
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 85: Congressman Claypool’s “$1 Per Day Pension” Ribbon
Founded in 1866 as fraternal organization for Union Veterans, the Grand Army of the Republic (GAR) embraced a new mission in the 1880s: political activism. The GAR formed a pension committee in 1881 for the express purpose of lobbying Congress for more generous pension benefits.
An artifact from the political wrangling over pensions is now part of the permanent collection of the National VA History Center in Dayton, Ohio. The item is a small pension ribbon displaying the message: “I endorse the $1 per day pension as recommended by the Departments of Ohio and Indiana G.A.R.” The button attached to the ribbon features two American flags and the phrase “saved by the boys of ’61-65.” The back of the ribbon bears the signature of Horatio C. Claypool, a Democratic judge who ran for the seat in Ohio’s eleventh Congressional district in the 1910 mid-term elections.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 81: World War I Insurance Certificate
An effort to remake the Veteran benefits system during World War I led to the 1917 War Risk Insurance Act that provided insurance benefits to Veterans well beyond their act of service was completed. A $10,000 policy could furnish the beneficiary a monthly income of over $57 in the early 20th Century.
It was a popular benefit, with 4 million applications before the end of the war. This program greatly impacted VA's future insurance efforts.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 79: VA Study of Former Prisoners of War
American prisoners of war from World War II, Korea, and Vietnam faced starvation, torture, forced labor, and other abuses at the hands of their captors. For those that returned home, their experiences in captivity often had long-lasting impacts on their physical and mental health. Over the decades, the U.S. government sought to address their specific needs through legislation conferring special benefits on former prisoners of war.
In 1978, five years after the United States withdrew the last of its combat troops from South Vietnam, Congress mandated VA carry out a thorough study of the disability and medical needs of former prisoners of war. In consultation with the Secretary of Defense, VA completed the study in 14 months and published its findings in early 1980. Like previous investigations in the 1950s, the study confirmed that former prisoners of war had higher rates of service-connected disabilities.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 78: French Cross at Cypress Hills National Cemetery in Brooklyn
In the waning days of World War I, French sailors from three visiting allied warships marched through New York in a Liberty Loan Parade. The timing was unfortunate as the second wave of the influenza pandemic was spreading in the U.S. By January, 25 of French sailors died from the virus.
These men were later buried at the Cypress Hills National Cemetery and later a 12-foot granite cross monument, the French Cross, was dedicated in 1920 on Armistice Day. This event later influenced changes to burial laws that opened up availability of allied service members and U.S. citizens who served in foreign armies in the war against Germany and Austrian empires.
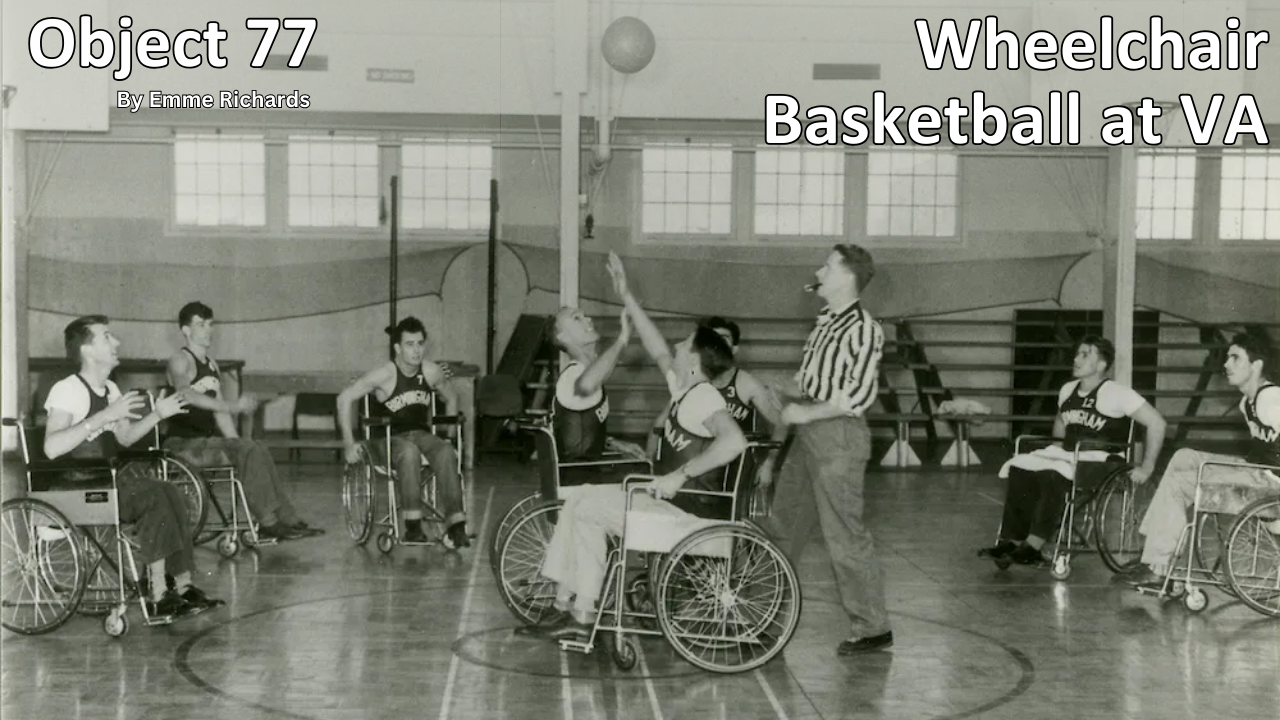
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 77: Wheelchair Basketball at VA
Basketball is one of the most popular sports in the nation. However, for paraplegic Veterans after World War II it was impossible with the current equipment and wheelchairs at the time. While VA offered these Veterans a healthy dose of physical and occupational therapy as well as vocational training, patients craved something more. They wanted to return to the sports, like basketball, that they had grown up playing. Their wheelchairs, which were incredibly bulky and commonly weighed over 100 pounds limited play.
However, the revolutionary wheelchair design created in the late 1930s solved that problem. Their chairs featured lightweight aircraft tubing, rear wheels that were easy to propel, and front casters for pivoting. Weighing in at around 45 pounds, the sleek wheelchairs were ideal for sports, especially basketball with its smooth and flat playing surface. The mobility of paraplegic Veterans drastically increased as they mastered the use of the chair, and they soon began to roll themselves into VA hospital gyms to shoot baskets and play pickup games.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 76: Senate Speech Proposing First Presumptive Conditions For Great War Veterans
After World War I, claims for disability from discharged soldiers poured into the offices of the Bureau of War Risk Insurance, the federal agency responsible for evaluating them. By mid-1921, the bureau had awarded some amount of compensation to 337,000 Veterans. But another 258,000 had been denied benefits. Some of the men turned away were suffering from tuberculosis or neuropsychiatric disorders. These Veterans were often rebuffed not because bureau officials doubted the validity or seriousness of their ailments, but for a different reason: they could not prove their conditions were service connected.
Due to the delayed nature of the diseases, which could appear after service was completed, Massachusetts Senator David Walsh and VSOs pursued legislation to assist Veterans with their claims. Eventually this led to the first presumptive conditions for Veteran benefits.

Exhibits
New Skills, New Freedoms: Occupational Therapy Artifacts from the National VA History Center
While Veterans engaged in activities and learned trades at the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers (NHDVS) since its inception after the Civil War, formal occupational therapy programs became components of rehabilitative care for Veterans beginning in the 20th century. This exhibit explores what type of activities were used to treat Veterans by showing items from the collection at the National VA History Center.

Featured Stories
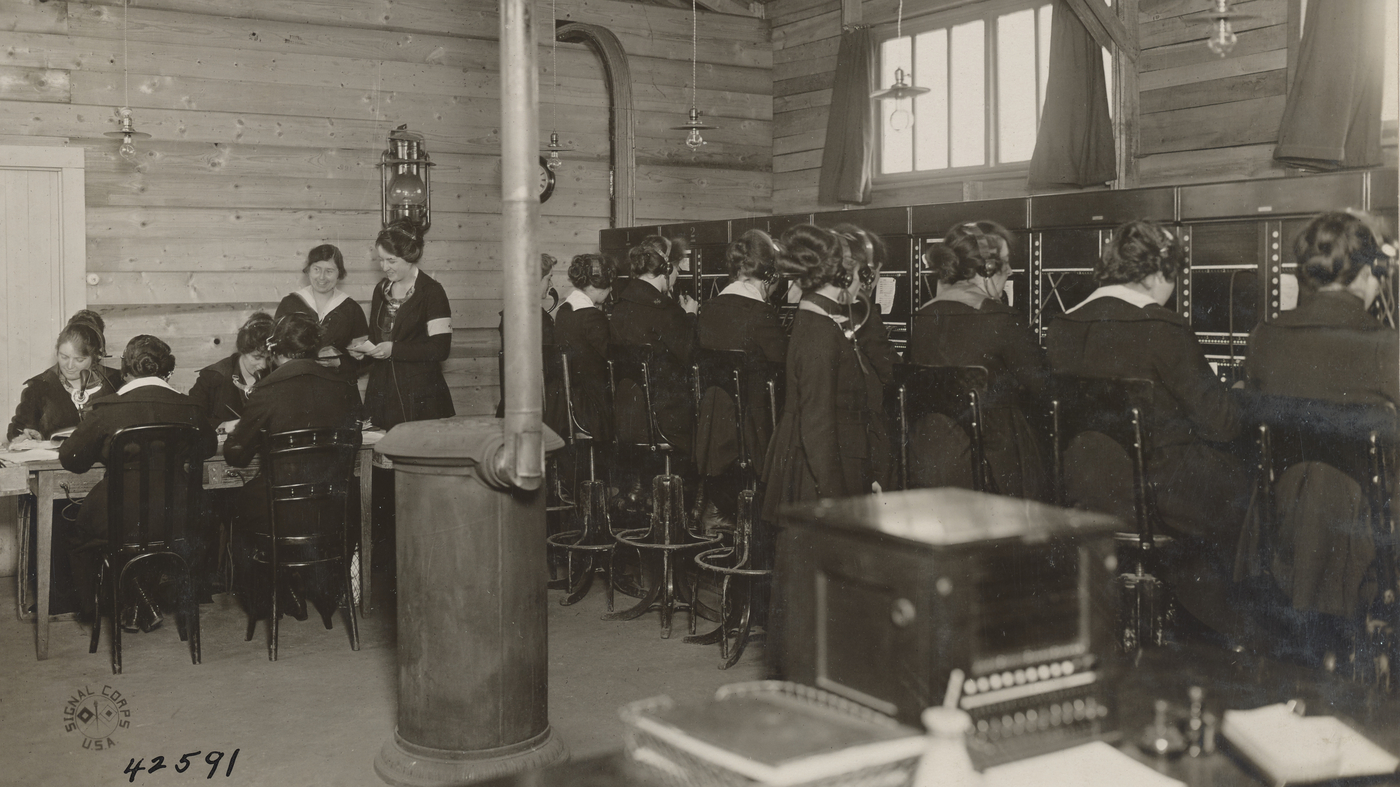
‘Hello Girls’ of World War I Quest for Veteran Recognition
After the United States entered World War I in 1917, American Expeditionary Force commander General John J. Pershing requested the recruitment of women telephone operators that were bi-lingual in English and French. Eventually 233 were selected out of over 10,000 applicants, and they served honorably through the war, earning the nickname of 'Hello Girls.'
However, their employment was not officially recognized as military service and therefore were neither honorably discharged, or eligible for the benefits other returning Veterans would receive. This kicked off a 60-year fight for 'Hello Girls' to receive legal Veteran status.

Exhibits
“Like Joan of Arc of Old”: The Origin of Health Care for Women Veterans
VA History Exhibit - While women have served in nearly all of America’s wars, some only achieved the right to Government-provided health care after World War One. This exhibit examines how women Veterans obtained admittance to the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers 100 years ago in 1923, and profiles what care looked like for these first women patients.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 66: Frank Lloyd Wright House for Disabled World War II Veteran
When the GI Bill became law in 1944, it included a home loan program for Veterans. After several changes to update the law to reflect current market prices and challenges, one area still needed addressed: support for Veterans who were dependent on wheelchairs for mobility. The answer was the Specially Adapted Housing program, and one of the earliest homes built with the grant money was designed by acclaimed builder Frank Lloyd Wright.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 64: U.S. Public Health Service Hospital #50
U.S. participation in the First World War produced a shift away from relying on long-term institutional care for Veterans in need to a model of Veteran welfare centered around short-term hospitalization. During the war, the War Department assumed responsibility for tending to the sick and wounded. Afterwards, when the Army dismantled its hospital system, the U.S. Public Health Service (PHS) stepped in to fill the breach, acquiring numerous facilities the Army and Navy no longer wanted as well as other properties that could be used for medical purposes.
History of VA in 100 Objects
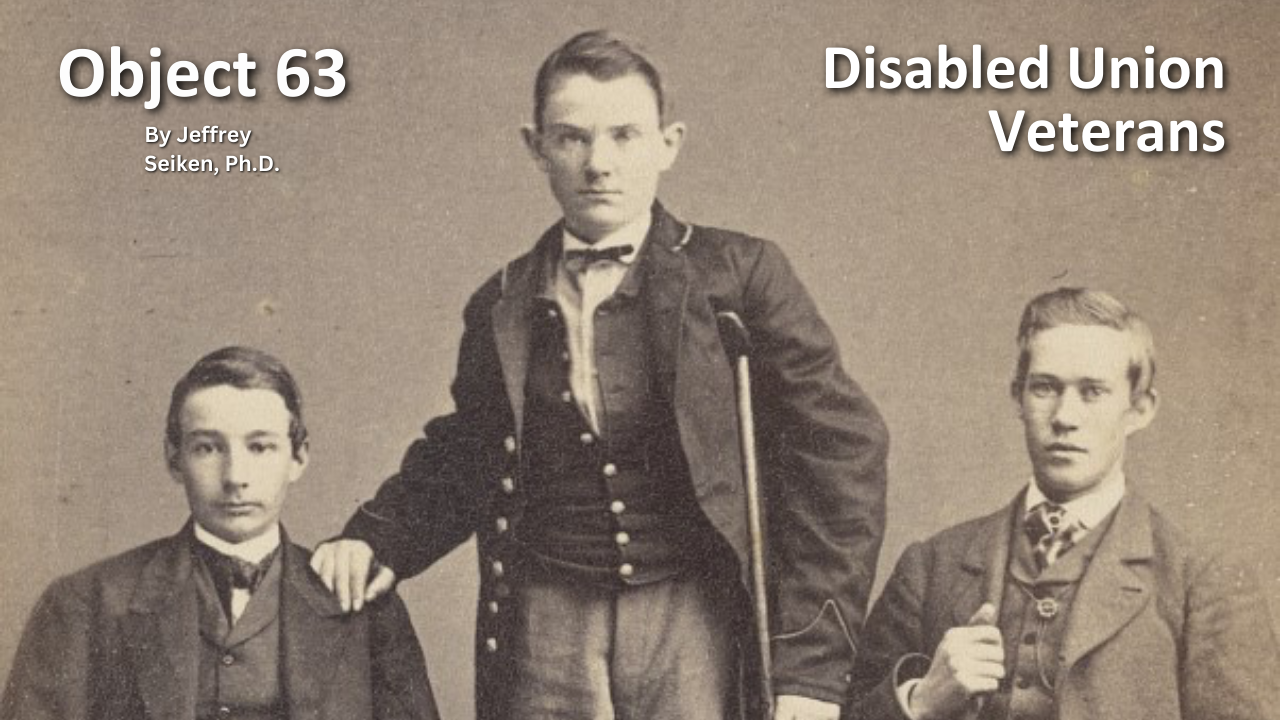
Object 63: Disabled Union Veterans
The North’s victory in the Civil War came at an enormous cost to the more than two million men who fought for the Union cause. Over 350,000 lost their lives due to battle or disease. Almost as many were wounded in action. According to Northern medical records, Union surgeons performed just under 30,000 amputations during the war. For these disabled Union Veterans, Congress made provisions to provide monetary compensation. In July 1861, lawmakers hastily passed a law for Union recruits making them eligible for the same pension allowances as soldiers in the Regular Army. Later in 1862, for the first time, a pension law explicitly granted benefits not just for men wounded in battle but also to those suffering from “disease contracted while in the service of the United States.”


