Featured Stories
Dr. Philip Matz: A Pioneer in VA Medical Research
After World War I and the establishment of the Veterans Bureau, one of the key focuses was developing a research program.
The intent was to have the necessary statistical studies and research information to help the Bureau treat Veterans not just from World War I but all future conflicts.
The man chosen to lead this task was Dr. Philip Matz, and his work was groundbreaking in the future of Veteran healthcare.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 80: LUKE/DEKA Prosthetic Arm
In the 19th century, the federal government left the manufacture and distribution of prosthetic limbs for disabled Veterans to private enterprise. The experience of fighting two world wars in the first half of the 20th century led to a reversal in this policy.
In the interwar era, first the Veterans Bureau and then the Veterans Administration assumed responsibility for providing replacement limbs and medical care to Veterans.
In recent decades, another federal agency, the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA), has joined VA as a supporter of cutting-edge research into artificial limb technology. DARPA’s efforts were spurred by the spike in traumatic injuries resulting from the emergence of improvised explosive devices as the insurgent’s weapon of choice in Iraq in 2003-04.
Out of that effort came the LUKE/DEKA prosthetic limb, named after the main character from "Star Wars."

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 57: Omaha VA Hospital Nuclear Reactor
In August 1945, the United States detonated atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, ending World War II and ushering in the dawn of the Atomic Age. Two years later, the Veterans Administrations started harnessing this technology for a very different purpose—to conduct medical research by installing a small nuclear reactor at the VA hospital in Omaha, Nebraska.
History of VA in 100 Objects
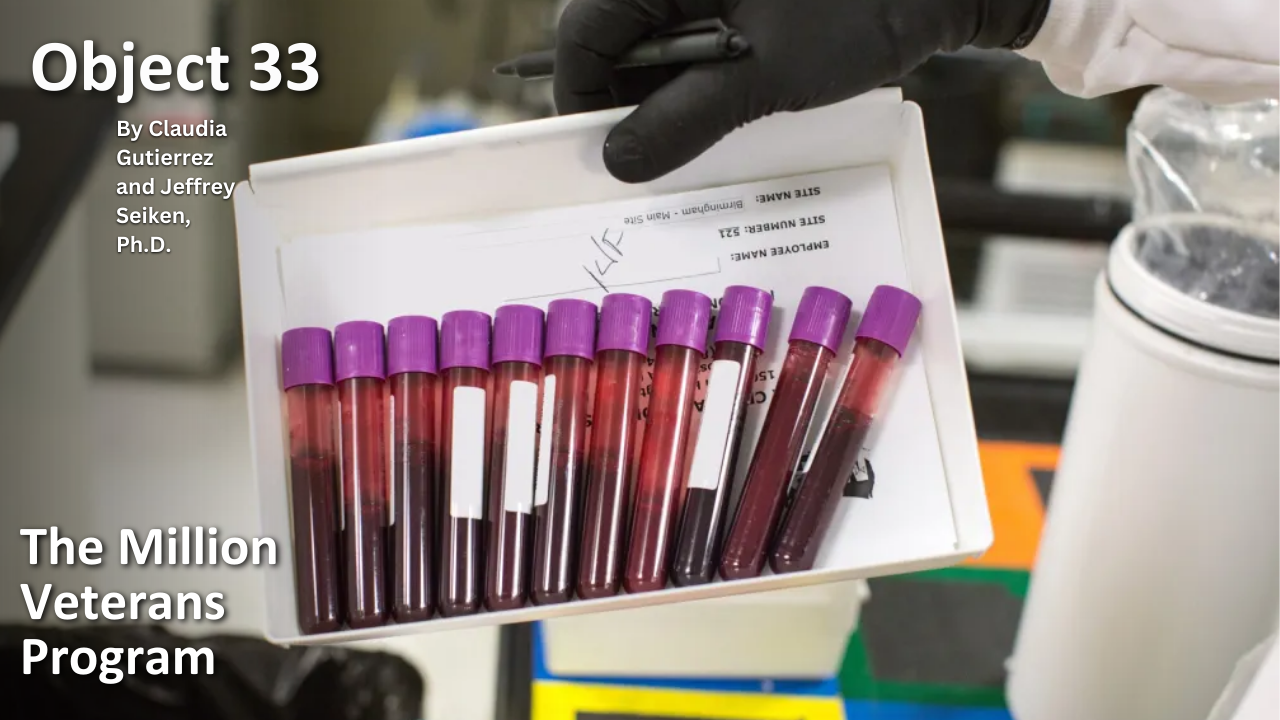
Object 33: The Million Veteran Program
In May 2009, twelve VA doctors and scientists gathered in a small conference room in Rockville, Maryland, to brainstorm about the design of VA’s first-ever large-scale genetic research program, the Million Veteran Program. They wanted to collect medical information from Veterans along with blood samples to extract DNA, with the goal of creating a genomic biobank or database for researchers to explore how genes affect health and disease
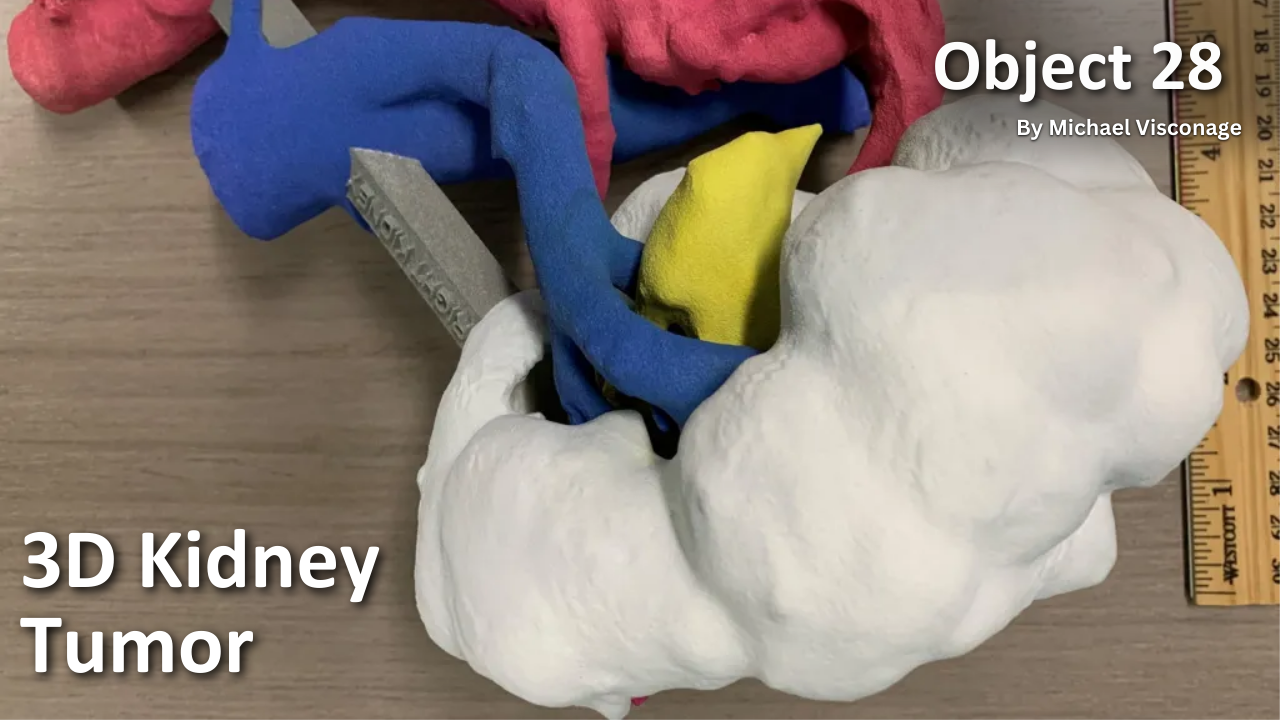

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 28: 3D Kidney Tumor
In early 2019, the VA Medical Center (VAMC) in Seattle, Washington, made a breakthrough - creating a 3D kidney tumor model to address a medical issue. A pending surgical procedure called for the removal of a tumor from a Veteran’s kidney, complicated by a unique congenital configuration of the veins and arteries.
History of VA in 100 Objects
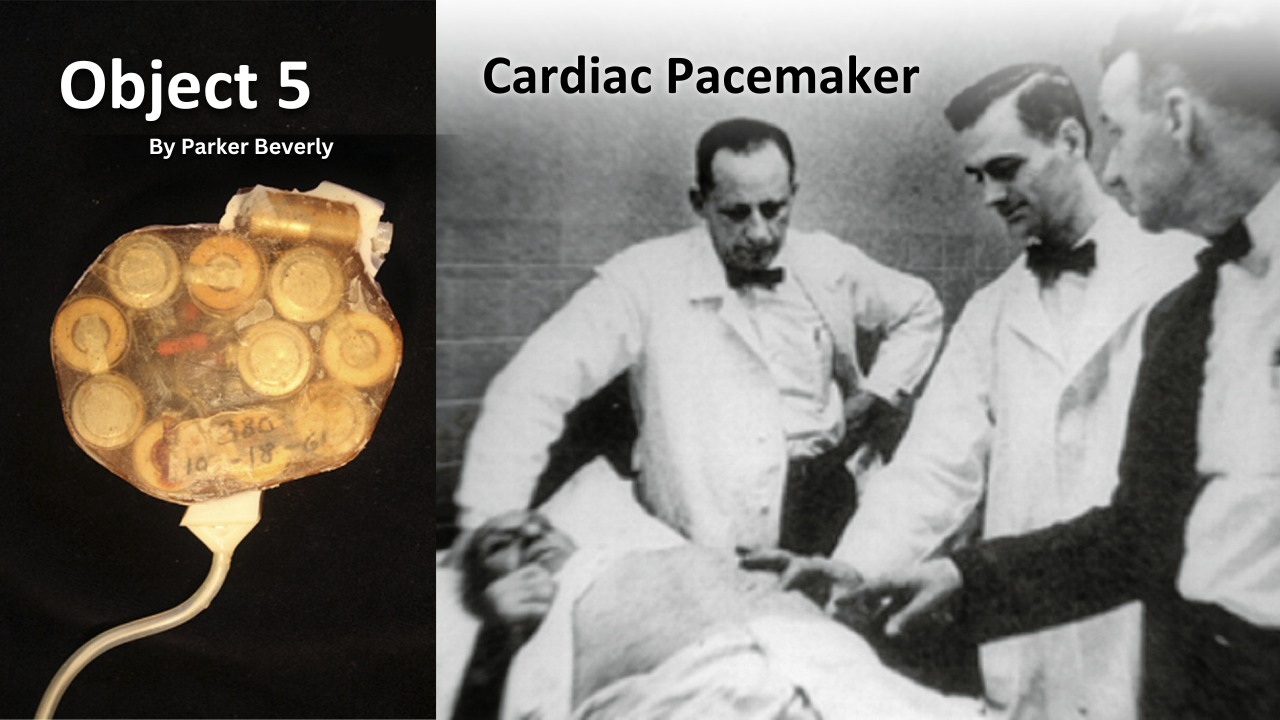
Object 5: Cardiac Pacemaker
In 1960, a VA research team led by surgeon William Chardack inserted what he described as a “battery-operated gadget about twice as big as a spool of Scotch tape and much the same shape” under the skin of a patient suffering from a complete heart block. The gadget was the first cardiac pacemaker.

Featured Stories
Dr. Andrew Schally: Nobel Prize Laureate
Dr. Andrew Schally was born in Poland, and through early struggles under German occupation during World War II, started a journey as a medical researcher that would take him to VA and groundbreaking research on hormones. In this feature by VA History intern Parker Beverly, follow along Dr. Schally's career as his medical research was recognized in 1977 with the Nobel Prize.