
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 71: Dade Pyramids And Monument
On the south side of Florida’s St. Augustine National Cemetery, three squat pyramids and a single taller obelisk rise from the ground above the other nearby markers and headstones. The Dade Pyramids and Monument, as they are known, mark the resting place of the U.S. soldiers who died in the opening engagement of the Second Seminole War (1835-42). The memorial honors lives lost while also serving as a grim reminder of the brutal conflict that erupted when the Federal government tried to evict the Seminole people from their tribal lands in Florida.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 70: VA Director Max Cleland at The 1980 Opening of The Atlanta Vet Center
After the Vietnam War, the nation was eager to put the divisive and unpopular conflict behind it. However, the 3.4 million Veterans who served in the Vietnam theater did not have that luxury. One of those Veterans was Max Cleland who lost his legs in the war. He made it a mission to advocate for his fellow Veterans, who struggled with the aftereffects of the war. Eventually, this led to Cleland turning to politics and at 34 being appointed as the youngest Administrator for the Veterans Administration.
During his tenure at VA, Cleland delivered on his goal of providing readily accessible mental health and readjustment counseling designed expressly for Vietnam Veterans. In 1979, VA launched an initiative called Operation Outreach to establish community-based Vet Centers across the country. In one year there were 91 Vet Centers. Today there are over 300.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 69: Stereograph of Landscaped Grounds at Dayton National Home
The federal government in the Civil War arranged to care for returning soldiers too weakened by their wounds, the lingering effects of disease, or the hardships of military life. In the decades after the war, the government established the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers.
The Board of Managers for the National Home added such amenities as chapels, libraries, theaters, and playing fields. Great care also went into the shaping of the physical environment. The board employed landscaping architects to design the grounds of each branch to create an attractive, idyllic setting for residents and visitors alike. Influenced by the picturesque landscape movement, they adorned the National Home campuses with man-made ponds and lakes, ornate flower gardens, elaborate plantings of shrubs and trees, winding trails, and other features to beautify the properties.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 68: Miller Cottage
At the VA Medical Center in Dayton, Ohio, Miller Cottage stands as a mostly forgotten reminder of women’s fight for inclusion in the benefits and health care system for Veterans. This long, multi-story brick building with a white-columned portico originated as a barracks built specifically to house female Veterans on the grounds of what was then called the Central Branch of the National Home for Disabled Volunteer Soldiers (NHDVS). The establishment of the residence represented a rare victory for the female Veterans of the First World War in their quest to obtain government support for all uniformed women who served and sacrificed during that conflict.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 67: USS Bennington Monument And Grave Plot
On July 21, 1905, one of the USS Bennington's boilers exploded, killing 49 sailors. Almost immediately after the accident, surviving crew and fellow sailors donated funds to build a monument at the grave site for their fallen comrades. This burial ground would later become Fort Rosecrans National Cemetery.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 66: Frank Lloyd Wright House for Disabled World War II Veteran
When the GI Bill became law in 1944, it included a home loan program for Veterans. After several changes to update the law to reflect current market prices and challenges, one area still needed addressed: support for Veterans who were dependent on wheelchairs for mobility. The answer was the Specially Adapted Housing program, and one of the earliest homes built with the grant money was designed by acclaimed builder Frank Lloyd Wright.

History of VA in 100 Objects
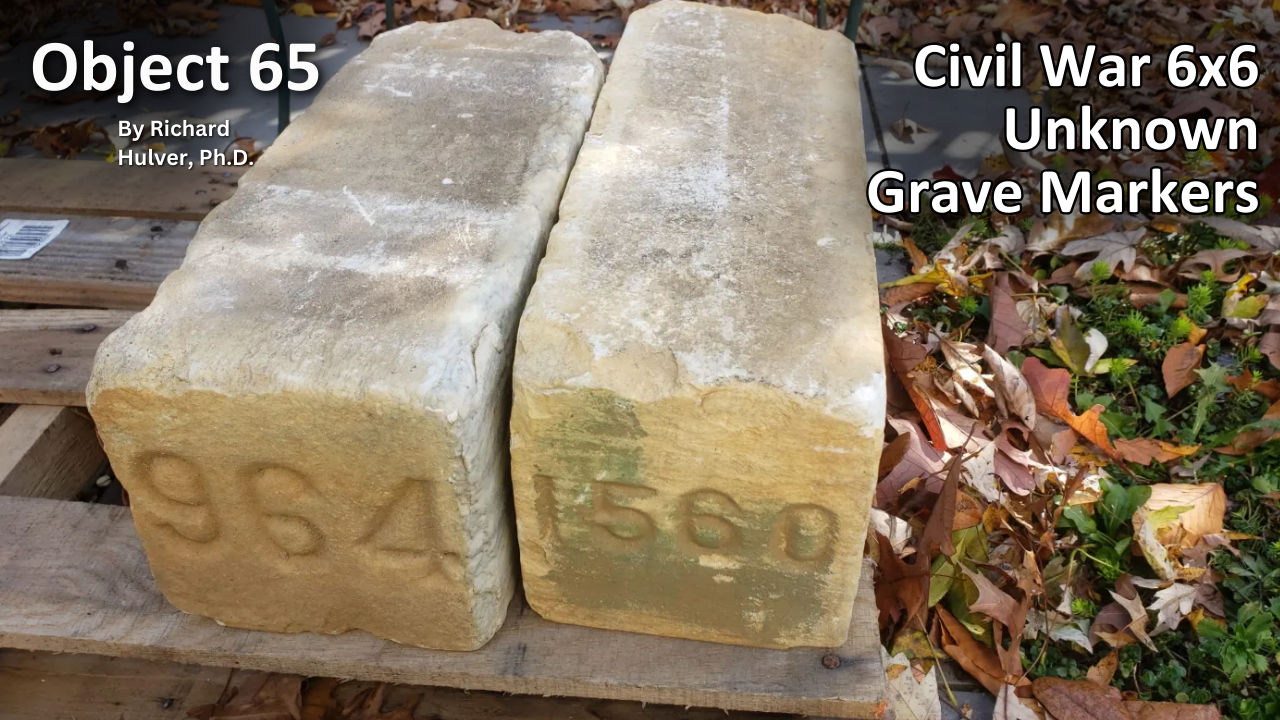
Object 65: Civil War 6×6 Unknown Grave Markers
Graves of unknown soldiers in the national cemeteries are commonplace and marked in many different ways. While the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in the Army’s Arlington National Cemetery is the most culturally recognizable unknown grave, VA national cemeteries also have less grand examples of unknown burials that span the early 19th century through the Korean War. The most common form of unknown marker, however, is the simple 6x6-inch stone that adorns the graves of thousands of Civil War soldiers.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 64: U.S. Public Health Service Hospital #50
U.S. participation in the First World War produced a shift away from relying on long-term institutional care for Veterans in need to a model of Veteran welfare centered around short-term hospitalization. During the war, the War Department assumed responsibility for tending to the sick and wounded. Afterwards, when the Army dismantled its hospital system, the U.S. Public Health Service (PHS) stepped in to fill the breach, acquiring numerous facilities the Army and Navy no longer wanted as well as other properties that could be used for medical purposes.
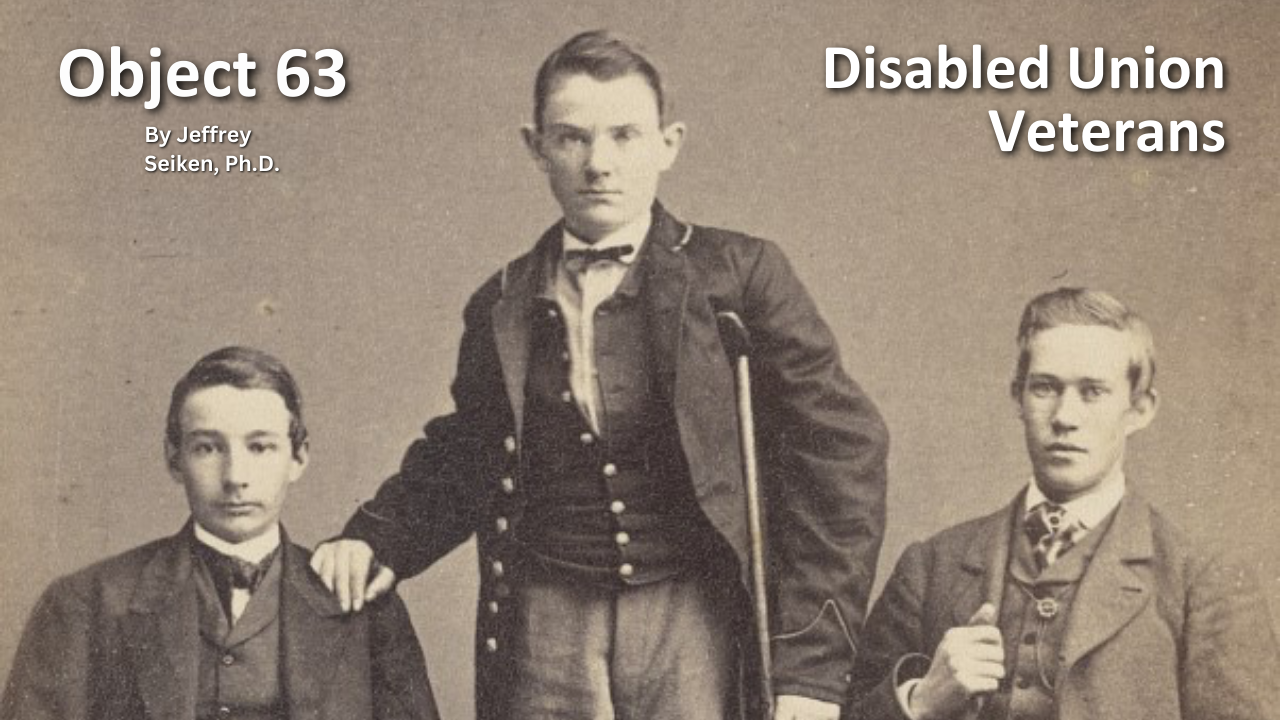
History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 63: Disabled Union Veterans
The North’s victory in the Civil War came at an enormous cost to the more than two million men who fought for the Union cause. Over 350,000 lost their lives due to battle or disease. Almost as many were wounded in action. According to Northern medical records, Union surgeons performed just under 30,000 amputations during the war. For these disabled Union Veterans, Congress made provisions to provide monetary compensation. In July 1861, lawmakers hastily passed a law for Union recruits making them eligible for the same pension allowances as soldiers in the Regular Army. Later in 1862, for the first time, a pension law explicitly granted benefits not just for men wounded in battle but also to those suffering from “disease contracted while in the service of the United States.”

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 62: 1956 “Clues to Suicide” Study
While suicide takes a toll on lives in every segment of society, Veterans in the post 9-11 era have statistically been more at risk than adults in the general population. VA’s efforts to combat the scourge of Veteran suicide owe a significant debt to the foundational research studies conducted by two VA psychologists in the 1950s. The work of Drs. Edwin S. Shneidman and Norman J. Farberow led to some of the earliest crisis intervention programs at VA and elsewhere and the establishment of the nation’s first dedicated Suicide Prevention Center in Los Angeles, California.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 61: Edmund Whitman’s 1869 Report on Reburying Union Dead in National Cemeteries
The U.S. Army’s plan for the recovery of Union dead across the South after the Civil War came about through the labors of a remarkable if little known officer, Edmund Whitman. He spent four years overseeing the collection of thousands of remains and creating “mortuary records” of reburials in new national cemeteries. After completing his “Harvest of Death,” to use his phrase, he produced in 1869 an extraordinary report that recounted the breadth, sequence, and challenges of his reinternment mission.

History of VA in 100 Objects
Object 60: VA Medal of Honor Recipients Wall Display
The Congressional Medal of Honor is the nation’s highest decoration for valor in the military. More than 1,000 have been awarded, and 98 of those recipients worked at VA. A wall display outside VA's Under Secretary for Benefits in Washington, D.C. pays tribute to each of those individuals, whose stories are tied to the legacy of Veterans serving Veterans.


