
Exhibits
VA Research at 100: A Century of Medical Advancements
In 1925, 100 years ago, the Veterans Bureau initiated the first hospital-based medical research studies to address Veteran-specific issues like mental health, tuberculosis, cancer and toxic exposure. The program has since made significant medical breakthroughs and innovations, impacting the world.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 89: VA Film “You Can Lick TB” (1949)
In 1949, VA produced a 19-minute film titled “You Can Lick TB.” The film follows a fictional conversation between a bedridden Veteran with tuberculosis and his VA doctor, dramatizing through brief vignettes the different stages of TB treatment and recovery.

Featured Stories
Dr. Philip Matz: A Pioneer in VA Medical Research
After World War I and the establishment of the Veterans Bureau, one of the key focuses was developing a research program.
The intent was to have the necessary statistical studies and research information to help the Bureau treat Veterans not just from World War I but all future conflicts.
The man chosen to lead this task was Dr. Philip Matz, and his work was groundbreaking in the future of Veteran healthcare.
History of VA in 100 Objects
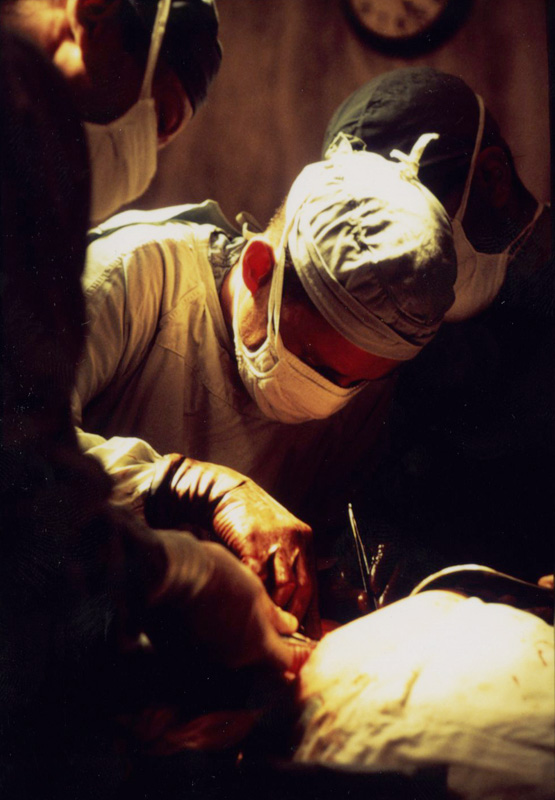
Object 83: First Liver Transplantation at VA Hospital
Prior to the 1960s, liver failure always ended in death. In May 1963, however, Dr. Thomas E. Starzl made medical history at the VA hospital in Denver, Colorado, when he performed the first liver transplantation on a patient who survived the operation.
Starzl's continued to refine his procedure, becoming a leading expert on liver transplants. The success rate for early transplants wasn't optimal, but that didn't stop him from researching new techniques and post-care practices. These innovations, coupled with new medications, improved the effectiveness and life-saving measures of that vital transplant surgery.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 80: LUKE/DEKA Prosthetic Arm
In the 19th century, the federal government left the manufacture and distribution of prosthetic limbs for disabled Veterans to private enterprise. The experience of fighting two world wars in the first half of the 20th century led to a reversal in this policy.
In the interwar era, first the Veterans Bureau and then the Veterans Administration assumed responsibility for providing replacement limbs and medical care to Veterans.
In recent decades, another federal agency, the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA), has joined VA as a supporter of cutting-edge research into artificial limb technology. DARPA’s efforts were spurred by the spike in traumatic injuries resulting from the emergence of improvised explosive devices as the insurgent’s weapon of choice in Iraq in 2003-04.
Out of that effort came the LUKE/DEKA prosthetic limb, named after the main character from "Star Wars."

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 57: Omaha VA Hospital Nuclear Reactor
In August 1945, the United States detonated atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, ending World War II and ushering in the dawn of the Atomic Age. Two years later, the Veterans Administrations started harnessing this technology for a very different purpose—to conduct medical research by installing a small nuclear reactor at the VA hospital in Omaha, Nebraska.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 51: VA Telehealth Cart
Long before high-speed internet networks made it fast and easy to transfer information, access services, and communicate with others the world over, VA had experimented with ways to deliver health care at a distance, such as with telehealth carts.
History of VA in 100 Objects
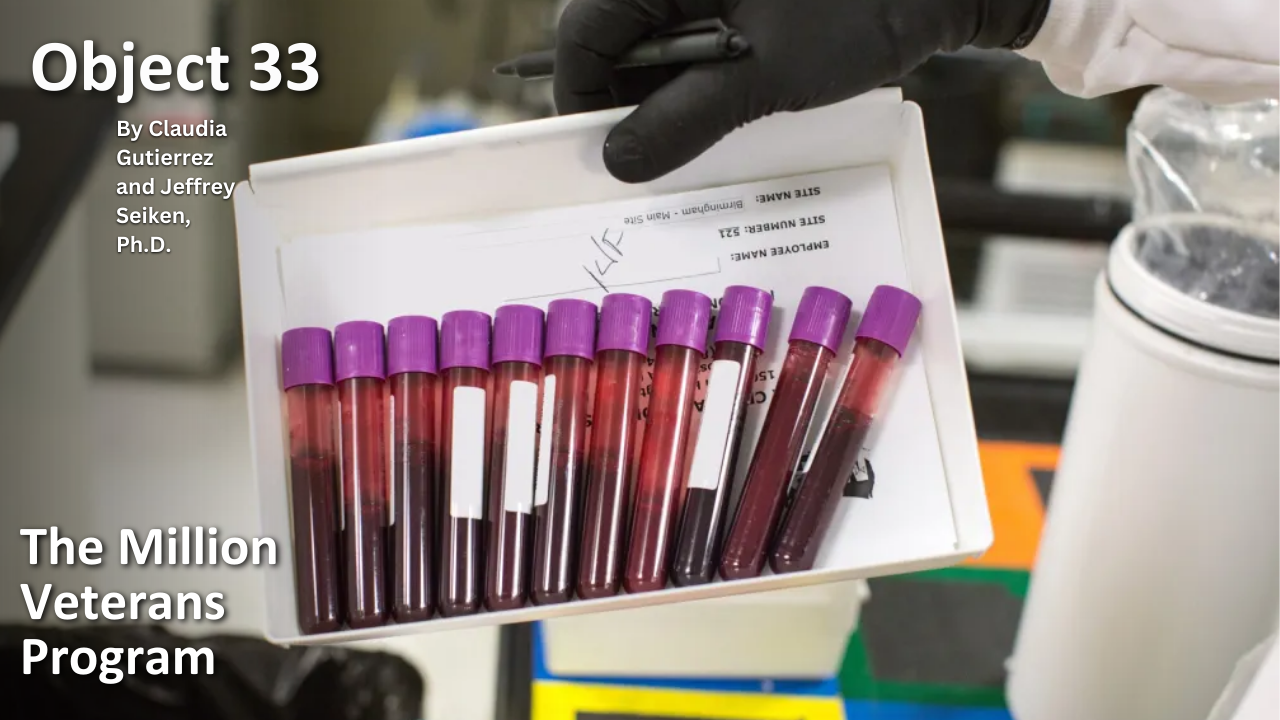
Object 33: The Million Veteran Program
In May 2009, twelve VA doctors and scientists gathered in a small conference room in Rockville, Maryland, to brainstorm about the design of VA’s first-ever large-scale genetic research program, the Million Veteran Program. They wanted to collect medical information from Veterans along with blood samples to extract DNA, with the goal of creating a genomic biobank or database for researchers to explore how genes affect health and disease

Featured Stories
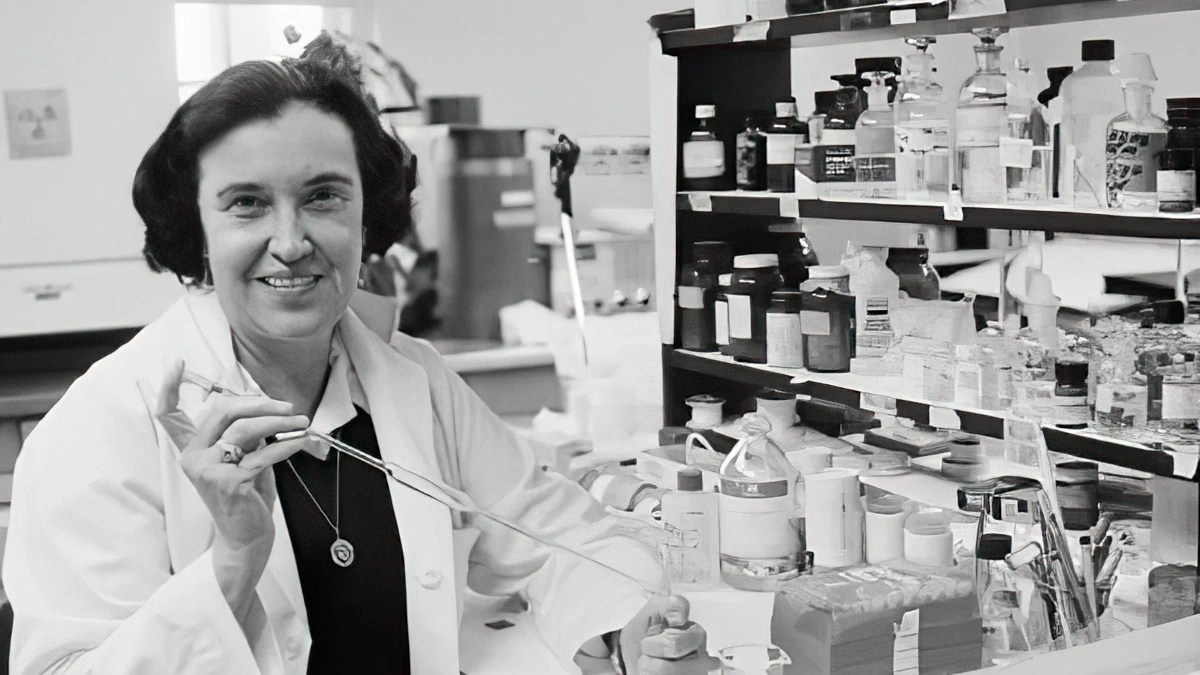
Dr. Rosalyn Yalow: Groundbreaking VA Medical Researcher and Nobel Prize Laureate
VA History Exhibit - In 1977, Dr. Rosalyn Yalow, a medical researcher and doctor at the Bronx VA Hospital, became the second woman awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. In an exhibit crafted by VA History intern Parker Beverly, learn how Dr. Yalow strived to break through gender barriers in the medical field to become an expert in radioimmunoassay.

History of VA in 100 Objects
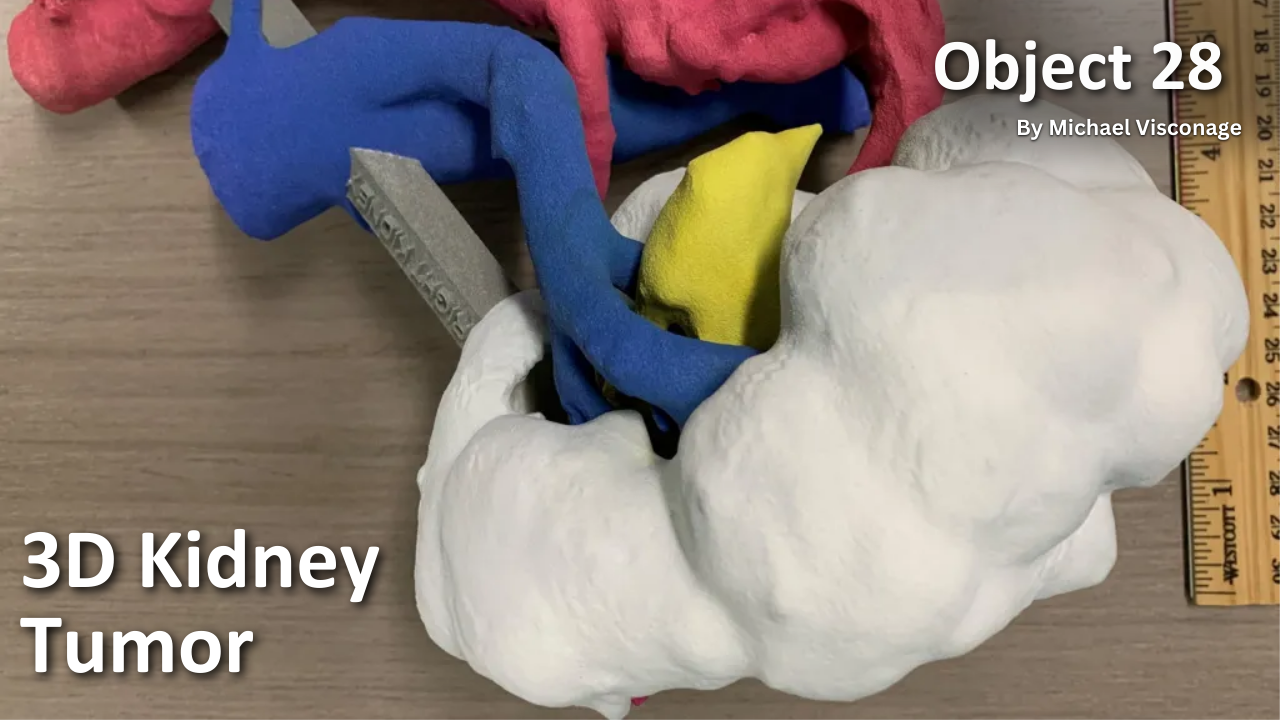
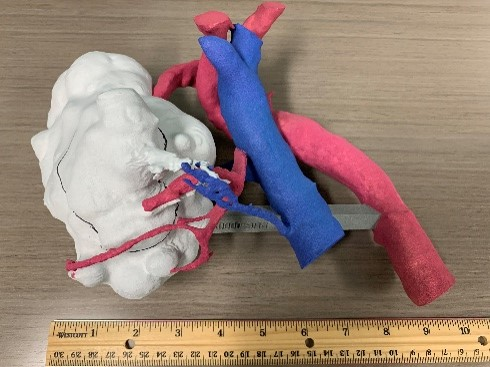
Object 28: 3D Kidney Tumor
In early 2019, the VA Medical Center (VAMC) in Seattle, Washington, made a breakthrough - creating a 3D kidney tumor model to address a medical issue. A pending surgical procedure called for the removal of a tumor from a Veteran’s kidney, complicated by a unique congenital configuration of the veins and arteries.
Curator Corner
From the Collection: Where’s the Tumor?
Curator Corner blog - There’s a 3D tumor out there and the VA History Center wants it. The quest for contemporary artifacts is a constant challenge. It’s not simply a question of what to collect, but when, where, and how to collect items of potential value to our collection. In this case, the hunt is on for an item used in an innovative collaboration at the Seattle VA Medical Center to safely remove a tumor from a Veteran’s kidney.



