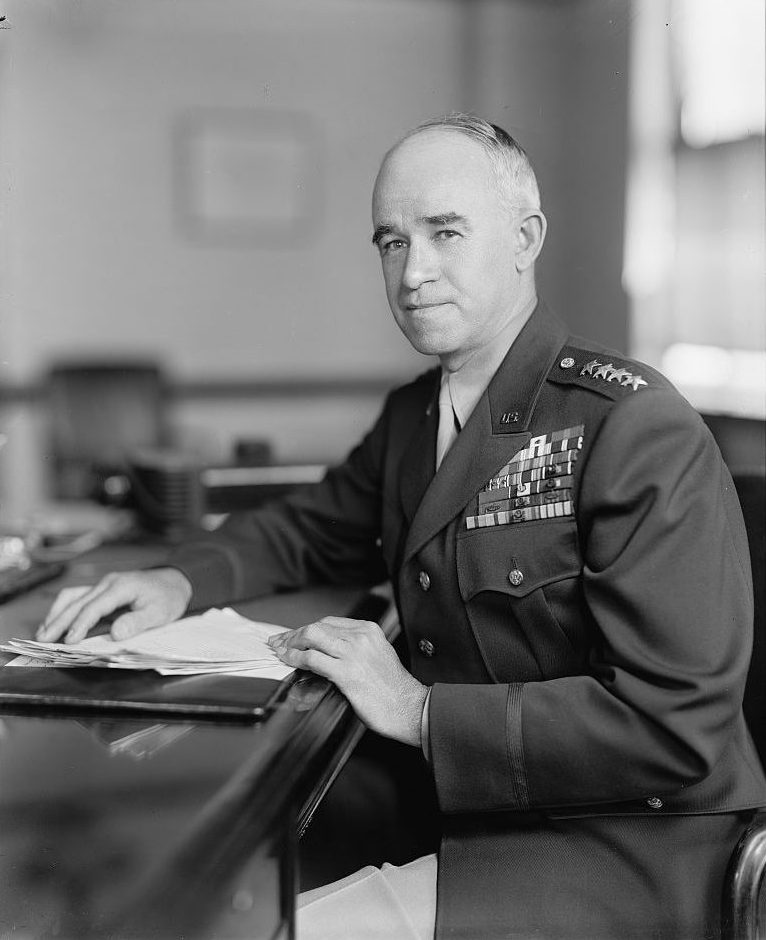
Within days of Germany’s surrender in May 1945, General Omar N. Bradley received word of his next assignment: he had been handpicked by President Harry S. Truman to replace Frank T. Hines as the next head of the Veterans Administration. For Bradley, who had commanded the 12th Army Group, the largest American fighting force ever assembled, in the campaign that liberated France and brought Germany to its knees, the president’s summons came as a shock. As he recalled in his autobiography, “I knew absolutely nothing about the Veterans Administration.”1
Truman, however, was certain he had the right man for the job. During the war, Bradley had acquired a reputation as the soldier’s general for his unassuming manner and devotion to the welfare of the troops. He had also earned the admiration of the public and Congress for his sterling record on the battlefield. As the war wound down, critics had assailed the VA for the quality of its medical care and its rigid bureaucracy. The VA needed a thorough overhaul and Truman believed Bradley possessed the judgment to make the necessary changes as well as the stature to restore trust and confidence in the embattled agency.
Bradley took the oath of office as Administrator of the VA on August 15, 1945, one day after Japan surrendered, ending World War II. A private law passed by Congress the previous month allowed him to remain on active duty and retain his four-star rank in the Army for the duration of his term. The magnitude of the task ahead of him was immense.
At the time of his appointment, the VA was already struggling to keep up with the demand for benefits and services from the 4.5 million Veterans on its rolls. Its predicament only grew worse when the Pentagon, responding to pressure from the public and politicians, sped up the pace of demobilization after the war.2 Between October 1945 and June 1946, nearly 13 million men and women in uniform returned to civilian life. Mail poured into the VA’s offices at a rate as high as 300,000 letters per day, swamping the agency with requests from Veterans seeking to use the education and loan provisions of the 1944 GI Bill or collect on the other benefits they were due.

Bradley moved swiftly after his swearing in to bring order to the chaos. He entrusted the transformation of the VA’s medical services to Major General Paul R. Hawley, who served as the Army’s chief surgeon in the European Theater of Operations during the war.3 He also brought in many of his trusted subordinates from the 12th Army Group to fill key administrative posts. To decentralize operations, Bradley launched a sweeping reorganization of the VA. He established 13 branch offices, each of which functioned, in his words, as “a small-scale VA.”4 Every branch had its own deputy administrator, who was responsible for making decisions and overseeing the smaller regional and contact offices that fell within his geographic area.
Bradley also went on a hiring spree, increasing the number of employees working throughout the VA from 65,000 in 1945 to 200,000 in 1947. He took advantage of the Veterans’ Preference Act passed in 1944 to ensure that the vast majority of the new hires were former service members themselves.
Bradley stayed at the VA for a little over two years. He stepped down from his post in November 1947 to assume the one desk job in Washington he truly coveted—Chief of Staff of the Army. He departed knowing that the VA had weathered the worst of the demobilization storm and delivered on the nation’s promises to the men and women who served bravely during World War II. By the end of his tenure, the VA had processed disability claims from over 3.5 million Veterans and helped millions more purchase homes, attend college, or enroll in job training programs through the GI Bill.
Footnotes
- Omar N. Bradley and Clay Blair, A General’s Life: An Autobiography by General of the Army Omar N. Bradley (New York: Simon and Schuster, 1983), p. 440. ↩︎
- For more on the military’s efforts to bring home the millions of soldiers serving overseas, see VA Insider, “Looking back at the end of a global war.” ↩︎
- For the reforms to the VA’s medical system carried out by General Hawley, see VA Insider, “Armistice Day 1945: How VA met the moment on Veteran health care 75 years ago. ↩︎
- Bradley and Blair, A General’s Life, p. 450. ↩︎
By Jeffrey Seiken
Ph.D., Historian, Veterans Benefits Administration
Share this story
Related Stories

Featured Stories
A Brief History of the Board of Veterans’ Appeals
On July 28, 1933, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt signed Executive Order 6230 creating the Board of Veterans’ Appeals (BVA). The BVA was created as part of the Veterans Administration (VA), which had been established only three years earlier.

Featured Stories
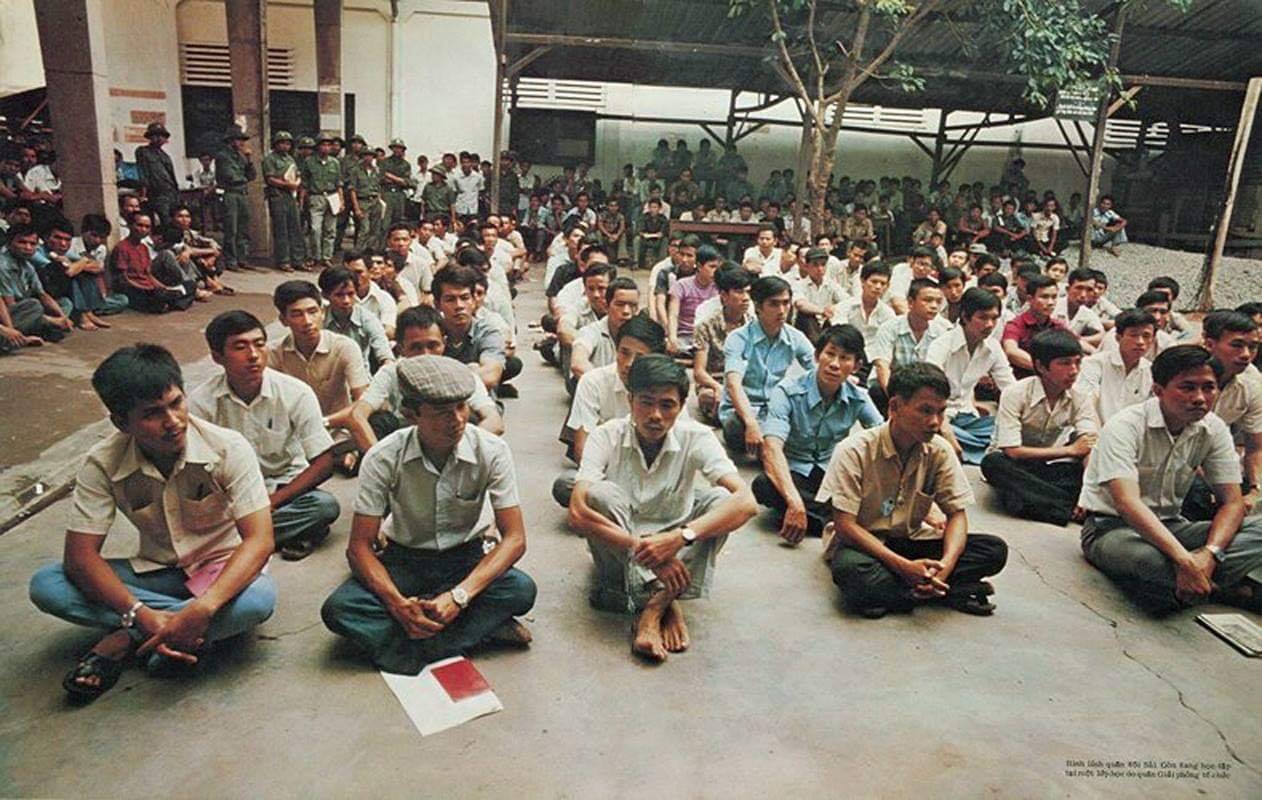
The Fall of Saigon 1975: A South Vietnamese Military Physician Remembers
"There was chaos in the streets when I made my way to the hospital on the morning of April 30, 1975. In a place of order, there was now great confusion. The director and vice director of the hospital were gone, making me, the chief of medicine, the highest-ranking medical officer."