture and manufacturing to business and photography.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 95: 1840 Census of Pensioners
In a first, the 1840 census collected data on Veterans and widows receiving a pension from the federal government. The government published its findings in a stand-alone volume titled “A Census of Pensioners for Revolutionary or Military Services.”
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 94: Southern Branch of the National Home
The Southern Branch of the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers opened in Hampton, Virginia, in late 1870. The circumstances surrounding the purchase of the property, however, prompted an investigation into the first president of the National Home’s Board of Managers, Benjamin Butler.




